Dentists Journal
Top Ten Stories of the Week
2/10/2024
All Dentists Journal · Previous Week · This Week · All Time List · Headlines
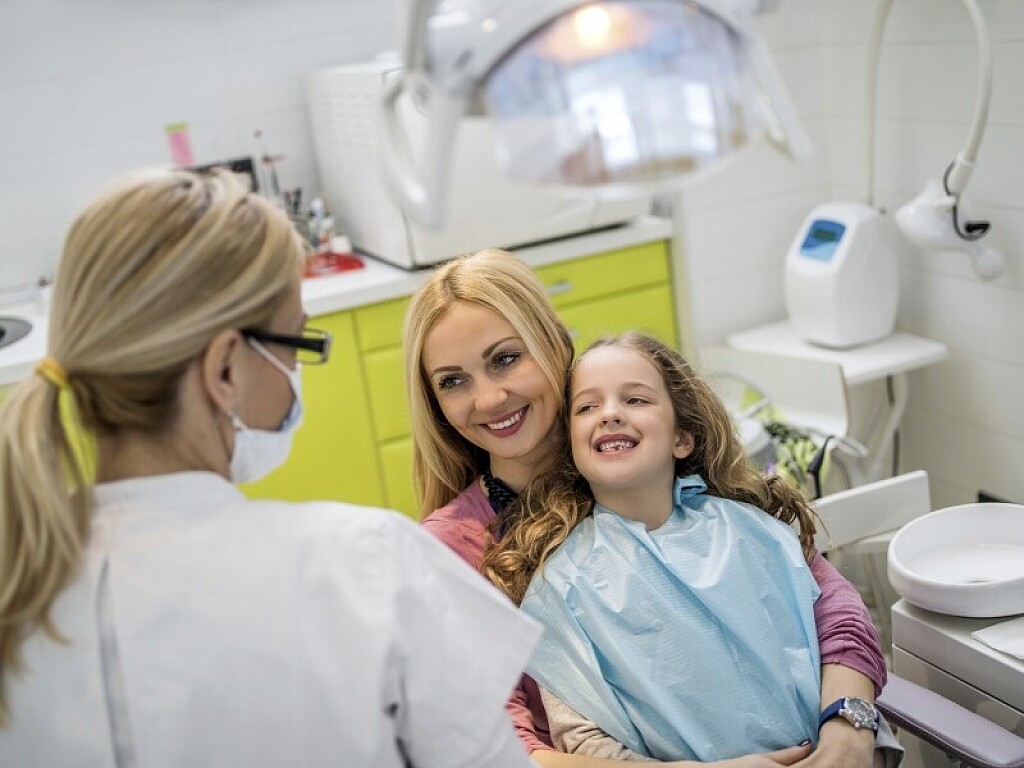
Important Things You Should Consider When Choosing A Dentist
Did you know National Dentist’s Day was on March 6th? This was a day where we celebrated our incredible team of doctors, which includes Dr. Rao, Dr. Brikina, and Dr. Kirakozova. We are truly honored to have some of the best dentists in the entire industry and these experts love providing top-of-the-line care for our patients.
While we can sit here all day and talk about our amazing team, we’d like to touch on a topic that should resonate with you. Do you ever feel lost when trying to choose a dentist? Not sure what to look for? In this post, we’ll discuss what you should consider when choosing a dentist. At the end of this blog, you should have full confidence when trying to find a dentist who is committed to your dental health and overall well-being.
Check out these key considerations below:
Treatments Provided
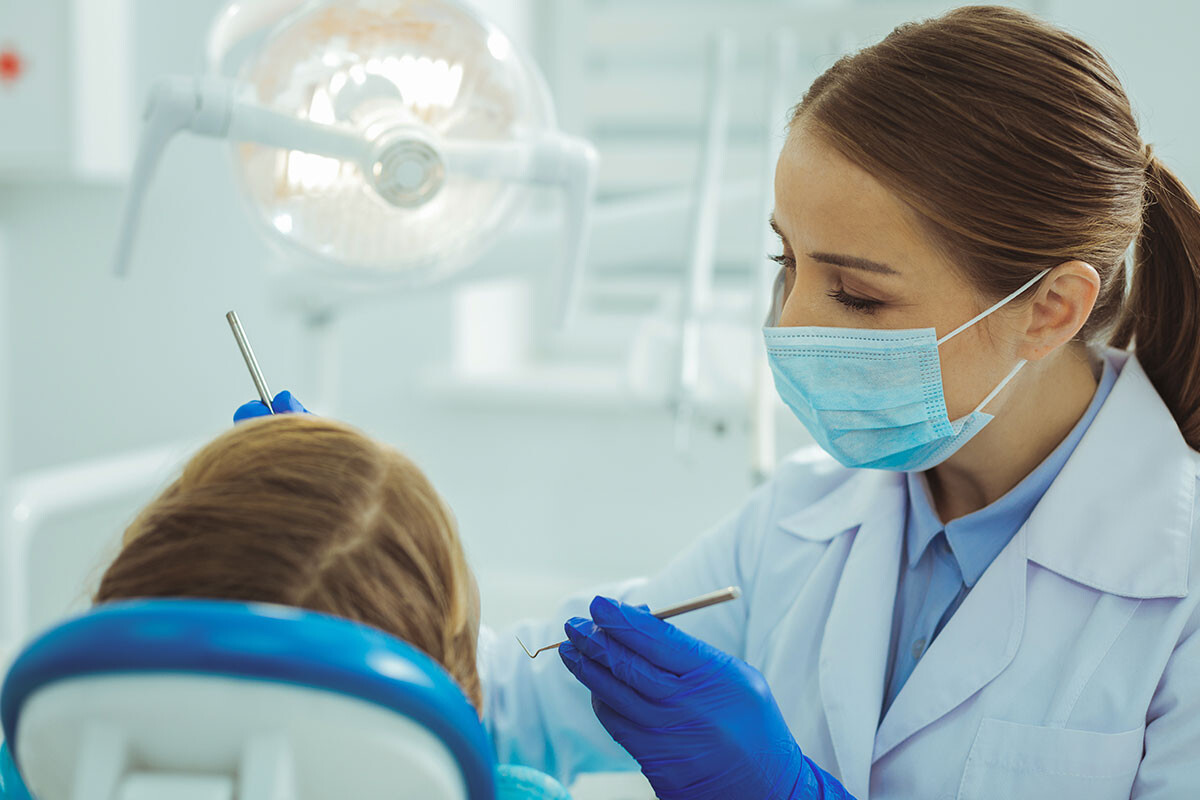

Trying to find a qualified dental care team is no easy task in this day and age. But as you’re browsing around, be sure to check out what treatments are offered by these dental offices.
Want to start Invisalign? Dealing with chipped teeth? Having complications with your gums? There are many dentists out there that actually specialize in certain treatments, so be sure to locate providers who are experts on the specific treatment you have in mind.
Proper Training
Not all dentists and dental care teams are trained the same. That being said, you should try to understand the level of training a prospective dentist has before scheduling an appointment. This information might be available on the dentist’s website, or you can give them a phone call to discuss their training process and credentials.

