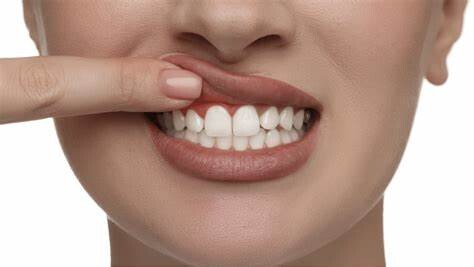
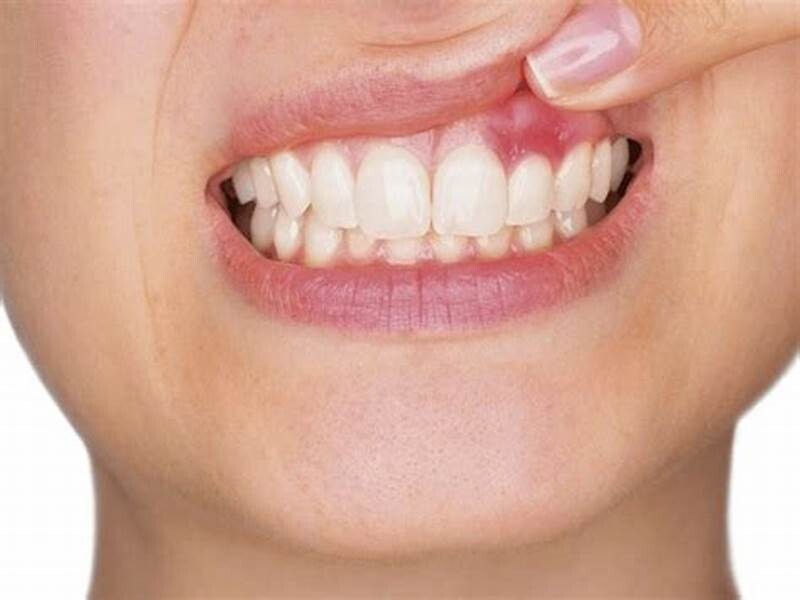
Browse by City / State:
Select State... AK AL AR AZ CA CO CT DC DE FL GA HI IA ID IL IN KS KY LA MA MD ME MI MN MO MS MT NC ND NE NH NJ NM NV NY OH OK OR PA PR RI SC SD TN TX UT VA VT WA WI WV WY Select... Anchor Point, AK Anchorage, AK Bethel, AK Chugiak, AK Craig, AK Dillingham, AK Dutch Harbor, AK Eagle River, AK Eielson AFB, AK Fairbanks, AK Fort Wainwright, AK Girdwood, AK Glennallen, AK Homer, AK JBER, AK Juneau, AK Kenai, AK Ketchikan, AK King Cove, AK Klawock, AK Kodiak, AK Naknek, AK Ninilchik, AK Nome, AK North Pole, AK Palmer, AK Petersburg, AK Seward, AK Sitka, AK Soldotna, AK Wasilla, AK Willow, AK Select... Adamsville, AL Alabaster, AL Albertville, AL Alexander City, AL Altoona, AL Andalusia, AL Anniston, AL Arab, AL Ashford, AL Ashville, AL Athens, AL Atmore, AL Auburn, AL Bay Minette, AL Bessemer, AL Birmingham, AL Blountsville, AL Boaz, AL Brewton, AL Brierfield, AL Butler, AL Calera, AL Centre, AL Chelsea, AL Childersburg, AL Clanton, AL Cleveland, AL Columbiana, AL Cullman, AL Daphne, AL Decatur, AL Demopolis, AL Dothan, AL Double Springs, AL Eclectic, AL Eight Mile, AL Elba, AL Elmore, AL Enterprise, AL Eufaula, AL Fairfield, AL Fairhope, AL Fayette, AL Florence, AL Foley, AL Fort Payne, AL Fort Rucker, AL Fyffe, AL Gadsden, AL Gardendale, AL Geneva, AL Gordo, AL Greensboro, AL Greenville, AL Grove Hill, AL Gulf Shores, AL Guntersville, AL Haleyville, AL Hartford, AL Hartselle, AL Harvest, AL Hazel Green, AL Headland, AL Helena, AL Huntsville, AL Jackson, AL Jacksonville, AL Jasper, AL Killen, AL Lafayette, AL Leeds, AL Lexington, AL Loxley, AL Madison, AL Maplesville, AL Marion, AL Mc Calla, AL Mc Intosh, AL Millbrook, AL Mobile, AL Monroeville, AL Montgomery, AL Moody, AL Moulton, AL Mount Vernon, AL Muscle Shoals, AL Northport, AL Oneonta, AL Opelika, AL Opp, AL Orange Beach, AL Oxford, AL Ozark, AL Pelham, AL Pell City, AL Phenix City, AL Phil Campbell, AL Piedmont, AL Pinson, AL Pleasant Grove, AL Prattville, AL Rainbow City, AL Rainsville, AL Red Bay, AL Reform, AL Robertsdale, AL Russellville, AL Saraland, AL Satsuma, AL Scottsboro, AL Selma, AL Sheffield, AL Smiths Station, AL Spanish Fort, AL Springville, AL Sumiton, AL Sylacauga, AL Talladega, AL Tallassee, AL Thomasville, AL Troy, AL Trussville, AL Tuscaloosa, AL Tuscumbia, AL Tuskegee, AL Union Springs, AL Valley, AL Vernon, AL Warrior, AL Wedowee, AL Winfield, AL Woodland, AL Woodstock, AL Select... Alma, AR Amity, AR Arkadelphia, AR Augusta, AR Bald Knob, AR Batesville, AR Bella Vista, AR Benton, AR Bentonville, AR Berryville, AR Blytheville, AR Brinkley, AR Bryant, AR Bull Shoals, AR Cabot, AR Calico Rock, AR Carlisle, AR Centerton, AR Charleston, AR Clarksville, AR Clinton, AR Conway, AR Corning, AR Cotter, AR Crossett, AR Danville, AR Dardanelle, AR De Queen, AR De Witt, AR Dermott, AR Des Arc, AR Dierks, AR El Dorado, AR Farmington, AR Fayetteville, AR Forrest City, AR Fort Smith, AR Gentry, AR Glenwood, AR Gravette, AR Greenbrier, AR Greenwood, AR Hardy, AR Harrison, AR Heber Springs, AR Helena, AR Hope, AR Hot Springs National Park, AR Hot Springs Village, AR Huntsville, AR Jacksonville, AR Jonesboro, AR Lavaca, AR Lepanto, AR Lincoln, AR Little Rock, AR Little Rock Air Force Base, AR Lonoke, AR Lowell, AR Mabelvale, AR Magnolia, AR Malvern, AR Mammoth Spring, AR Manila, AR Mansfield, AR Marianna, AR Marion, AR Maumelle, AR Mc Gehee, AR Mena, AR Monette, AR Monticello, AR Morrilton, AR Mount Ida, AR Mountain Home, AR Mountain View, AR Murfreesboro, AR Nashville, AR Newport, AR North Little Rock, AR Osceola, AR Ozark, AR Paragould, AR Paris, AR Pea Ridge, AR Piggott, AR Pine Bluff, AR Pocahontas, AR Prairie Grove, AR Rector, AR Rogers, AR Russellville, AR Searcy, AR Sheridan, AR Sherwood, AR Shirley, AR Siloam Springs, AR Springdale, AR Stuttgart, AR Texarkana, AR Trumann, AR Van Buren, AR Vilonia, AR Walnut Ridge, AR Warren, AR West Helena, AR West Memphis, AR Wynne, AR Select... APACHE JUNCTION, AZ Avondale, AZ Benson, AZ Bisbee, AZ Buckeye, AZ Bullhead City, AZ Camp Verde, AZ Carefree, AZ CASA GRANDE, AZ Cave Creek, AZ Chandler, AZ Chinle, AZ Chino Valley, AZ Clifton, AZ Coolidge, AZ Cottonwood, AZ Dewey, AZ Douglas, AZ Eagar, AZ El Mirage, AZ Elfrida, AZ Flagstaff, AZ FLORENCE, AZ Fort Defiance, AZ Fort Huachuca, AZ Fort Mohave, AZ Fountain Hills, AZ Fredonia, AZ Gilbert, AZ Glendale, AZ Globe, AZ GOLD CANYON, AZ Golden Valley, AZ Goodyear, AZ Green Valley, AZ Higley, AZ Kayenta, AZ KEARNY, AZ Kingman, AZ Lake Havasu City, AZ Lakeside, AZ Laveen, AZ Litchfield Park, AZ Littlefield, AZ Luke Air Force Base, AZ Marana, AZ Maricopa, AZ Mesa, AZ Nogales, AZ Page, AZ Paradise Valley, AZ Parker, AZ Payson, AZ Peoria, AZ Phoenix, AZ Pinetop, AZ Polacca, AZ Prescott, AZ Prescott Valley, AZ Queen Creek, AZ Rio Verde, AZ Sacaton, AZ Safford, AZ Sahuarita, AZ Saint Johns, AZ San Carlos, AZ San Luis, AZ San Tan Valley, AZ Scottsdale, AZ Sedona, AZ Show Low, AZ Sierra Vista, AZ Snowflake, AZ Sun City, AZ Sun City West, AZ Surprise, AZ Teec Nos Pos, AZ Tempe, AZ Tuba City, AZ Tucson, AZ Wickenburg, AZ Winslow, AZ Youngtown, AZ Yuma, AZ Select... Acton, CA Agoura Hills, CA Alameda, CA Alamo, CA Albany, CA Alhambra, CA Aliso Viejo, CA Alpine, CA Altadena, CA Altaville, CA Alturas, CA American Canyon, CA Anaheim, CA Anderson, CA Angels Camp, CA Angwin, CA Antelope, CA Antioch, CA Apple Valley, CA Aptos, CA Arbuckle, CA