Another point to understand is that some dentists might be highly trained in one specific area, but lack training in another treatment. Be sure to contact the dental office and discuss their training as it pertains to the service you need.
Modern and Clean Office
Cleanliness should also be a top consideration when looking for a dental care office. Given how oral health procedures and dental visits involve many tools and devices that are entered into your mouth, you’ll want the entire environment to be sparkly clean.
To get a sense of the cleanliness at a dental office, try to find pictures on their website or stop by for a visit.
Welcoming Staff
When looking for a dentist, you should always pay attention to the level of customer service. As you’re looking through providers online, read through some of their content and try to get a feel for their culture and how they treat their patients.
Another option is to give the office a call. If the staff members don’t appear attentive, caring, and focused on your needs, then they probably aren’t the dental care provider for you.
Dental Technology
Another aspect to consider is the dentist’s technology used. With the advanced dental technology of today, it’s a good idea to only work with dentists who utilize the newest, most advanced technology on the market.
Cedar Walk Dentistry is Here for You!
If you’re looking for a dentist who has all of the qualities listed above and so many more, then you have to pick up the phone and call Cedar Walk Dentistry today! Here are just a few reasons why you should choose us:
Personalized care
Many payment options
Wide variety of services
Gentle treatments
Holistic-driven
Focused on preventative care
Dedicated to our patients
Invisalign specialists
Many dental certifications
Cedar Walk Dentistry is a family and cosmetic dental office located in South Charlotte, North Carolina. Our dentists, Dr. Rao, Dr. Brikina, Dr. Nelson and Dr. Anna, all provide exceptional dental care and they also have an outstanding reputation in the community.
Whether you’re having issues with your gums, teeth, or you’re dealing with any other oral health complication, we provide top-notch, gentle services at all times!
(02/05/2024)by Cedar Walk Family
More Information: N
Views: 545
Can Gums Pull Away From Teeth?
What is gum recession?
Gum recession, also known as gingival recession, refers to the progressive loss of gum tissue that covers the roots of the teeth. When the margin of gum tissue pulls away from the crown of the tooth, it exposes more of the tooth root and bone beneath the gumline.
As the gums recede, “pockets” or gaps form between the gumline and the tooth. These pockets allow more plaque and bacteria to build up, which can weaken gum tissue connections and underlying bone support for the teeth.
Gum recession is a common problem among adults, but it develops gradually over time. The early signs are often subtle changes in the position of the gumline relative to the teeth. Without treatment, moderate to severe gum recession can lead to problems like tooth sensitivity, decay, loose teeth, and eventual tooth loss.
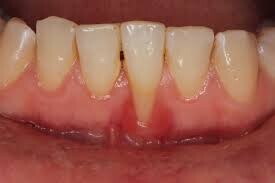
How do healthy gums attach to teeth?
In a healthy mouth, the gums firmly attach to the teeth in a specialized connective tissue junction called the gingival sulcus. This attachment forms a tight seal or adhesion around each tooth.
The gingival sulcus contains dense collagen fibers that connect the tooth enamel to the gum tissue. This collagen-rich attachment apparatus is strong yet flexible, allowing the gums to tightly hug the teeth without detachment.
The gumline meets the tooth surface a few millimeters above the root junction, known as the cementoenamel junction. A slight variation in gumline height around different teeth is normal. As long as the gum completely covers and protects the bony sockets surrounding the tooth roots, periodontal health is maintained.

Why do gums recede from teeth?
There are several potential causes of gum recession:
Gum disease – Bacterial plaque accumulation inflames the gums and triggers chronic infection. This periodontal disease breaks down collagen fibers and supporting bone, leading to shrinking, weakened gum tissue.
Aggressive brushing – Habitual brushing with excessive force can traumatize the gums. Bristles gouging the gums overtime cause them to shrink away.
Misaligned teeth – Crooked teeth or poor bites make gums more prone to injury. Recessed gums may form due to excessive forces on gum tissue.
Grinding/Clenching – Chronic grinding and clenching puts severe pressure on teeth, pulling gums downward. This eventually loosens the gums.
Smoking – Chemical compounds in tobacco smoke impair gum blood flow. This leads to gum detachment and slowed healing.
Genetic factors – Some people are predisposed to thinner gum tissue or gum heights that make them more susceptible to recession. This is more prevalent in older individuals.
Medical conditions – Diseases like diabetes or autoimmune disorders increase vulnerability to gum infections and damage.
Certain medications – Drugs like blood pressure medications, oral contraceptives, anti-depressants, and more may reduce gum tissue resilience. Consult your dentist.
Why is gum recession problematic?
Receding gums cannot grow back or reattach once they detach past a certain critical point. The lost gum tissue leads to several oral health issues:
Tooth sensitivity – Gum recession exposes dentin tubules in the root surface. These allow hot/cold liquids to stimulate nerve endings, causing sharp pain.
Root decay – With the protective gum tissue layer gone, tooth roots are more vulnerable to cavities and decay.
Bone loss – The bony sockets around roots can deteriorate due to infection spreading from receded gums.
Tooth loosening – Advanced recession and bone loss undermine the support system for teeth, allowing them to loosen or fall out.
Poor aesthetics – Increased tooth length and visible roots due to gum recession are unsightly. It makes smiles appear “toothy” and unattractive.
Severe gum recession can lead to impaired chewing function, crooked teeth, and eventual tooth loss. Seeking treatment in the early stages is critical.
Risk factors for gum recession
Certain lifestyle habits, health factors, and medications raise your risk for receding gums:
Smoking/tobacco use – Nicotine and smoke compounds restrict blood flow to gums, causing tissue breakdown.
Aggressive brushing – Excessive scrubbing force erodes gums, as do stiff-bristled brushes.
Periodontal disease – Preexisting gum infection destroys connective tissue fibers that attach gums to teeth.
Grinding & Clenching – Chronic teeth grinding (bruxism) exerts extreme pressure on teeth, detaching gums over time.
Age – Gums weaken and recede more easily due to reduced blood supply as we age.
Hormones – Fluctuating hormones in puberty, menopause, and pregnancy increase gum sensitivity.
Diabetes – Poor blood sugar control impairs immunity and healing, increasing gum infection risks.
Genetics – Some people inherit thinner gum tissue or tooth positions prone to recession.
Misaligned teeth – Crooked, crowded, or gap teeth create areas that are hard to clean and maintain.
Toothbrush abrasion – Using stiff-bristled brushes or abrasive toothpaste erodes gums after repetitive brushing.
Bruxism nightguard – Ill-fitting nightguards that rub the gums can progressively damage the gumline after nightly wear.
Lip/tongue piercings – Oral jewelry that constantly rubs against gums can wear away gum tissue.
Clenching behaviors – Chronic teeth clenching due to stress or habits can traumatize gum attachments.
Nutrient deficiencies – Deficiencies in vitamin C and B12 may make gums more vulnerable to problems.
Stages and symptoms
Gum recession can range from mild to severe. Knowing the signs at each stage is important for getting timely treatment:
Stage 1: Early-stage recession
Symptoms:
Gums appear slightly lower on some teeth
Mild sensitivity from minimal root exposure
No obvious gaps between teeth
Slightly longer tooth appearance
Minor inflammation/bleeding when brushing
This early stage of recession is often invisible to the eye unless you look very closely. But dentists can detect subtle changes in gum height relative to past records. Taking action with improved oral hygiene can help stabilize gums at this point.
Stage 2: Moderate recession
Symptoms are now more visible:
Gumline is clearly lower than normal
More noticeable gaps between some teeth
Yellowish root exposure is visible
Teeth appear longer
Sensitivity to hot/cold stimuli
Tenderness when chewing hard foods
At this point, loose teeth and bone loss may begin without treatment. Your dentist can determine how much supporting bone remains using dental X-rays.
Stage 3: Advanced recession
Severe symptoms:
Widespread gaps between most teeth
Extensive root exposure
Bone loss visible in X-rays
Loose or migrating teeth
Constant sensitivity and pain
Altered bite due to tooth positions changing
Aggressive periodontitis and rapid bone loss undermine the tooth roots. Seeking prompt treatment is critical to try and save teeth.
Diagnosing receding gums
Dentists diagnose receding gums using a combination of visual exams, physical tests, and dental imaging:
Visual inspection
The dentist will visually compare current gumlines to past photos/records for any recession. They check for signs like longer teeth, root exposure, and interdental gaps.
Physical examination
Probing – A periodontal probe is used to measure and record the depth of gum pockets. Deeper pockets indicate detached gums.
Mobility testing – Teeth are wiggled to detect any increased loosening or shifting.
Bite evaluation – Bite irregularities from changing tooth positions may develop.
Sensitivity testing – Specialized tests can reproduce sensitivity pain in problem areas.
Dental imaging
X-rays – Dental radiographs show bone loss patterns which reveal recession severity.
Cone beam CT scans – 3D scans provide detailed views of gum and bone levels.
Intraoral camera – Close-up mouth photos clearly show affected areas.
Your dentist will also ask about symptoms, oral hygiene habits, health conditions, medications, and risk factors. Together, these help determine the cause and how to treat receding gums.
Treating receding gums
The treatment options for receding gums include:
Nonsurgical treatments
Mild cases may be stabilized and reversed using:
Improved oral hygiene – Gentle flossing and brushing helps gum health when done consistently. Regular dental cleanings support this.
Desensitizing toothpaste – Special toothpastes relieve sensitivity pain from exposed roots. However, they do not restore lost gum tissue.
Mouthguards – Wearing nightguards protects against grinding forces during sleep which can damage gum attachments.
Dietary changes – Limiting acidic and sugary foods helps protect vulnerable areas where the root is exposed.
Quitting smoking – Smoking cessation allows gum tissues to rebound after the chemical irritants are removed.
Medication changes – Switching medications linked to gum problems may support gum stability on advice of your physician.
These help stabilize areas of mild recession, but moderate to severe recession requires surgical intervention.
Surgical treatments
A periodontist can perform procedures like:
Gum grafting – Soft tissue grafts taken from the roof of the mouth (palate) are sutured over exposed roots. Over time, they protect receding areas.
Bone grafting – Materials like donated bone or bovine bone are placed under detached gums to encourage reattachment.
Tissue regeneration – Special membranes are inserted between the gum and root to regrow lost tissue in that space via guided tissue regeneration (GTR).
Pinhole surgery – Small pinholes are made in the gum to gently loosen and slide it down over the exposed roots without sutures.
Dental implants – Implants can replace teeth lost from advanced recession and restore chewing function.
Complex cases may involve flap procedures to remove infected gum tissue before regenerative techniques are applied. Your periodontist will advise the most suitable surgical approach based on the degree of recession and your individual mouth anatomy.
Prevention
Preventing receding gums from worsening involves:
Using a soft-bristled toothbrush and brushing gently – no vigorous scrubbing
Choosing non-abrasive toothpaste to avoid gum irritation
Daily flossing to clear plaque, being careful not to snap floss against the gums
Getting professional cleanings at the dentist every 6 months
Not smoking and avoiding other tobacco products
Wearing a nightguard if you grind your teeth
Monitoring gums for any changes and reporting them quickly
Treating gum disease early if it develops to limit tissue damage
Managing health conditions like diabetes to optimize gum healing
Changing habits that strain gums like oral jewelry or teeth clenching when stressed
With diligent daily oral hygiene and regular dental visits, gum recession can often be caught early and treated successfully. However, advanced recession may still eventually require procedures to protect remaining gum health.
How quickly do receding gums progress?
When caused by periodontal disease, gum recession can progress rapidly in just years. Poor brushing habits can also lead to faster recession. However, factors like genetics and aging lead to gradual recession over many years. Proper dental care reduces the speed of further recession.
Can gum recession affect only one tooth?
Yes, it commonly begins by affecting just a single tooth or area. Certain teeth are more prone to gum recession like lower front teeth and molars. As time passes, more teeth often develop receding gums if the causes are not addressed.
Does gum recession require surgery to fix?
Non-surgical options can sometimes stabilize early gum recession. But in moderate to severe cases, surgery like grafting is needed to cover exposed tooth roots and halt further detachment. The stage of recession determines which procedures provide meaningful benefits.
Can receding gums regrow without treatment?
Spontaneous regrowth without any treatment only occurs in the very mildest cases caught extremely early. Once recession reaches the radicular dentin, active intervention is required to restore lost gum tissue. Severe recession won’t improve on its own.
What happens if receding gums are left untreated?
Untreated gum recession tends to steadily worsen over time. It can lead to severe gum disease, persistent tooth sensitivity, loose teeth, jawbone loss, and eventual tooth loss. The risks of damage extend to both the soft and hard tissues supporting the teeth.
Catching receding gums early and taking preventive steps offers the best chance of stabilizing areas affected by recession. Work closely with your dentist if you notice any suspicious gum changes before substantial damage occurs. Gum grafting and regeneration procedures depend on having sufficient remaining gum tissue to work with.
(02/02/2024)by CDHP Dental Health
More Information: N
Views: 478

Recognizing the Early Signs of Gum Disease
Nearly half of all American adults over age 30 have some form of gum disease, and for those 65 and older, that number jumps to almost three-quarters. Considering gum disease is the leading cause of tooth loss for adults, those are some really concerning numbers.
The key to battling gum disease successfully is catching it in its early stages, before it has a chance to cause serious damage to your gums and teeth. At Novi Family Dentistry, in Novi, Michigan, Abir Faraj, DDS, and her team offer comprehensive care for gum disease. They use advanced techniques to diagnose and treat gum disease, no matter what stage it’s in. Here’s what you should know about gum disease, including how to spot it early.
The basics of gum disease
Your mouth is full of bacteria. Some of it is good, and some of it is not so good. Brushing and flossing help keep the bad bacteria under control. But, even with good at-home hygiene, food film can build up between your teeth and gums and form sticky deposits called plaque.
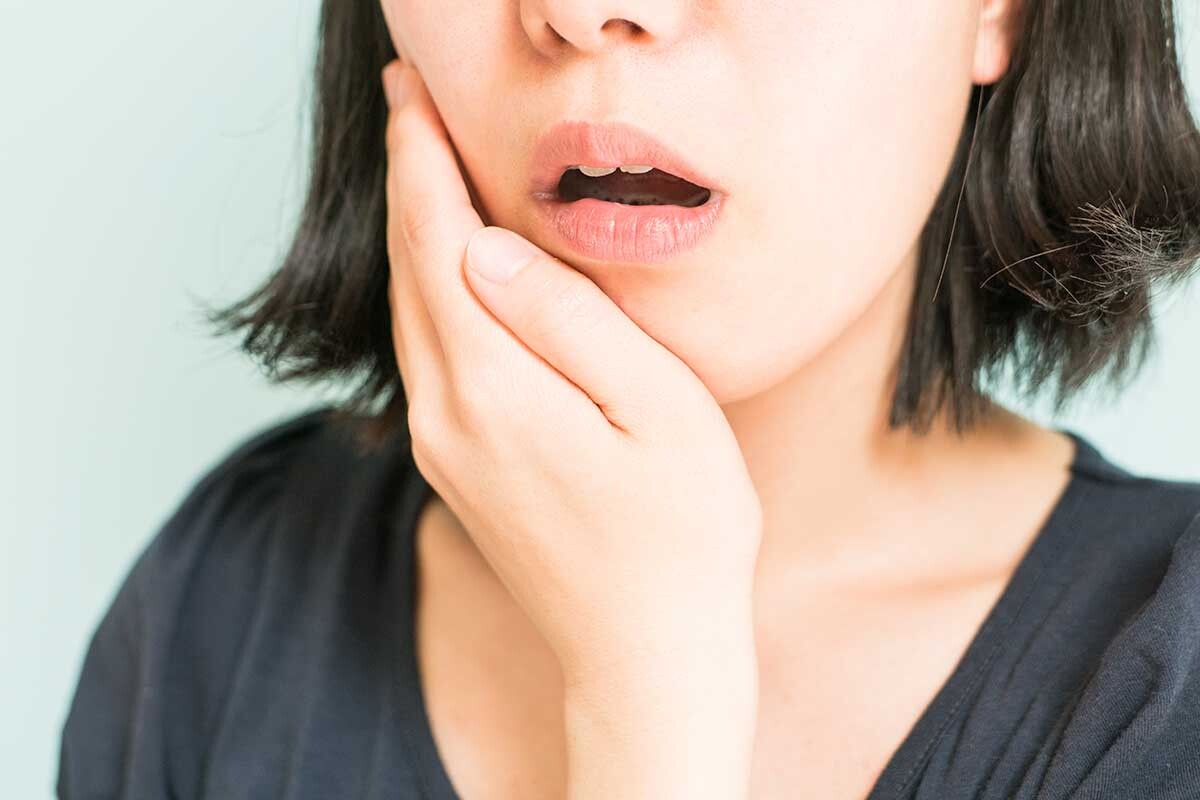