Arcadia, CA Arcata, CA Arnold, CA Arroyo Grande, CA Artesia, CA Arvin, CA Atascadero, CA Atherton, CA Atwater, CA Auberry, CA Auburn, CA Avenal, CA Azusa, CA Bakersfield, CA Baldwin Park, CA Banning, CA Barstow, CA Beale AFB, CA Beaumont, CA Bell Gardens, CA Bellflower, CA Belmont, CA Belvedere Tiburon, CA Ben Lomond, CA Benicia, CA Berkeley, CA Beverly Hills, CA Big Bear City, CA Big Bear Lake, CA Big Sur, CA Bishop, CA Blairsden-Graeagle, CA Bloomington, CA Blythe, CA Bonita, CA Bonsall, CA Boulder Creek, CA Brawley, CA Brea, CA Brentwood, CA Brisbane, CA Buellton, CA Buena Park, CA Burbank, CA Burlingame, CA Burney, CA Buttonwillow, CA Calabasas, CA Calexico, CA California City, CA Calimesa, CA Calistoga, CA Camarillo, CA Cambria, CA Camp Pendleton, CA Campbell, CA Canby, CA Canoga Park, CA Canyon Country, CA Capitola, CA Cardiff by the Sea, CA Carlsbad, CA Carmel, CA Carmel Valley, CA Carmichael, CA Carnelian Bay, CA Carpinteria, CA Carson, CA Caruthers, CA Castaic, CA Castro Valley, CA Cathedral City, CA Cayucos, CA Ceres, CA Cerritos, CA Chatsworth, CA Chico, CA Chino, CA Chino Hills, CA Chowchilla, CA Chula Vista, CA Citrus Heights, CA Claremont, CA Clayton, CA Clearlake, CA Cloverdale, CA Clovis, CA Coachella, CA Coalinga, CA Coarsegold, CA Colfax, CA Colton, CA Colusa, CA Compton, CA Concord, CA Cool, CA Copperopolis, CA Corning, CA Corona, CA Corona del Mar, CA Coronado, CA Corte Madera, CA Costa Mesa, CA Cotati, CA Covina, CA Crescent City, CA Crockett, CA Culver City, CA Cupertino, CA Cypress, CA Daly City, CA Dana Point, CA Danville, CA Davis, CA Del Mar, CA Delano, CA Desert Hot Springs, CA Diamond Bar, CA Dinuba, CA Discovery Bay, CA Dixon, CA Dos Palos, CA Downey, CA Duarte, CA Dublin, CA Dunsmuir, CA East Irvine, CA Edwards, CA El Cajon, CA El Centro, CA El Cerrito, CA El Dorado, CA El Dorado Hills, CA El Monte, CA El Segundo, CA El Sobrante, CA Elk Grove, CA Emeryville, CA Encinitas, CA Encino, CA Escondido, CA Etna, CA Eureka, CA Exeter, CA Fair Oaks, CA Fairfax, CA Fairfield, CA Fallbrook, CA Fillmore, CA Firebaugh, CA Folsom, CA Fontana, CA Foothill Ranch, CA Foresthill, CA Forestville, CA Fort Bragg, CA Fort Irwin, CA Fort Jones, CA Fortuna, CA Foster City, CA Fountain Valley, CA Freedom, CA Freemont, CA Fremont, CA French Camp, CA Fresno, CA Fullerton, CA Galt, CA Garberville, CA Garden Grove, CA Garden Valley, CA Gardena, CA Gilroy, CA Glendale, CA Glendora, CA Goleta, CA Gonzales, CA Granada Hills, CA Grand Terrace, CA Granite Bay, CA Grass Valley, CA Greenbrae, CA Greenfield, CA Gridley, CA Groveland, CA Grover Beach, CA Gualala, CA Guasti, CA Guerneville, CA Hacienda Heights, CA Half Moon Bay, CA Hanford, CA Harbor City, CA Hawaiian Gardens, CA Hawthorne, CA Hayfork, CA Hayward, CA Healdsburg, CA Hemet, CA Hercules, CA Hermosa Beach, CA Hesperia, CA Highland, CA Hilmar, CA Hollister, CA Hoopa, CA Huntington Beach, CA Huntington Park, CA Huron, CA Imperial, CA Imperial Beach, CA Indian Wells, CA Indio, CA Inglewood, CA Ione, CA Irvine, CA Jackson, CA Jamestown, CA Jamul, CA Kelseyville, CA Kerman, CA King City, CA Kings Beach, CA Kingsburg, CA La Canada Flintridge, CA La Crescenta, CA La Habra, CA La Jolla, CA La Mesa, CA La Mirada, CA La Palma, CA La Puente, CA La Quinta, CA La Verne, CA Ladera Ranch, CA Lafayette, CA Laguna Beach, CA Laguna Hills, CA Laguna Niguel, CA Laguna Woods, CA Lake Arrowhead, CA Lake Elsinore, CA Lake Elsinore,, CA Lake Forest, CA Lake Isabella, CA Lakeport, CA Lakeside, CA Lakewood, CA Lamont, CA Lancaster, CA Larkspur, CA Lathrop, CA Lawndale, CA Lebec, CA Lemon Grove, CA Lemoore, CA Lincoln, CA Lindsay, CA Live Oak, CA Livermore, CA Livingston, CA Lodi, CA Loma Linda, CA Lomita, CA Lompoc, CA Long Beach, CA Loomis, CA Los Alamitos, CA Los Altos, CA Los Angeles, CA Los Banos, CA Los Gatos, CA Los Osos, CA Loyalton, CA Lynwood, CA Madera, CA Magalia, CA Malibu, CA Mammoth Lakes, CA Manhattan Beach, CA Manteca, CA Marina, CA Marina del Rey, CA Mariposa, CA Martinez, CA Marysville, CA Maywood, CA McClellan, CA McKinleyville, CA Meadow Vista, CA Mendocino, CA Menifee, CA Menlo Park, CA Merced, CA Middletown, CA Midway City, CA Mill Valley, CA Millbrae, CA Milpitas, CA Mira Loma, CA Mission Hills, CA Mission Viejo, CA Modesto, CA Mojave, CA Monrovia, CA Montclair, CA Montebello, CA Monterey, CA Monterey Park, CA Montrose, CA Moorpark, CA Moraga, CA Moreno Valley, CA Morgan Hill, CA Morro Bay, CA Mount Shasta, CA Mountain View, CA Murrieta, CA Napa, CA National City, CA Needles, CA Nevada City, CA Newark, CA Newbury Park, CA Newhall, CA Newport Beach, CA Newport Coast, CA Nipomo, CA Norco, CA North Highlands, CA North Hills, CA North Hollywood, CA Northridge, CA Norwalk, CA Novato, CA Oak Park, CA Oak View, CA Oakdale, CA Oakhurst, CA Oakland, CA Oakley, CA Occidental, CA Oceanside, CA Ojai, CA Ontario, CA Orange, CA Orange Cove, CA Orangevale, CA Orinda, CA Orland, CA Orosi, CA Oroville, CA Oxnard, CA Pacific Grove, CA Pacific Palisades, CA Pacifica, CA Pacoima, CA Palm Desert, CA Palm Springs, CA Palmdale, CA Palo Alto, CA Palo Cedro, CA Palos Verdes Peninsula, CA Panorama City, CA Paradise, CA Paramount, CA Parlier, CA Pasadena, CA Paso Robles, CA Patterson, CA Pebble Beach, CA Penn Valley, CA Perris, CA Petaluma, CA Phelan, CA Pico Rivera, CA Pine Grove, CA Pine Valley, CA Pinole, CA Pioneer, CA Pismo Beach, CA Pittsburg, CA Placentia, CA Placerville, CA Planada, CA Playa del Rey, CA Playa Vista, CA Pleasant Hill, CA Pleasanton, CA Point Reyes Station, CA Pollock Pines, CA Pomona, CA Port Hueneme, CA Port Hueneme CBC Base, CA Porter Ranch, CA Porterville, CA Portola Valley, CA Poway, CA Quail Valley, CA Quincy, CA Ramona, CA Rancho Cordova, CA Rancho Cucamonga, CA Rancho Mirage, CA Rancho Palos Verdes, CA Rancho Santa Margarita, CA Red Bluff, CA Redding, CA Redlands, CA Redondo Beach, CA Redway, CA Redwood City, CA Redwood Valley, CA Reedley, CA Represa, CA Reseda, CA Rialto, CA Richmond, CA Ridgecrest, CA Rio Dell, CA Rio Linda, CA Rio Vista, CA Ripon, CA Riverside, CA Rocklin, CA Rodeo, CA Rohnert Park, CA Rosamond, CA Rosemead, CA Roseville, CA Round Mountain, CA Rowland Heights, CA Sacramento, CA Saint Helena, CA Salida, CA Salinas, CA San Andreas, CA San Anselmo, CA San Bernardino, CA San Bruno, CA San Carlos, CA San Clemente, CA San Diego, CA San Dimas, CA San Fernando, CA San Francisco, CA San Gabriel, CA San Jacinto, CA San Joaquin, CA San Jose, CA San Juan Capistrano, CA San Leandro, CA San Lorenzo, CA San Luis Obispo, CA San Marcos, CA San Marino, CA San Mateo, CA San Pablo, CA San Pedro, CA San Quentin, CA San Rafael, CA San Ramon, CA San Ysidro, CA Sanger, CA Santa Ana, CA Santa Barbara, CA Santa Clara, CA Santa Clarita, CA Santa Cruz, CA Santa Fe Springs, CA Santa Maria, CA Santa Monica, CA Santa Paula, CA Santa Rosa, CA Santa Ynez, CA Santee, CA Saratoga, CA Sausalito, CA Scotia, CA Scotts Valley, CA Seal Beach, CA Seaside, CA Sebastopol, CA Selma, CA Shasta Lake, CA Sherman Oaks, CA Shingle Springs, CA Sierra Madre, CA Signal Hill, CA Simi Valley, CA Sloughhouse, CA Smith River, CA Solana Beach, CA Soledad, CA Solvang, CA Somis, CA Sonoma, CA Sonora, CA Soquel, CA South El Monte, CA South Gate, CA South Lake Tahoe, CA South Pasadena, CA South San Francisco, CA Spring Valley, CA Stanford, CA Stanton, CA Stevenson Ranch, CA Stockton, CA Studio City, CA Sugarloaf, CA Suisun City, CA Sun City, CA Sun Valley, CA Sunland, CA Sunnyvale, CA Susanville, CA Sutter Creek, CA Sylmar, CA Taft, CA Tahoe City, CA Tarzana, CA Tehachapi, CA Temecula, CA Temple City, CA Templeton, CA Thermal, CA Thousand Oaks, CA Three Rivers, CA Torrance, CA Trabuco Canyon, CA Tracy, CA Travis AFB, CA Truckee, CA Tujunga, CA Tulare, CA Tuolumne, CA Turlock, CA Tustin, CA Twain Harte, CA Twentynine Palms, CA Ukiah, CA Union City, CA Upland, CA Vacaville, CA Valencia, CA Vallejo, CA Valley Center, CA Valley Springs, CA Valley Village, CA Van Nuys, CA Venice, CA Ventura, CA Victorville, CA Villa Park, CA Visalia, CA Vista, CA Walnut, CA Walnut Creek, CA Walnut Grove, CA Wasco, CA Waterford, CA Watsonville, CA Weed, CA West Covina, CA West Hills, CA West Hollywood, CA West Sacramento, CA Westlake Village, CA Westminster, CA Westwood, CA Wheatland, CA Whittier, CA Wildomar, CA Williams, CA Willits, CA Willow Creek, CA Willows, CA Wilmington, CA Windsor, CA Winnetka, CA Winters, CA Woodland, CA Woodland Hills, CA Yorba Linda, CA Yountville, CA Yreka, CA Yuba City, CA Yucaipa, CA Yucca Valley, CA Select... Akron, CO Alamosa, CO Arvada, CO Aspen, CO Aurora, CO Avon, CO Basalt, CO Bayfield, CO Bennett, CO Berthoud, CO Boulder, CO Breckenridge, CO Brighton, CO Broomfield, CO Brush, CO Buena Vista, CO Canon City, CO Carbondale, CO Castle Rock, CO Cedaredge, CO Colorado Springs, CO Commerce City, CO Conifer, CO Cortez, CO Craig, CO Crested Butte, CO Delta, CO Denver, CO Dillon, CO Dove Creek, CO Durango, CO Eagle, CO Eaton, CO Edwards, CO Elizabeth, CO Englewood, CO Erie, CO Estes Park, CO Evergreen, CO Florence, CO Fort Collins, CO Fort Lupton, CO Fort Morgan, CO Fountain, CO Franktown, CO Frederick, CO Frisco, CO Fruita, CO Georgetown, CO Glenwood Springs, CO Golden, CO Granby, CO Grand Junction, CO Greeley, CO Gypsum, CO Hotchkiss, CO Idaho Springs, CO Ignacio, CO Johnstown, CO Julesburg, CO La Junta, CO Lafayette, CO Lamar, CO Leadville, CO Limon, CO Littleton, CO Lone Tree, CO Longmont, CO Louisville, CO Loveland, CO Lyons, CO Mancos, CO Meeker, CO Monte Vista, CO Montrose, CO Monument, CO Morrison, CO New Castle, CO Niwot, CO Norwood, CO Olathe, CO Pagosa Springs, CO Palisade, CO Paonia, CO Parachute, CO Parker, CO Peyton, CO Pueblo, CO Rangely, CO Ridgway, CO Rifle, CO Rocky Ford, CO Salida, CO Silverthorne, CO Snowmass Village, CO South Fork, CO Steamboat Springs, CO Sterling, CO Strasburg, CO Telluride, CO Thornton, CO Trinidad, CO USAF Academy, CO Vail, CO Walsenburg, CO Walsh, CO Wellington, CO Westminster, CO Wheat Ridge, CO Windsor, CO Winter Park, CO Woodland Park, CO Select... Ansonia, CT Avon, CT Bantam, CT Berlin, CT Bethany, CT Bethel, CT Bloomfield, CT Bozrah, CT Branford, CT Bridgeport, CT Bristol, CT Brookfield, CT Burlington, CT Canaan, CT Canton, CT Cheshire, CT Chester, CT Clinton, CT Colchester, CT Columbia, CT Cos Cob, CT Coventry, CT Cromwell, CT Danbury, CT Danielson, CT Darien, CT Dayville, CT Deep River, CT Derby, CT Durham, CT East Hampton, CT East Hartford, CT East Haven, CT East Lyme, CT East Windsor, CT Ellington, CT Enfield, CT Essex, CT Fairfield, CT Farmington, CT Gales Ferry, CT Glastonbury, CT Granby, CT Greenwich, CT Groton, CT Guilford, CT Hamden, CT Hartford, CT Harwinton, CT Hebron, CT Higganum, CT Jewett City, CT Kent, CT Ledyard, CT Litchfield, CT Madison, CT Manchester, CT Mansfield Center, CT Marion, CT Marlborough, CT Meriden, CT Middlebury, CT Middletown, CT Milford, CT Monroe, CT Moodus, CT Mystic, CT Naugatuck, CT New Britain, CT New Canaan, CT New Fairfield, CT New Haven, CT New London, CT