Plaque provides a good home for many disease-causing bacteria, which thrive on sugars from the foods you eat. Unless plaque is removed regularly, it can harden and turn into tartar. Tartar is really hard — so hard, in fact, that your dentist needs special tools to remove it. It also provides an almost impermeable shelter for bad bacteria.
Once tartar forms, it’s only a matter of time before bacteria start invading your gums, moving down teeth and hiding beneath the gums where they can cause more inflammation and even infection. Eventually, the bacteria can travel all the way down to the roots of your teeth and cause abscesses to form, which, in turn, can weaken the roots and lead to tooth loss.
Dr. Faraj offers treatments for all stages of gum disease, including the early stage — which is called gingivitis — and the later stage — which is called periodontitis. The best option is to catch gum disease early, when treatment is a lot simpler.
Signs of gum disease

Unless you’re a dental professional, gum disease can be very difficult to identify in its early stages. That’s because in those early days, gum disease typically doesn’t cause any major symptoms.
Stage 1: Gingivitis
The most common symptom to look for in this first stage of gum disease is bleeding when you floss or brush. Early on, inflammation begins, making your gums more tender than usual and more prone to bleeding. Your gums might look a little puffy, too.
Stage 2: Periodontitis
In the later stages, pain, significant swelling, and gum recession, can occur. This is because infection and inflammation can spread to deeper areas of gum tissue and even to the tooth roots.
Protect your smile by protecting your gums
Because early symptoms can be difficult to spot on your own, having regular checkups is very important for your gum health. During a checkup, Dr. Faraj and the hygienist look for early signs of disease and areas of plaque and tartar buildup.
If early gum disease is present, it can usually be treated by a regular cleaning to remove plaque and tartar. In more advanced stages of the disease, you might need a deeper cleaning and antibiotics to kill germs around the deeper parts of your teeth and roots.
Don’t let gum disease rob you of your beautiful smile. Having regular cleanings and checkups is the best way to spot and treat gum disease early.
(02/02/2024)by Novi Family Dentistry
More Information: https://www.novifamilydentistry.com/blog/recognizing-the-early-signs-of-gum-disease
Views: 405

What Causes a Tingling Tongue?
Nearly everyone has experienced that uncomfortable feeling of "pins and needles" at some point. Perhaps you were kneeling on the floor for longer than you'd planned, and when you stood up, you realize your legs were asleep! Or perhaps you've woken up with a numb hand after spending the night asleep with your arm in an awkward position. This tingling feeling, known as paresthesia, often occurs in the hands and feet. But did you know it can also occur in other body parts, including the tongue? Let's go over the potential causes of a tingling tongue and when you should see a medical or dental professional about your symptoms.
The University of Rochester Medical Center explains that paresthesia results from a "traffic jam in your nervous system." This analogy refers to a "roadblock" that's created when constant pressure is on a nerve. This pressure prevents the electric impulses from traveling up and down the nerves as they normally would. Once the pressure is removed, the impulses can travel freely again. But when the blockage is first released, the electric impulses will pick up faster than usual, causing a tingling sensation in the affected area.
However, the tingling you may feel in your tongue is rarely from falling asleep in a strange position or holding your tongue in a particular spot for too long. Let's go over a few things that can cause a tingling tongue.
Nerve Damage After Surgery