New Milford, CT Newington, CT Newtown, CT Niantic, CT North Branford, CT North Haven, CT Northford, CT Norwalk, CT Norwich, CT Old Greenwich, CT Old Lyme, CT Old Saybrook, CT Orange, CT Pawcatuck, CT Plainfield, CT Plainville, CT Plantsville, CT Portland, CT Prospect, CT Putnam, CT Redding, CT Ridgefield, CT Riverside, CT Rocky Hill, CT Salem, CT Seymour, CT Sharon, CT Shelton, CT Sherman, CT Simsbury, CT Somers, CT South Glastonbury, CT South Windsor, CT Southbury, CT Southington, CT Southport, CT Stamford, CT Storrs Mansfield, CT Stratford, CT Suffield, CT Terryville, CT Thomaston, CT Tolland, CT Torrington, CT Trumbull, CT Uncasville, CT Unionville, CT Vernon Rockville, CT Wallingford, CT Waterbury, CT Waterford, CT Watertown, CT Weatogue, CT West Hartford, CT West Haven, CT West Simsbury, CT Westbrook, CT Westport, CT Wethersfield, CT Willimantic, CT Willington, CT Wilton, CT Windsor, CT Windsor Locks, CT Winsted, CT Wolcott, CT Woodbridge, CT Woodbury, CT Select... Washington, DC Washington Navy Yard, DC Select... Bear, DE Camden Wyoming, DE Claymont, DE Dagsboro, DE Dover, DE Georgetown, DE Hockessin, DE Lewes, DE Middletown, DE MILFORD, DE Millsboro, DE Montchanin, DE New Castle, DE Newark, DE Ocean View, DE Rehoboth Beach, DE Seaford, DE Smyrna, DE Wilmington, DE Select... Alachua, FL Altamonte Springs, FL Apalachicola, FL Apollo Beach, FL Apopka, FL Arcadia, FL Atlantic Beach, FL Auburndale, FL Avon Park, FL Babson Park, FL Bartow, FL Bay Pines, FL Belle Glade, FL Belleview, FL Beverly Hills, FL Big Pine Key, FL Blountstown, FL Boca Raton, FL Bonifay, FL Bonita Springs, FL Boynton Beach, FL Bradenton, FL Bradenton Beach, FL Brandon, FL Branford, FL Bristol, FL Bronson, FL Brooker, FL Brooksville, FL Bunnell, FL Bushnell, FL Callahan, FL Cantonment, FL Cape Coral, FL Casselberry, FL Century, FL Chattahoochee, FL Chiefland, FL Chipley, FL Citra, FL Clearwater, FL Clermont, FL Clewiston, FL Cocoa, FL Cocoa Beach, FL Cortez, FL Crawfordville, FL Crescent City, FL Crestview, FL Crystal River, FL Dade City, FL Dania, FL Davenport, FL Davie, FL Daytona Beach, FL Debary, FL Deerfield Beach, FL Defuniak Springs, FL Deland, FL Delray Beach, FL Deltona, FL Destin, FL Dover, FL Dundee, FL Dunedin, FL Dunnellon, FL Ebro, FL Edgewater, FL Eglin AFB, FL Ellenton, FL Englewood, FL Estero, FL Eustis, FL Fellsmere, FL Fernandina Beach, FL Flagler Beach, FL Fleming Island, FL Fort Lauderdale, FL Fort Meade, FL Fort Myers, FL Fort Myers Beach, FL Fort Pierce, FL Fort Walton Beach, FL Freeport, FL Frostproof, FL Fruitland Park, FL Gainesville, FL Gibsonton, FL Graceville, FL Grand Island, FL Green Cove Springs, FL Groveland, FL Gulf Breeze, FL Haines City, FL Hallandale, FL Hastings, FL Havana, FL Hawthorne, FL Hernando, FL Hialeah, FL High Springs, FL Hobe Sound, FL Holiday, FL Hollywood, FL Homestead, FL Homosassa, FL Hudson, FL Hurlburt Field, FL Immokalee, FL Indialantic, FL Indiantown, FL Inverness, FL Islamorada, FL Jacksonville, FL Jacksonville Beach, FL Jasper, FL Jay, FL Jensen Beach, FL Jupiter, FL Key Biscayne, FL Key Largo, FL Key West, FL Keystone Heights, FL Kissimmee, FL Labelle, FL Lady Lake, FL Lake Alfred, FL Lake City, FL Lake Mary, FL Lake Placid, FL Lake Wales, FL Lake Worth, FL Lakeland, FL Land O Lakes, FL Largo, FL Lecanto, FL Leesburg, FL Lehigh Acres, FL Lithia, FL Live Oak, FL Longboat Key, FL Longwood, FL Loxahatchee, FL Lutz, FL Lynn Haven, FL Macclenny, FL Madison, FL Maitland, FL Marathon, FL Marco Island, FL Marianna, FL Mary Esther, FL Melbourne, FL Melbourne Beach, FL Melrose, FL Merritt Island, FL Miami, FL Miami Beach, FL Miami Gardens, FL Middleburg, FL Milton, FL Miramar Beach, FL Monticello, FL Moore Haven, FL Mount Dora, FL Mulberry, FL Myakka City, FL Naples, FL Navarre, FL Neptune Beach, FL New Port Richey, FL New Smyrna Beach, FL Newberry, FL Niceville, FL Nokomis, FL North Fort Myers, FL North Miami Beach, FL North Palm Beach, FL North Port, FL Ocala, FL Ocoee, FL Odessa, FL Okeechobee, FL Oldsmar, FL Opa Locka, FL Orange City, FL Orange Park, FL Orlando, FL Ormond Beach, FL Osprey, FL Oviedo, FL Oxford, FL Pahokee, FL Palatka, FL Palm Bay, FL Palm Beach, FL Palm Beach Gardens, FL Palm City, FL Palm Coast, FL Palm Harbor, FL Palmetto, FL Panacea, FL Panama City, FL Panama City Beach, FL Parrish, FL Patrick AFB, FL Pembroke Pines, FL Pensacola, FL Perry, FL Pinellas Park, FL Plant City, FL Plantation, FL Polk City, FL Pompano Beach, FL Ponte Vedra, FL Ponte Vedra Beach, FL Port Charlotte, FL Port Orange, FL Port Richey, FL Port Saint Joe, FL Port Saint Lucie, FL Punta Gorda, FL Quincy, FL Riverview, FL Rockledge, FL Ruskin, FL Safety Harbor, FL Saint Augustine, FL Saint Cloud, FL Saint James City, FL Saint Johns, FL Saint Petersburg, FL Sanford, FL Sanibel, FL Santa Rosa Beach, FL Sarasota, FL Satellite Beach, FL Sebastian, FL Sebring, FL Seffner, FL Seminole, FL Shalimar, FL Silver Springs, FL Sorrento, FL South Bay, FL Spring Hill, FL ST. CLOUD, FL Starke, FL Stuart, FL Summerfield, FL Summerland Key, FL Sumterville, FL Sun City Center, FL Tallahassee, FL Tallevast, FL Tampa, FL Tarpon Springs, FL Tavares, FL Tavernier, FL The Villages, FL Titusville, FL Trenton, FL Umatilla, FL Valparaiso, FL Valrico, FL Venice, FL Vero Beach, FL Wauchula, FL Wellington, FL Wesley Chapel, FL West Palm Beach, FL Wewahitchka, FL Wildwood, FL Williston, FL Windermere, FL Winter Garden, FL Winter Haven, FL Winter Park, FL Winter Springs, FL Yulee, FL Zephyrhills, FL