Some people get a tingling feeling in their tongue after oral surgery, like a wisdom tooth extraction or a root canal procedure. A case report in the Journal of Dental Anesthesia and Pain Medicine (JDAPM) notes that it will usually occur directly after the procedure for those who do experience paresthesia from oral surgery. In rare cases, a person can have a delayed-onset tingling of the tongue.
Two of the most likely nerves contributing to a tingling feeling in the tongue after oral surgery are the lingual nerve (LN) and the inferior alveolar nerve (IAN). The JDAPM notes that IAN paresthesia occurs in 0.35 to 8.4 percent of people who undergo oral surgery.
If you've recently had oral surgery and have noticed that your tongue feels tingly, don't worry. Most paresthesia cases due to oral surgery disappear on their own within a few months at the latest. You should schedule a visit with your dental professional if you are particularly concerned about the sensation or if it has lingered for longer than a few months.
Oral Allergies
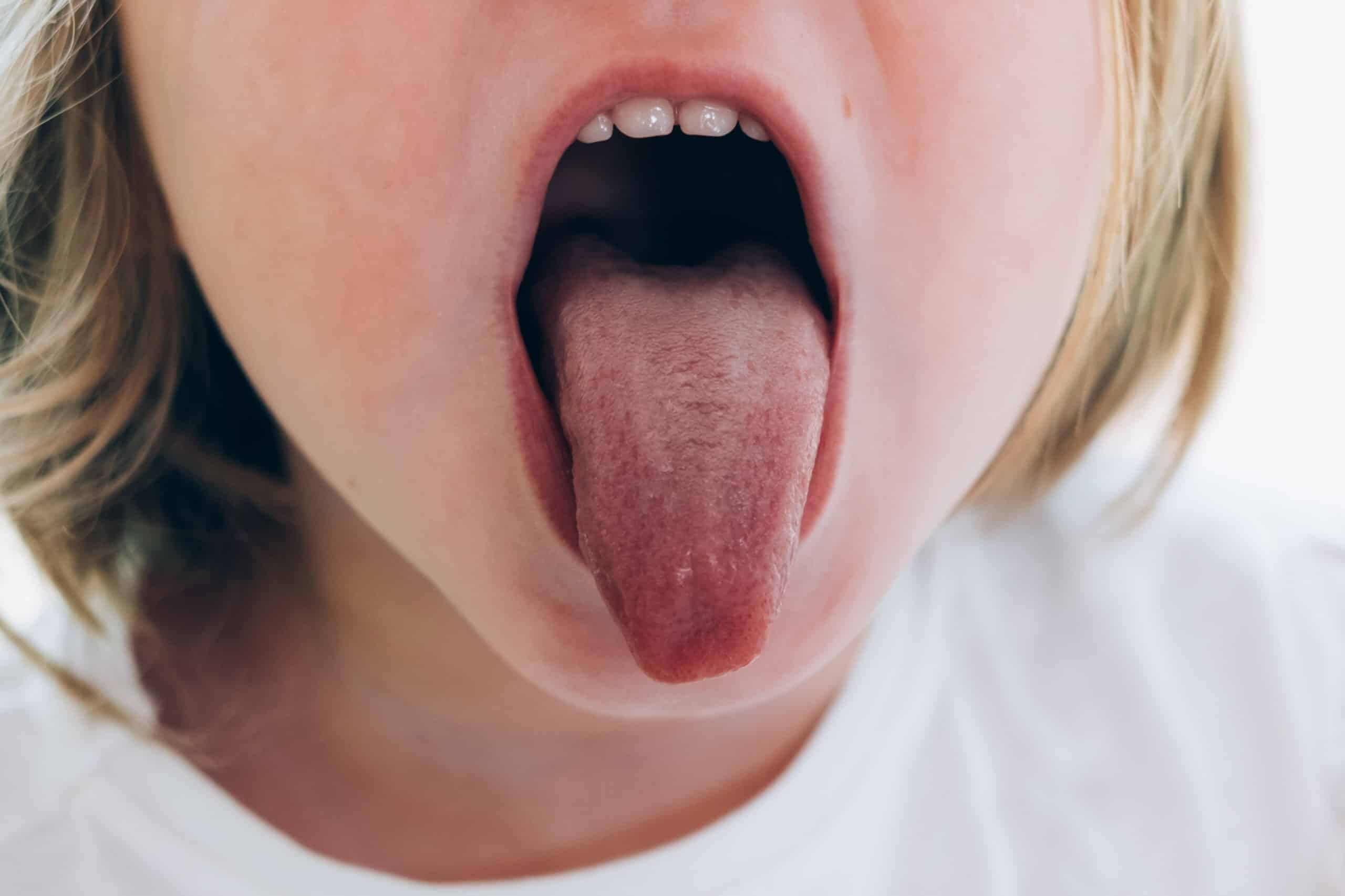
While many of us may not be aware of every type of substance we could be allergic to, there's an interesting relationship between the allergy to certain pollens and a tingly or itchy tongue you may want to be aware of. The American Academy of Allergy, Asthma, and Immunology reports that up to three-quarters of adults with a birch pollen allergy also have oral allergy syndrome. One of this syndrome's symptoms is a tingling and itchy tongue after eating certain raw fruits and vegetables, such as apples, peaches, cherries, and carrots. If you have oral allergy syndrome, your best bet to avoiding a tingling tongue is to eliminate from your diet the raw fruits and vegetables that can trigger an allergic reaction.
Canker Sores on the Tongue
You may be familiar with canker sores, a prevalent oral condition of small, white swellings that aren't contagious but can be a nuisance. They can develop almost anywhere on the soft tissue inside the mouth, including the lips, cheeks, soft palate, and tongue. While canker sores' exact cause is unknown, risk factors range from genetics to a weakened immune system to smoking cigarettes.
As noted by the Mayo Clinic, a tingling or burning sensation in your mouth and tongue can develop a couple of days before the sore itself is visible. This means you may be able to tell when a canker sore is coming on! Canker sores may be painful, but they usually clear up on their own and don't require treatment. If you notice your canker sores are large or don't clear up within two weeks, schedule an appointment with your medical professional. They can evaluate the sore and discuss your treatment options.
"Hypo" Causes of a Tingling Tongue
A tingling tongue means that you are missing one of the substances your body needs to thrive. For example, low blood sugar and low calcium levels can be the cause of your tongue's paresthesia. There are two important things worth noting about "hypo" causes of a tingling tongue:
A "hypo" cause of a tingling tongue is relatively rare.
If a deficiency in blood sugar or calcium is the cause of paresthesia, this tingling sensation does not occur until your calcium or blood sugar levels are severely low. It's essential to note that tingling and numbness in the tongue, lips, or cheeks are some of the more severe signs of low blood sugar. And Merck Manual connects tingling in the tongue with tetany, an involuntary contraction of the muscles that often develops when calcium levels are deficient.
Working with your doctor to manage the situation can help you avoid a tingling tongue and other complications. This is especially true if you have a condition that causes low calcium levels or diabetes, which is the usual reason for a dip in blood sugar. In most cases, a tingling sensation is nothing to worry about. But we always advocate for immediate professional care if you are experiencing a symptom of diabetes. This will ensure that you are fully knowledgeable about the signs and symptoms of a diabetic blood sugar low. You deserve to be confident in your oral and overall health. That's why education and open conversations with your medical professionals is vital!
While there's a wide range of possible reasons for your tingling tongue, you don't need to panic! Consider what you already know about your body and current health. Did you recently have oral surgery? Have you experienced cold sores in the past? Are you diagnosed with diabetes? Discussing your health and diagnoses with a dental or medical professional can help them figure out why you are experiencing a tingling tongue and get you on the correct treatment path if necessary.
(02/03/2024)by Colgate
More Information: https://www.colgate.com/en-us/oral-health/mouth-and-teeth-anatomy/what-causes-a-tingling-tongue
Views: 346
Seven Reasons Your Mouth Isn’t Healthy And What To Do About It
Poor oral health has many unfortunate side effects, from bad breath and cavities to a weakened immune system and cardiovascular risk. For these reasons and many more, your Marietta dentist will recommend dental cleanings and oral exams at least every six months. Regular visits to a dentist will identify issues in their earliest stages, helping prevent health issues that can extend beyond your teeth and gums.
There’s no doubt about it; your oral health plays a significant factor in your overall health and wellness. Unfortunately, many people tend to do the bare minimum when it comes to taking care of their teeth and gums, which sometimes doesn’t cut it.
7 Common Oral Health Issues You Need to Know
Most oral health problems will likely come down to a small selection of treatable issues. During a scheduled checkup, your dentist looks at areas of concern and puts a plan to treat the matter in place. Let’s examine the common reasons your mouth is unhealthy and what you can do about it.