Select... Acworth, GA Adairsville, GA Adel, GA Albany, GA Alpharetta, GA Americus, GA Arlington, GA Ashburn, GA Athens, GA Atlanta, GA Auburn, GA Augusta, GA Austell, GA Bainbridge, GA Barnesville, GA Baxley, GA Blackshear, GA Blairsville, GA Blakely, GA Blue Ridge, GA Bogart, GA Bowdon, GA Braselton, GA Bremen, GA Brunswick, GA Buford, GA Cairo, GA Calhoun, GA Canton, GA Carrollton, GA Cartersville, GA Cedartown, GA Chatsworth, GA Clarkesville, GA Clarkston, GA Clayton, GA Cleveland, GA Cochran, GA Colquitt, GA Columbus, GA Commerce, GA Conyers, GA Cordele, GA Cornelia, GA Covington, GA Cumming, GA Cuthbert, GA Dacula, GA Dahlonega, GA Dallas, GA Dalton, GA Danielsville, GA Darien, GA Dawson, GA Dawsonville, GA Decatur, GA Dillard, GA Donalsonville, GA Douglas, GA Douglasville, GA Dublin, GA Duluth, GA Eastanollee, GA Eastman, GA Eatonton, GA Elberton, GA Ellenwood, GA Ellijay, GA Evans, GA Fairburn, GA Fairmount, GA Fayetteville, GA Fitzgerald, GA Flintstone, GA Flowery Branch, GA Forest Park, GA Forsyth, GA Fort Benning, GA Fort Oglethorpe, GA Fort Stewart, GA Fort Valley, GA Fortson, GA Gainesville, GA Glennville, GA Gray, GA Grayson, GA Greensboro, GA Griffin, GA Grovetown, GA Hamilton, GA Hampton, GA Hazlehurst, GA Hephzibah, GA Hiawassee, GA Hinesville, GA Hiram, GA Homerville, GA Hoschton, GA Jackson, GA Jasper, GA Jefferson, GA Jesup, GA Jonesboro, GA Kennesaw, GA Kingsland, GA Lagrange, GA Lake Park, GA Lawrenceville, GA Leesburg, GA Lilburn, GA Lincolnton, GA Lithia Springs, GA Lithonia, GA Locust Grove, GA Loganville, GA Mableton, GA Macon, GA Madison, GA Manchester, GA Marietta, GA Mc Rae, GA McDonough, GA Metter, GA Midway, GA Milledgeville, GA Monroe, GA Monticello, GA Morrow, GA Moultrie, GA Murrayville, GA Nahunta, GA Nashville, GA Newnan, GA Norcross, GA Oakwood, GA Oglethorpe, GA Palmetto, GA Peachtree City, GA Pelham, GA Perry, GA Pine Mountain, GA Pooler, GA Powder Springs, GA Quitman, GA Reidsville, GA Richmond Hill, GA Rincon, GA Ringgold, GA Riverdale, GA Rochelle, GA Rockmart, GA Rome, GA Rossville, GA Roswell, GA Rutledge, GA Saint Marys, GA Saint Simons Island, GA Sandersville, GA Savannah, GA Smyrna, GA Snellville, GA Social Circle, GA Springfield, GA Statesboro, GA Stockbridge, GA Stone Mountain, GA Summerville, GA Suwanee, GA Swainsboro, GA Sylvania, GA Sylvester, GA Temple, GA Thomaston, GA Thomasville, GA Thomson, GA Tifton, GA Toccoa, GA Tucker, GA Tybee Island, GA Tyrone, GA Union City, GA Valdosta, GA Vidalia, GA Villa Rica, GA Warner Robins, GA Washington, GA Watkinsville, GA Waycross, GA West Point, GA Willacoochee, GA Williamson, GA Winder, GA Winterville, GA Woodbine, GA Woodstock, GA Zebulon, GA Select... Aiea, HI Ewa Beach, HI Fort Shafter, HI Haleiwa, HI Hanapepe, HI Hilo, HI Honolulu, HI Jbphh, HI Kahului, HI Kailua, HI Kailua Kona, HI Kamuela, HI Kaneohe, HI Kapolei, HI Kaunakakai, HI Keaau, HI Kealakekua, HI Kihei, HI Kilauea, HI Kula, HI Lahaina, HI Lanai City, HI Lihue, HI Makawao, HI Mcbh Kaneohe Bay, HI Mililani, HI Naalehu, HI Pearl City, HI Tripler Army Medical Center, HI Wahiawa, HI Waianae, HI Wailuku, HI Waimanalo, HI Waipahu, HI Select... Ackley, IA Adel, IA Albia, IA Algona, IA Allison, IA Altoona, IA Amana, IA Ames, IA Anamosa, IA Ankeny, IA Atlantic, IA Belle Plaine, IA Bellevue, IA Bettendorf, IA Boone, IA Buffalo Center, IA Burlington, IA Carroll, IA Carter Lake, IA Cascade, IA Cedar Falls, IA Cedar Rapids, IA Center Point, IA Chariton, IA Charles City, IA Cherokee, IA Clarion, IA Clear Lake, IA Clinton, IA Clive, IA Colfax, IA Columbus City, IA Coralville, IA Corning, IA Council Bluffs, IA Cresco, IA Creston, IA Davenport, IA De Witt, IA Decorah, IA Denison, IA Des Moines, IA Dubuque, IA Durant, IA Dyersville, IA Dysart, IA Eagle Grove, IA Earlham, IA Eldora, IA Eldridge, IA Emmetsburg, IA Epworth, IA Estherville, IA Evansdale, IA Fairfield, IA Farley, IA Forest City, IA Fort Dodge, IA Garner, IA Glenwood, IA Greenfield, IA Grimes, IA Grinnell, IA Guthrie Center, IA Hampton, IA Harlan, IA Hiawatha, IA Holstein, IA Hudson, IA Hull, IA Humboldt, IA Ida Grove, IA Independence, IA Indianola, IA Iowa, IA Iowa City, IA Iowa Falls, IA Jefferson, IA Johnston, IA Keokuk, IA Kingsley, IA Knoxville, IA La Porte City, IA Lake Mills, IA Lansing, IA Laurens, IA Le Claire, IA Le Mars, IA Lenox, IA Leon, IA Manchester, IA Manly, IA Mapleton, IA Maquoketa, IA Marengo, IA Marion, IA Marshalltown, IA Mason City, IA Milford, IA Missouri Valley, IA Monticello, IA Mount Pleasant, IA Mount Vernon, IA Muscatine, IA Nevada, IA New Hampton, IA New London, IA Newton, IA North Liberty, IA Norwalk, IA Odebolt, IA Oelwein, IA Ogden, IA Onawa, IA Orange City, IA Osceola, IA Oskaloosa, IA Ottumwa, IA Parkersburg, IA Pella, IA Peosta, IA Perry, IA Pleasant Hill, IA Pocahontas, IA Red Oak, IA Reinbeck, IA Remsen, IA Rock Rapids, IA Sanborn, IA Sheldon, IA Shenandoah, IA Sioux Center, IA Sioux City, IA Solon, IA Spencer, IA Spirit Lake, IA Storm Lake, IA Stuart, IA Sumner, IA Tama, IA Tiffin, IA Tipton, IA Urbandale, IA Van Horne, IA Vinton, IA Walcott, IA Wapello, IA Washington, IA Waterloo, IA Waukee, IA Waverly, IA Webster City, IA West Burlington, IA West Des Moines, IA West Liberty, IA West Union, IA Williamsburg, IA Wilton, IA Woodbine, IA Select... American Falls, ID Blackfoot, ID Boise, ID Bonners Ferry, ID Burley, ID Caldwell, ID Coeur D Alene, ID Council, ID Craigmont, ID Driggs, ID Eagle, ID Emmett, ID Fort Hall, ID Fruitland, ID Garden City, ID Grangeville, ID Hailey, ID Hayden, ID Homedale, ID Idaho Falls, ID Jerome, ID Kellogg, ID Ketchum, ID Kimberly, ID Kuna, ID Lapwai, ID Lewiston, ID Malad City, ID McCall, ID Melba, ID Meridian, ID Middleton, ID Montpelier, ID Moscow, ID Mountain Home, ID Mountain Home AFB, ID Nampa, ID Orofino, ID Parma, ID Payette, ID Pinehurst, ID Plummer, ID Pocatello, ID Ponderay, ID Post Falls, ID Preston, ID Rathdrum, ID Rexburg, ID Rigby, ID Rupert, ID Saint Anthony, ID Saint Maries, ID Salmon, ID Sandpoint, ID Shelley, ID Soda Springs, ID Star, ID Sugar City, ID Twin Falls, ID Victor, ID Weiser, ID Select... Addison, IL Aledo, IL Algonquin, IL Alsip, IL Altamont, IL Alton, IL Amboy, IL Anna, IL Annawan, IL Antioch, IL Arlington Heights, IL Auburn, IL Augusta, IL Aurora, IL Barrington, IL Barry, IL Bartlett, IL Batavia, IL Beecher, IL Belleville, IL Bellwood, IL Belvidere, IL Bensenville, IL Benton, IL Berkeley, IL Berwyn, IL Bethalto, IL Biggsville, IL Bismarck, IL Bloomingdale, IL Bloomington, IL Blue Island, IL Blue Mound, IL Bolingbrook, IL Bourbonnais, IL Bradley, IL Breese, IL Bridgeview, IL Brighton, IL Brookfield, IL Buffalo Grove, IL Burbank, IL Bushnell, IL Byron, IL Cairo, IL Calumet City, IL Canton, IL Carbondale, IL Carlinville, IL Carlyle, IL Carmi, IL Carol Stream, IL Carpentersville, IL Carrollton, IL Carterville, IL Carthage, IL Cary, IL Centralia, IL Cerro Gordo, IL Champaign, IL Channahon, IL Charleston, IL Chatham, IL Cherry Valley, IL Chester, IL Chicago, IL Chicago Heights, IL Chicago Ridge, IL Chillicothe, IL Cicero, IL Cissna Park, IL Clarendon Hills, IL Clinton, IL Coal City, IL Collinsville, IL Columbia, IL Crest Hill, IL Crete, IL Crystal Lake, IL Dahinda, IL Danville, IL Darien, IL Decatur, IL Deerfield, IL Dekalb, IL Des Plaines, IL Dixon, IL Dolton, IL Downers Grove, IL Du Quoin, IL Dundee, IL Dunlap, IL East Alton, IL East Dubuque, IL East Moline, IL East Peoria, IL East Saint Louis, IL Edwardsville, IL Effingham, IL Elburn, IL Eldorado, IL Elgin, IL Elk Grove Village, IL Elmhurst, IL Elmwood Park, IL Energy, IL Eureka, IL Evanston, IL Evergreen Park, IL Fairbury, IL Fairfield, IL Fairview Heights, IL Farmington, IL Flora, IL Flossmoor, IL Forest Park, IL Forreston, IL Forsyth, IL Fox Lake, IL Fox River Grove, IL Frankfort, IL Franklin Park, IL Freeburg, IL Freeport, IL Galena, IL Galesburg, IL Galva, IL Geneseo, IL Geneva, IL Genoa, IL Gibson City, IL Gillespie, IL Glen Carbon, IL Glen Ellyn, IL Glencoe, IL Glendale Heights, IL Glenview, IL Godfrey, IL Granite City, IL Granville, IL Grayslake, IL Great Lakes, IL Greenville, IL Gridley, IL Gurnee, IL Hampshire, IL Hampton, IL Hanover Park, IL Harvard, IL Harwood Heights, IL Havana, IL Hazel Crest, IL Hebron, IL Henry, IL Herrin, IL Herscher, IL Hickory Hills, IL Highland, IL Highland Park, IL Highwood, IL Hillsboro, IL Hillside, IL Hinckley, IL Hinsdale, IL Hoffman Estates, IL Homer Glen, IL Hometown, IL Homewood, IL Huntley, IL Ingleside, IL Island Lake, IL Itasca, IL Jacksonville, IL Jerseyville, IL Johnston City, IL Joliet, IL Justice, IL Kankakee, IL Kenilworth, IL Kewanee, IL Kirkland, IL La Grange, IL La Grange Park, IL La Salle, IL Lake Bluff, IL Lake Forest, IL Lake in the Hills, IL Lake Villa, IL Lake Zurich, IL Lansing, IL Lawrenceville, IL Le Roy, IL Lebanon, IL Lemont, IL Libertyville, IL Lincoln, IL Lincolnshire, IL Lincolnwood, IL Lisle, IL Litchfield, IL Lockport, IL Lombard, IL Loves Park, IL Lyons, IL Machesney Park, IL Macomb, IL Mahomet, IL Makanda, IL Manteno, IL Marengo, IL Marion, IL Marseilles, IL Marshall, IL Maryville, IL Mascoutah, IL Mason City, IL Matteson, IL Mattoon, IL Maywood, IL Mc Leansboro, IL McHenry, IL Melrose Park, IL Mendota, IL Metamora, IL Metropolis, IL Midlothian, IL Milan, IL Millstadt, IL Minooka, IL Mokena, IL Moline, IL Monee, IL Monmouth, IL Montgomery, IL Monticello, IL Morris, IL Morrison, IL Morton, IL Morton Grove, IL Mount Carmel, IL Mount Carroll, IL Mount Prospect, IL Mount Pulaski, IL Mount Vernon, IL Mt Zion, IL Mundelein, IL Murphysboro, IL Naperville, IL Nashville, IL New Athens, IL New Baden, IL New Lenox, IL Niles, IL Normal, IL North Aurora, IL North Chicago, IL Northbrook, IL O Fallon, IL Oak Brook, IL Oak Forest, IL Oak Lawn, IL Oak Park, IL Oglesby, IL Olney, IL Olympia Fields, IL Oquawka, IL Oregon, IL Orland Park, IL Oswego, IL Ottawa, IL Palatine, IL Palos Heights, IL Palos Hills, IL Palos Park, IL Paris, IL Park Forest, IL Park Ridge, IL Pekin, IL Peoria, IL Peoria Heights, IL Peotone, IL Peru, IL Petersburg, IL Pinckneyville, IL Pittsfield, IL Plainfield, IL Plano, IL Pontiac, IL Princeton, IL Prospect Heights, IL Quincy, IL Rantoul, IL Red Bud, IL Richmond, IL Richton Park, IL River Forest, IL River Grove, IL Riverdale, IL Riverside, IL Robinson, IL Rochelle, IL Rochester, IL Rock Falls, IL Rock Island, IL Rockford, IL Rockton, IL Rolling Meadows, IL Romeoville, IL Roscoe, IL Roselle, IL Roseville, IL Rossville, IL Round Lake, IL Saint Charles, IL Salem, IL Sandwich, IL Savanna, IL Savoy, IL Schaumburg, IL Scott Air Force Base, IL Sesser, IL Shelbyville, IL Sherman, IL Shorewood, IL Skokie, IL Smithton, IL South Elgin, IL South Holland, IL Spring Grove, IL Springfield, IL Staunton, IL Steeleville, IL Steger, IL Sterling, IL Stockton, IL Streamwood, IL Streator, IL Stronghurst, IL Sugar Grove, IL Summit Argo, IL Sycamore, IL Taylorville, IL Teutopolis, IL Tinley Park, IL Tolono, IL Toluca, IL Toulon, IL Trenton, IL Troy, IL Tuscola, IL