1. Your Teeth Are Stained
When you smile, the first thing most people notice is the color of your teeth. While some people’s teeth are a beautiful white color, many people have teeth that are stained a yellowish or brownish color. Because of this they don’t smile as much and tend to be self-conscious of their teeth.
While this is certainly a cosmetic issue it’s also a functionality issue. Teeth that are stained yellow or brown can be a sign of tooth decay, which is a problem you don’t want in your mouth.
For patients with surface staining, professional, in-office teeth whitening can lighten your teeth several shades in a short amount of time. For more severe problems such as tooth decay, we recommend that you schedule an appointment with Dr. Mohip-Chahwala so that you can have a full oral exam and get recommendations on how to proceed with fixing your teeth.
2. Your Teeth Are Crooked
While most people think that crooked teeth are simply a cosmetic or orthodontic issue, it can actually hurt the health of your teeth and gums. Teeth that are either crowded or have gaps in them along the gum line can become a breeding ground for harmful bacteria.
While brushing and flossing are always important, it’s extremely important that your teeth are not too far apart, crowded, or crooked in any way. For patients who have severely crooked teeth and are also suffering from dental decay, dental implants with crowns or bridges may be an excellent option. Here’s a page dedicated to dental implants where you can learn more.
3. Maybe Your Jaw Hurts, Too
In certain cases, crooked teeth can actually be a symptom of a problem with your jaw.Temporomandibular joint disorder (commonly referred to as TMD or TMJ) is a painful condition where the TMJ (a joint that acts much link a hinge) fails to move smoothly.Think about it like a door that doesn’t fit perfectly and drags on the floor a bit when you push or pull on it; that’s quite painful when it’s going on between your mandible and temporal bone!
A few common symptoms patients with TMJ disorder report are:
Clicking or popping in the jaw area
Ear that feels painful or full
The inability to close or open the mouth
A bite that is out of alignment (the teeth no longer fit together properly)
Dr. Mohip-Chahwala treats TMJ right here at Shining Smiles Family Dentistry in Marietta, GA.
4. Your Gums Are Red, Swollen, or Bleed When You Brush
If your gums frequently have the appearance of being swollen, angry, or inflamed, it’s time for a visit to the dentist to see what is going on, as these are potential signs of gum disease.
There are three stages of gum disease:
Gingivitis
This is the first stage of gum disease commonly characterized by gum inflammation and plaque buildup. Catching gum disease at this stage is important, as it can be reversed with minimal treatment and a solid oral hygiene routine.
Periodontitis
At this point, your teeth are (unfortunately) permanently damaged. Now, this doesn’t mean you can’t take an active approach to minimizing your damage and it doesn’t mean that more advanced treatments, such as dental implants, aren’t a great option for you.
Advanced Periodontitis
When you see someone who has lost several teeth or has several teeth that are yellow/brown, loose, and soft, they are likely in the advanced stage of periodontitis. At this point, your teeth will likely need to be removed and replaced with dental implants, a fixed bridge, or some other similar treatment.
Also, your teeth shouldn’t bleed when you brush them (it could happen on occasion, but it definitely should be the exception, not the rule)!
You can learn more about how we help patients with gum disease by visiting this page.
5. You Constantly Deal With Bad Breath
If your bad breath is more than just, “Oops, I ate some onions,” then you could have chronic bad breath (known as halitosis). There are many conditions that could cause halitosis and poor oral hygiene is certainly one of them.
If someone you love or care for is constantly telling you that your breath doesn’t smell great (and offering you some chewing gum), it’s time to get the issue checked!
6. Your Diet Isn’t Right
We’re not saying you have to eat like a triathlete, but your diet does play a significant role in your oral health. For instance, eating too much sugar can create a breeding ground of harmful bacteria in your mouth that can lead to decay.
Another example is dark cola or coffee. While the occasional dark drink shouldn’t hurt your teeth much, drinking them day after day can stain your teeth. If you are going to drink dark colas or coffee, we recommend drinking them through a straw so they can bypass your teeth and gums (for the most part).
If you avoid sugar and dark-colored drinks it can go a long way to keeping your mouth healthy and in good shape!
7. You Need to Revamp Your Oral Hygiene Routine
A rock-solid oral hygiene routine isn’t difficult to find or master, but consistency is the key. At Shining Smiles Family Dentistry, we tell our patients they should brush their teeth twice a day for a period of two minutes each time and floss once daily.
It’s also a good idea to supplement with mouthwash. Also, many patients enjoy using an oral irrigator or water flosser to reach some of those stubborn spots that only water can reach.
Again, the routine is easy; become disciplined to follow it day after day without exception. Also, if you have a young child we recommend that you monitor their oral hygiene until they are at least 8 years old. While you want to encourage a young child to learn how to “do it themselves,” parents should still watch to ensure they are doing it correctly.
So What Should You Do if You’re Experiencing Any of These Problems?
If you are experiencing any of the above problems and feel that your mouth isn’t as healthy as it should be, it’s time to see a different kind of dentist! At Shining Smiles Family Dentistry, Dr. Mohip-Chahwala focuses, not only on providing patients with the best treatment for them, but has an overarching philosophy of preventative care.
Once we correct the issue you are experiencing, we’re going to share with you a personalized care plan to help you keep your teeth and gums healthy and happy for the rest of your life.As a family dental practice, Shining Smiles cares about the long-term oral health of all your loved ones. With our welcoming office, friendly team and services like sedation dentistry, we want everyone to feel comfortable and positive about their oral examinations and cleanings.
Only regular dental visits make it possible to monitor changes to your teeth and gums. And with a skilled professional relationship (including understanding any health concerns), it’s possible to deliver the best in dental care.
(02/03/2024)by Shining Smiles Family Dentistry
More Information: https://www.shiningsmilesga.com/dental-care-blog/7-reasons-your-mouth-isnt-healthy-and-what-to-do-about-it/
Views: 387

Six Signs To Identify Dental Problems Before They Become Worse
Your body has a way of sending you signals when it needs help. A headache is often the first indication of dehydration. Fatigue could be a sign of sleep apnea. As long as you pay attention to the messages your body provides, you can identify and reverse problems before they take control of your body.
Your oral health is no exception! We tend to think of our mouth as a separate entity from our body, but the truth is that oral health and general wellness are closely linked together. If you have an unhealthy mouth, these signals are trying to let you know.
1.- Bad Breath… All Day Long!
Chronic bad breath, also known as halitosis, can develop for a few different reasons, but the main trigger is poor oral health.

As soon as you eat or drink, food particles breakdown all around your teeth. If you don’t brush and floss regularly to remove food remnants, they accumulate into a thick coating of plaque that spreads over your teeth, tongue, and gums. Odor-causing bacteria thrives inside this plaque and emits the foul odor we call “bad breath”.
Your eating habits have the power to reduce or aggravate bad breath because they directly influence the types of particles that cover your mouth until the next time you brush and floss.
Bad breath sounds like it would be easy to identify, but many people can’t assess the odor of their own mouths. If you suspect that halitosis is influencing your oral health, you can ask a close friend or spouse to check your breath and give honest feedback. You can also perform a breath test yourself by licking your wrist, giving the saliva time to dry, and then smelling it.
Your oral hygiene habits set the pace for your mouth health. If you’ve been slacking on your brushing and flossing, you can begin to improve your oral hygiene habits with these techniques:

Brush and floss at least twice a day
Scrape your tongue each morning with a tongue scraper
Replace your toothbrush every two to three months
Start oil pulling
Drink plenty of water
These simple yet effective steps will prevent bacteria from building up and generating a foul odor.
2.- Sensitivity to Hot and Cold Foods and Drinks
The sensation caused by sensitive teeth is nearly impossible to describe, but there’s no mistaking that awful zinging feeling whenever you drink something too cold or hot. In addition to the pain it causes, sensitivity is also a sign of an unhealthy mouth.
Factors like brushing too hard, overuse of acidic beverages like soda and coffee, and excessive use of whitening products all expose tiny canals that lead right to your dental nerves. As soon as anything hot or cold reaches the nerves, you experience a “zing”.
Gum disease is also known to cause severe tooth sensitivity since gums recede from the teeth and lose their support system. If you have gum disease, you also probably have excessive plaque in your mouth, which also erodes tooth enamel and exposes nerve endings.
There are a few ways to treat sensitivity teeth, but it’s important to ask for your dentist’s advice before you choose:
Desensitizing toothpaste
In-office fluoride treatment
White fillings or crowns
Root canal
Laser gum therapy
3.- Chronic Sinus Infections From an Unhealthy Mouth
The bacteria that live in your mouth and gut are responsible for maintaining balanced immune responses throughout your body. This means that the health of your mouth directly impacts the strength of your immune system.
If you always seem to be coming down with a cold or sinus infection, that could be your body’s way of sending SOS messages Anything that harms or alters the microbiota communities in your mouth or digestive system has the potential to trigger immune dysfunction that leads to chronic sinus infections.
Improving your unhealthy mouth will create a direct improvement on your sinuses as well.
4.- Dry Mouth
You have three main salivary glands and hundreds of minor salivary glands that are responsible for producing saliva in your mouth. Saliva is essential to the health of your teeth and gums, so when you develop dry mouth, it puts our oral health in danger.
Consider the roles that saliva performs:
Neutralizes acids in the mouth
Washes away food debris, bacteria, and other lingering toxins
Keeps the mouth moist and hydrated, even while eating dry foods or exercising
Breaks food down with enzymes and carries it from the mouth to the gut.
Bombarding your mouth with potent sugars and acids all day, every day compromises your mouth’s ability to produce saliva. This leads to a dry, unhealthy mouth.
Remain alert for these possible dry mouth symptoms:
Chronic bad breath
Cracked lips and inner cheeks
Difficulty tasting foods
Pain and inflammation on the tongue
Frequent tooth decay
Trouble speaking, swallowing, and chewing
The feeling of sticky or stringy saliva
Dry mouth can be treated in a few different ways. The first step is to improve your general oral health with more frequent brushing, flossing, and dental appointments. Adjust your diet to nutritious, wholesome foods, and switch to medications that don’t cause the side effect of dry mouth. If those changes still don’t resolve your dry mouth, ask your dentist about other professional treatments.
5.- Tooth Discoloration From an Unhealthy Mouth
Poor oral care is a common cause of tooth discoloration. If you fail to brush and floss regularly, it’s all too easy for bacteria, acid, and plaque to accumulate and harden into tartar. Plaque and tartar both create an unsightly yellow coating around your teeth that leads to other issues like bad breath, decay, and tooth loss.
Fortunately, it can all be avoided with better oral hygiene! The simple actions of brushing, flossing, and visiting your dentist twice a year help prevent discoloration before it begins.
6.- Digestive Issues
The mouth is so much more than another part of the body. It’s where everything begins. There’s a direct and powerful link between oral health and whole body wellness.
As the entry point to the digestive system, the condition of your mouth directly influences your gastrointestinal health. This explains why poor oral health is shown to contribute to inflammatory bowel disease, Crohn’s disease, and ulcerative colitis.
When an unhealthy mouth becomes overwhelmed by pathogens, oral bacteria can constantly move into the gut and trigger serious complications. Some strains of bacteria found in unhealthy saliva are even resistant to antibiotics and believed to trigger intense gut inflammation.
(02/04/2024)by Ablantis Dental
More Information: https://ablantisdental.com/6-signs-you-have-an-unhealthy-mouthand-what-to-do-about-it/
Views: 342

What Happens To Your Teeth When You Get Ill?
When it comes to illness, we usually focus on the symptoms and the effects of the disease on the body, such as fever, fatigue or cough. However, the impact of illness on oral health, especially teeth, is often overlooked. The connection between systemic infection and dental health is essential, and understanding this can help us take better care of our overall health. We will look at what happens to your teeth when you are sick and offer advice on maintaining good oral hygiene during illness.
Dry Mouth:
A common side effect of many illnesses, especially those accompanied by fever and medications, is dry mouth. When dehydration is caused by disease or taking certain medications, the mouth produces less saliva. Saliva plays a vital role in neutralising acids, cleaning teeth and preventing the growth of harmful bacteria. Without enough saliva, the risk of tooth decay and gum disease increases.
Tip: Drink water throughout the day to stay hydrated. Consider using sugar-free lozenges or mouthwash to relieve dry mouth symptoms if dry mouth persists.

Weakened Immune System:
Illness can weaken your immune system and make you more susceptible to bacterial infections, including infections affecting your teeth and gums. While your body is busy fighting off illness, it may not be able to effectively fight off oral bacteria.
Tip: Maintain oral hygiene during illness, including regular brushing and flossing. It will help reduce the risk of bacterial buildup and gum inflammation!
Increased Sugar Consumption:
Comfort foods and sugary cough drops can be tempting during illness. Unfortunately, sugar can feed harmful oral bacteria, leading to tooth decay and cavities. In addition, some medications may contain sugar or acids that can erode tooth enamel.
Tips: Choose sugar-free cough drops and avoid sugary snacks and drinks. Rinse your mouth with water after taking medication to minimise the impact on your teeth.
Acidic Medications:
Certain medications, such as aspirin or vitamin C supplements, can be acidic and cause tooth enamel erosion. Taking these medications regularly during an illness can increase the risk of tooth sensitivity and decay.
Tip: If possible, take acidic medications with meals to reduce their contact with your teeth. You can also discuss alternative medicines with your healthcare provider.
Compromised Oral Hygiene:
Neglecting your oral hygiene routine when you’re not feeling well is easy. Brushing and flossing can seem daunting when you’re not feeling well. However, ignoring these practices can lead to plaque buildup and inflamed gums.
Tip: Strive to brush and floss at least twice a day, even when you are not feeling well. Consider using a soft-bristled toothbrush if you have a sore throat or mouth.
Medication Side Effects:
Some medications, including antibiotics, can cause changes in oral health. For example, they may cause oral thrush (a fungal infection of the mouth) or discoloured teeth.
Tip: If you notice any unusual symptoms in your mouth while taking your medication, consult your dentist or healthcare provider, who will be able to guide you on how to manage these side effects.
Stress and Teeth Grinding:
Illness can cause stress, and stress can manifest itself in various ways, including teeth grinding (bruxism). Teeth grinding, especially at night, can lead to worn tooth enamel, jaw pain and headaches.
Tip: If you suspect you are grinding your teeth, consider using a mouth guard, especially at night, to protect your teeth from damage!
It is vital to recognise the potential impact of disease on oral health. Maintaining good oral hygiene, staying hydrated, and being mindful of your medication choices can help mitigate these effects. Remember, oral health is an integral part of your overall health, and taking care of your teeth during an illness is a small but vital step toward a full recovery.
(02/06/2024)by Ideal Smile Dentistry
More Information: https://www.idealsmiledentistry.pk/what-happens-to-your-teeth-when-you-get-ill/
Views: 589

How to Manage a Sore Throat From Allergies
Seasonal allergies typically occur around springtime, with trees pollinating from August until October. Grass pollen then takes over and can trigger allergic reactions from November to March. If you experience hay fever, you may be developing a runny nose, nasal congestion and sneezing, among other symptoms. Sometimes, you can even get a sore throat from allergies. Here's why this happens and what you can do about it.
How Allergies Can Cause a Sore Throat
The glands in your nose and throat make about one to two quarts of mucus every day.This mucus has many important functions, such as keeping your nose clean and moistening the air you breathe, and you usually swallow it without realising. Other times, people may notice mucus dripping down the back of their nose or pooling in their throat. This unpleasant sensation is known as postnasal drip, and it can be caused by allergies.
If you have postnasal drip, the trickle of mucus can irritate your throat and cause soreness and other symptoms, such as feeling a lump in the throat or swallowing more frequently. It may also make you feel the need to clear your throat more often.
Soothing a Sore Throat at Home
Here are several home remedies that may help soothe a sore throat from allergies.
Stay well-hydrated to help thin the mucus.
Consume more hot liquids, such as chicken soup.

Use a humidifier or inhale steam.
Prop yourself up with a few extra pillows at night, since mucus can collect in the back of your throat when you lie flat.
There are also many over-the-counter medications available, including oral decongestants and antihistamines. Nasal decongestants may also be helpful, though Harvard Medical School cautions that they shouldn't be used for more than one to two days. For help choosing the most appropriate product, talk to your doctor or a pharmacist.
While these steps can help soothe a sore throat from allergies, they won't prevent future allergy symptoms. Pollen, whether from grass, trees or ragweed, is a common culprit of seasonal allergies, so avoiding exposure to it can help. Stay indoors on dry, windy days and, if possible, keeping your doors and windows closed on days with high pollen counts. If you need to do outdoor chores, such as lawn mowing or weed pulling, wear a pollen mask.
When to Seek Medical Help
Postnasal drip can be annoying, but it usually isn't dangerous, as Harvard Medical School explains. However, there are some circumstances when you should seek medical help. See your doctor or dentist if your symptoms get worse or if they aren't relieved by home remedies. You should also see your doctor if your sore throat is accompanied by other worrying symptoms, such as an unexplained fever or bloody mucus.
While you may experience a sore throat from allergies during hay fever season, rest assured that there are many home remedies that can help to soothe your symptoms. If these home remedies aren't enough, don't hesitate to seek medical advice.
(02/06/2024)by Colgate
More Information: https://www.colgate.com/en-za/oral-health/respiratory-conditions/how-to-manage-a-sore-throat-from-allergies
Views: 512