Urbana, IL Vandalia, IL Vernon Hills, IL Vienna, IL Villa Park, IL Virden, IL Virginia, IL Wadsworth, IL Warrenville, IL Washington, IL Waterloo, IL Watseka, IL Wauconda, IL Waukegan, IL West Chicago, IL West Frankfort, IL Westchester, IL Western Springs, IL Westmont, IL Wheaton, IL Wheeling, IL Willow Springs, IL Willowbrook, IL Wilmette, IL Wilmington, IL Winchester, IL Winfield, IL Winnetka, IL Winthrop Harbor, IL Wonder Lake, IL Wood Dale, IL Wood River, IL Woodridge, IL Woodstock, IL Worth, IL Yorkville, IL Zion, IL Select... Albany, IN Albion, IN Alexandria, IN Anderson, IN Angola, IN Argos, IN Atlanta, IN Attica, IN Auburn, IN Aurora, IN Austin, IN Avon, IN Bainbridge, IN Batesville, IN Bedford, IN Beech Grove, IN Berne, IN Bloomington, IN Bluffton, IN Boonville, IN Brazil, IN Bremen, IN Brookville, IN Brownsburg, IN Brownstown, IN Camby, IN Carmel, IN Cedar Lake, IN Centerville, IN Charlestown, IN Chesterton, IN Churubusco, IN Cicero, IN Clarksville, IN Clinton, IN Columbia City, IN Columbus, IN Connersville, IN Corydon, IN Covington, IN Crawfordsville, IN Crown Point, IN Culver, IN Dale, IN Danville, IN Decatur, IN Delphi, IN Demotte, IN Dunkirk, IN Dyer, IN East Chicago, IN Edinburgh, IN Elizabeth, IN Elkhart, IN Ellettsville, IN Evansville, IN Fishers, IN Flora, IN Floyds Knobs, IN Fort Branch, IN Fort Wayne, IN Fortville, IN Fowler, IN Frankfort, IN Franklin, IN Fremont, IN French Lick, IN Gary, IN Gas City, IN Georgetown, IN Goshen, IN Grabill, IN Granger, IN Greencastle, IN Greenfield, IN Greensburg, IN Greentown, IN Greenwood, IN Griffith, IN Hammond, IN Harlan, IN Hartford City, IN Hebron, IN Highland, IN Hoagland, IN Hobart, IN Holland, IN Hope, IN Huntingburg, IN Huntington, IN Indianapolis, IN Jasper, IN Jeffersonville, IN Kendallville, IN Knightstown, IN Knox, IN Kokomo, IN La Porte, IN Lafayette, IN Lagrange, IN Lake Station, IN Lapel, IN Lawrenceburg, IN Lebanon, IN Leo, IN Ligonier, IN Linton, IN Logansport, IN Loogootee, IN Lowell, IN Lynn, IN Lyons, IN Madison, IN Marion, IN Martinsville, IN Mc Cordsville, IN Merrillville, IN Michigan City, IN Middlebury, IN Middletown, IN Millersburg, IN Mishawaka, IN Mitchell, IN Monroeville, IN Monrovia, IN Monticello, IN Montpelier, IN Mooresville, IN Morristown, IN Mount Vernon, IN Muncie, IN Munster, IN Nappanee, IN New Albany, IN New Castle, IN New Haven, IN New Palestine, IN Newburgh, IN Noblesville, IN North Liberty, IN North Manchester, IN North Vernon, IN Oakland City, IN Oaktown, IN Odon, IN Ossian, IN Owensville, IN Paoli, IN Pendleton, IN Peru, IN Plainfield, IN Plymouth, IN Portage, IN Portland, IN Princeton, IN Remington, IN Rensselaer, IN Richmond, IN Rising Sun, IN Roanoke, IN Rochester, IN Rockport, IN Rockville, IN Rossville, IN Rushville, IN Saint John, IN Salem, IN Schererville, IN Scottsburg, IN Sellersburg, IN Seymour, IN Shelbyville, IN South Bend, IN South Whitley, IN Spencer, IN Sullivan, IN Syracuse, IN Tell City, IN Terre Haute, IN Thorntown, IN Tipton, IN Topeka, IN Trafalgar, IN Valparaiso, IN Vevay, IN Vincennes, IN Wabash, IN Wanatah, IN Warren, IN Warsaw, IN Washington, IN Waterloo, IN West Lafayette, IN Westfield, IN Westville, IN Whiteland, IN Whiting, IN Williamsport, IN Winamac, IN Winchester, IN Woodburn, IN Worthington, IN Yorktown, IN Zionsville, IN Select... Abilene, KS Andover, KS Anthony, KS Arkansas City, KS Atchison, KS Atwood, KS Augusta, KS Beloit, KS Bennington, KS Bonner Springs, KS Buhler, KS Burlington, KS Caldwell, KS Chanute, KS Cheney, KS Cherryvale, KS Clearwater, KS Coffeyville, KS Colby, KS Columbus, KS Concordia, KS Council Grove, KS De Soto, KS Derby, KS Dodge City, KS Downs, KS El Dorado, KS Ellis, KS Ellsworth, KS Emporia, KS Erie, KS Fort Riley, KS Frontenac, KS Garden City, KS Gardner, KS Goddard, KS Goodland, KS Great Bend, KS Harper, KS Hays, KS Haysville, KS Hesston, KS Hillsboro, KS Holton, KS Horton, KS Hoxie, KS Humboldt, KS Hutchinson, KS Independence, KS Iola, KS Junction City, KS Kansas City, KS Kingman, KS La Crosse, KS Lacygne, KS Lakin, KS Lansing, KS Larned, KS Lawrence, KS Leavenworth, KS Leawood, KS Lenexa, KS Leoti, KS Liberal, KS Lindsborg, KS Lyons, KS Maize, KS Manhattan, KS Marysville, KS Mc Louth, KS McConnell AFB, KS McPherson, KS Meade, KS Minneapolis, KS Mission, KS Mount Hope, KS Mulvane, KS Newton, KS Norton, KS Oakley, KS Olathe, KS Osage City, KS Osawatomie, KS Oskaloosa, KS Ottawa, KS Overland Park, KS Paola, KS Parsons, KS Phillipsburg, KS Pittsburg, KS Plainville, KS Prairie Village, KS Pratt, KS Rose Hill, KS Russell, KS Sabetha, KS Saint Francis, KS Saint John, KS Salina, KS Sedan, KS Seneca, KS Shawnee, KS Smith Center, KS Spring Hill, KS Syracuse, KS Tonganoxie, KS Topeka, KS Ulysses, KS Valley Center, KS Wamego, KS Wellington, KS Wichita, KS Winfield, KS Select... Albany, KY Alexandria, KY Allen, KY Arjay, KY Ashland, KY Barbourville, KY Bardstown, KY Bardwell, KY Battletown, KY Beattyville, KY Beaver Dam, KY Bellevue, KY Benton, KY Berea, KY Bowling Green, KY Brandenburg, KY Brooksville, KY Burkesville, KY Burlington, KY Cadiz, KY Calvert City, KY Campbellsville, KY Caneyville, KY Carrollton, KY Catlettsburg, KY Central City, KY Columbia, KY Corbin, KY Corinth, KY Covington, KY Crestwood, KY Crittenden, KY Cumberland, KY Cynthiana, KY Danville, KY Dry Ridge, KY Eddyville, KY Elizabethtown, KY Elkhorn City, KY Erlanger, KY Falmouth, KY Flatwoods, KY Flemingsburg, KY Florence, KY Fort Campbell, KY Fort Knox, KY Fort