What Causes Submandibular Gland Swelling?
Most of us treat our salivary glands with an "out of sight, out of mind" mentality. But if something goes wrong with them, we'll quickly notice the problem. We rely on these glands to supply the saliva we need to chew, swallow and speak and to wash food debris away from our teeth. Submandibular gland swelling can be associated with dry mouth, infection and other conditions. However, most causes of gland swelling can be treated.
Where Are the Submandibular Glands?
Firstly, what is the submandibular gland? There is one walnut-sized submandibular gland on each side of the face, just in front of the curve of the lower jaw at the back of the mouth. Along with your other salivary glands, these glands supply saliva that contains enzymes to help break down food and minerals that reduce the damaging effects of food acids on your tooth enamel. Saliva also makes the food you chew wet and easy to swallow.
Causes of Submandibular Gland Swelling
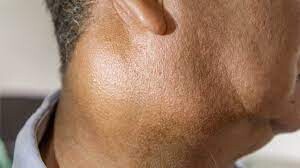
If you feel swelling underneath your lower jaw, it could be a swollen submandibular gland. Swollen submandibular glands are usually caused by tiny stones blocking the ducts that channel saliva into the mouth. According to the Merck Manual, these stones can develop from the salts in saliva, especially if a person is dehydrated. When a stone blocks a salivary gland, a condition known as sialolithiasis, an individual may experience swelling and pain over the affected gland. Why these stones form isn't clearly known, though they can be associated with liver disease and gout. According to The Journal of Medical Research, sialolithiasis is the most common salivary gland disease, and the submandibular gland is affected in 83 percent of cases.
Salivary gland infections can result from blocked ducts. In these cases, swelling of the gland may be accompanied by redness and pus.
More rarely, salivary gland swelling occurs due to a tumor. Merck Manuals explains that swelling caused by a cancerous or noncancerous tumor on the salivary glands may be firmer than swelling caused by an infection. A cancerous tumor will likely be very hard and fixed to the gland tissue, while a noncancerous tumor may be movable.
See your dentist to determine what's causing your submandibular gland swelling. They will help you put an effective treatment plan in place.

Treatments for Swollen Salivary Glands
Early treatment of a swollen salivary gland — particularly when caused by a stone — could save you from developing an infection. The National Health Service recommends increasing your saliva production by drinking plenty of water and chewing sugar-free gum. The Government of Alberta suggests gently massaging the stone to help dislodge it.
If you are unable to treat it at home, your doctor or dentist may be able to push the stone out by pressing the submandibular gland or pull it out by using a small instrument, according to Merck Manuals. In rare cases, the stone may need to be removed surgically. If you suffer from a condition that causes salivary gland stones, receiving treatment to alleviate other symptoms may also reduce your risk of developing stones.
If you have an infection in your submandibular gland, your doctor can prescribe antibiotics and, if necessary, drain any pus from an abscess. Swelling caused by a tumor can be addressed by removing the tumor through a surgical procedure. Cancerous tumors should be treated urgently and will likely require monitoring.
To ease the pain of submandibular gland swelling, apply a warm compress to the gland area and rinse your mouth with salt water.
How to Prevent Salivary Gland Swelling
Maintaining a thorough oral care routine reduces mouth bacteria and is an effective first step in preventing swollen salivary glands. Increase your water intake and avoid smoking and using chewing tobacco, because these habits may increase your risk of mouth infections.
Submandibular gland swelling may be caused by a blocked salivary gland that can be easily treated. However, make sure to see your doctor or dentist for an accurate diagnosis to assess this oral care condition.
(02/07/2024)by Colgate
More Information: https://www.colgate.com/en-us/oral-health/threats-to-dental-health/what-causes-submandibular-gland-swelling
Views: 499

Warning Signs From Your Tongue You Shouldn't Ignore
If you have a bleeding mouth sore or pain that lingers for more than a couple of weeks, don’t igore it.
“We see patients all the time who had an irritation around their tooth that ends up being squamous cell cancer, which may have been bothering them for up to a year,” says ear, nose and throat specialist Brian Burkey, MD, MEd.
Some oral cancers are not obvious to us as we look in a mirror and can even be hiding behind the teeth or under the tongue.
“The good news is that when picked up early, these cancers are highly, highly curable,” says Dr. Burkey. “Early detection is key.”

Seven symptoms to look out for
It’s important not to ignore these symptoms, which could signal medical problems or, in limited cases, oral cancer:
Nagging mouth pain.
Bleeding sore in the mouth that won’t heal and lasts for more than two weeks.
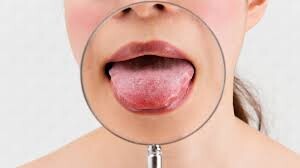
Swelling in the neck that lasts for more than two weeks.
An area in your mouth that becomes discolored and stays that way.
A lump or thickening in your cheek that doesn’t go away.
Numbness in your tongue or another part of your mouth.
Constant feeling of something caught in your throat or a change in your voice that lasts longer than two weeks.
While not an exhaustive list, these are symptoms that can slip under the radars of our busy lives.
“That’s why it’s important to notice when they don’t resolve,” says Dr. Burkey. “If symptoms last for more than two weeks, get them checked out by a doctor or dentist.”
Regular oral cancer screenings are crucial
Besides watching for any symptoms, it’s important to get regular oral cancer screenings to catch problems at their earliest stages. Here, Dr. Burkey explains what you need to know — and what to expect:
Who does the screenings? Your dentist is often your first line of defense when screening for oral cancer, but oral surgeons and ear, nose and throat specialists can also perform screenings.
How often do I need a screening? While there are no official recommendations for screenings, it’s important to get screenings during your usual dental checkups, twice a year.
Do I need to request a screening from my dentist or are they routine? Screenings are generally part of your normal dental exam, but ask your dentist to do one if they haven’t.
How long to screenings take? Oral cancer screenings take less than 10 minutes. Your doctor or dentist will perform a visual screening and feel the tongue looking for abnormal color and firm lesions. You also fill out an information form so that the doctor or dentist can pay close attention to any specific areas of concern.
Do the screenings hurt? No, they are generally painless.
How to reduce your risk
Here are ways to lower your risk of getting oral and head and neck cancers:
Quit tobacco. About 90% of people with oral cancer use tobacco (smoking or chewing), and their risk increases with the amount and length of time they use. Tobacco is most closely associated with ‘oral cavity’ cancer specifically, which affects the mouth, including lips, teeth and gums.
Take precautions against HPV. There is a dramatic rise in oropharyngeal cancer, or cancer in the tonsil and base of tongue associated with the human papilloma virus (HPV). You can’t see this area yourself, so finding it requires an exam from an ear, nose and throat physician. HPV is a sexually transmitted disease and is preventable with a vaccine and/or appropriate safe sex precautions, depending on one’s age.
Drink alcohol in moderation. Though less a risk factor than those above, alcohol use can also increase your risk of oral cancers.
Limit time in the sun. You want to protect your face to combat skin cancer, but in particular, don’t forget to protect your lips with sunscreen. They are often forgotten but they need protection too. If you work outside, try to avoid being in the midday sun. You should also wear a hat that shades your face whenever possible.
Good oral hygiene. Alongside getting your dental checkups twice a year, continue good oral hygiene at home by brushing twice a day and flossing once a day. Talk to your dentist about which mouth rinse they recommend, especially if you have mouth sores.
Incorporate a healthy diet. Keeping your teeth health go beyond just brushing. The American Dental Association recommends having a diet filled with plenty of water, vegetables, whole grains, fruits and lean protein. Make sure to avoid sugary treats and snacks to help keep harmful bacteria away.
(02/07/2024)by Health Digest
More Information: N
Views: 430