Thomas, KY Frankfort, KY Franklin, KY Ft Mitchell, KY Fulton, KY Garrett, KY Georgetown, KY Glasgow, KY Greensburg, KY Greenville, KY Harlan, KY Harrodsburg, KY Hartford, KY Hawesville, KY Hazard, KY Hebron, KY Henderson, KY Hopkinsville, KY Horse Cave, KY Hyden, KY Independence, KY Inez, KY Irvine, KY La Center, KY La Grange, KY Lancaster, KY Latonia, KY Lawrenceburg, KY Lebanon, KY Lebanon Junction, KY Leitchfield, KY Lexington, KY Livermore, KY London, KY Louisville, KY Madisonville, KY Marion, KY Martin, KY Mayfield, KY Maysville, KY Mc Dowell, KY Mc Kee, KY Middlesboro, KY Minnie, KY Monticello, KY Morehead, KY Mount Sterling, KY Mount Vernon, KY Mount Washington, KY Munfordville, KY Murray, KY Nancy, KY Neon, KY Newport, KY Nicholasville, KY Owensboro, KY Paducah, KY Paintsville, KY Paris, KY Pendleton, KY Pewee Valley, KY Pikeville, KY Prestonsburg, KY Prospect, KY Providence, KY Radcliff, KY Richmond, KY Rineyville, KY Russell, KY Russellville, KY Salyersville, KY Scottsville, KY Shelbyville, KY Shepherdsville, KY Somerset, KY South Williamson, KY Springfield, KY Stanford, KY Tompkinsville, KY Union, KY Versailles, KY Vicco, KY Vine Grove, KY Walton, KY West Liberty, KY Whitesburg, KY Wilmore, KY Winchester, KY Select... Abbeville, LA Abita Springs, LA Albany, LA Alexandria, LA Amite, LA Baker, LA Ball, LA Barksdale AFB, LA Bastrop, LA Baton Rouge, LA Belle Chasse, LA Bogalusa, LA Bossier City, LA Boutte, LA Breaux Bridge, LA Broussard, LA Bunkie, LA Calhoun, LA Carencro, LA Chalmette, LA Chauvin, LA Clinton, LA Columbia, LA Cottonport, LA Coushatta, LA Covington, LA Crowley, LA Cut Off, LA Delcambre, LA Delhi, LA Denham Springs, LA Deridder, LA Destrehan, LA Donaldsonville, LA Dry Prong, LA Eunice, LA Ferriday, LA Folsom, LA Fort Polk, LA Franklin, LA Geismar, LA Gonzales, LA Greensburg, LA Greenwell Springs, LA Gretna, LA Hammond, LA Harvey, LA Haughton, LA Homer, LA Houma, LA Innis, LA Iota, LA Iowa, LA Jeanerette, LA Jena, LA Jennings, LA Jonesboro, LA Kaplan, LA Kenner, LA Kentwood, LA Kinder, LA La Place, LA Lafayette, LA Lafitte, LA Lake Charles, LA Leesville, LA Livingston, LA Lockport, LA Loreauville, LA Luling, LA Lutcher, LA Madisonville, LA Mandeville, LA Mansfield, LA Mansura, LA Maringouin, LA Marrero, LA Metairie, LA Minden, LA Monroe, LA Morgan City, LA Napoleonville, LA Natchitoches, LA New Iberia, LA New Orleans, LA New Roads, LA Oakdale, LA Opelousas, LA Pearl River, LA Pineville, LA Plaquemine, LA Port Allen, LA Prairieville, LA Raceland, LA Rayne, LA Rayville, LA Reserve, LA Ruston, LA Saint Francisville, LA Saint Gabriel, LA Saint Martinville, LA Saint Rose, LA Scott, LA Shreveport, LA Simmesport, LA Slidell, LA Springfield, LA Springhill, LA Sulphur, LA Sunset, LA Tallulah, LA Thibodaux, LA Vacherie, LA Vidalia, LA Ville Platte, LA Vinton, LA Walker, LA West Monroe, LA Westlake, LA Winnfield, LA Youngsville, LA Zachary, LA Select... Abington, MA Acton, MA Agawam, MA Allston, MA Amherst, MA Andover, MA Arlington, MA Ashburnham, MA Ashland, MA Assonet, MA Attleboro, MA Attleboro Falls, MA Auburn, MA Auburndale, MA Avon, MA Ayer, MA Barnstable, MA Bedford, MA Belchertown, MA Bellingham, MA Belmont, MA Berlin, MA Beverly, MA Billerica, MA Blackstone, MA Bolton, MA Boston, MA Boxborough, MA Braintree, MA Brewster, MA Bridgewater, MA Brighton, MA Brockton, MA Brookline, MA Burlington, MA Buzzards Bay, MA Byfield, MA Cambridge, MA Canton, MA Carlisle, MA Carver, MA Centerville, MA Charlestown, MA Chatham, MA Chelmsford, MA Chelsea, MA Chestnut Hill, MA Chicopee, MA Clinton, MA Cohasset, MA Concord, MA Cotuit, MA Dalton, MA Danvers, MA Dedham, MA Dennis, MA Dorchester, MA Dorchester Center, MA Douglas, MA Dover, MA Dracut, MA Duxbury, MA East Bridgewater, MA East Longmeadow, MA East Weymouth, MA Easthampton, MA Easton, MA Edgartown, MA Essex, MA Everett, MA Fairhaven, MA Fall River, MA Falmouth, MA Feeding Hills, MA Fitchburg, MA Florence, MA Forestdale, MA Foxboro, MA Framingham, MA Franklin, MA Gardner, MA Gloucester, MA Great Barrington, MA Greenfield, MA Groton, MA Groveland, MA Hadley, MA Hampden, MA Hanover, MA Hanscom AFB, MA Hanson, MA Harvard, MA Harwich, MA Harwich Port, MA Haverhill, MA Hingham, MA Holbrook, MA Holden, MA Holliston, MA Holyoke, MA Hopedale, MA Hopkinton, MA Hudson, MA Hull, MA Huntington, MA Hyannis, MA Hyde Park, MA Ipswich, MA Jamaica Plain, MA Kingston, MA Lakeville, MA Lancaster, MA Lawrence, MA Lee, MA Leeds, MA Leicester, MA Lenox, MA Leominster, MA Lexington, MA Lincoln, MA Littleton, MA Longmeadow, MA Lowell, MA Ludlow, MA Lunenburg, MA Lynn, MA Lynnfield, MA Malden, MA Manchester, MA Mansfield, MA Marblehead, MA Marion, MA Marlborough, MA Marshfield, MA Mashpee, MA Mattapan, MA Mattapoisett, MA Maynard, MA Medfield, MA Medford, MA Medway, MA Melrose, MA Merrimac, MA Methuen, MA Middleboro, MA Middleton, MA Milford, MA Millis, MA Milton, MA Monson, MA Nantucket, MA Natick, MA Needham, MA Needham Heights, MA New Bedford, MA Newburyport, MA Newton, MA Newton Center, MA Newton Highlands, MA Newton Upper Falls, MA Newtonville, MA Norfolk, MA North Adams, MA North Andover, MA North Attleboro, MA North Billerica, MA North Chelmsford, MA North Dartmouth, MA North Easton, MA North Falmouth, MA North Grafton, MA North Reading, MA Northampton, MA Northborough, MA Norton, MA Norwell, MA Norwood, MA Oak Bluffs, MA Orange, MA Orleans, MA Osterville, MA Oxford, MA Paxton, MA Peabody, MA Pembroke, MA Pepperell, MA Pittsfield, MA Plainville, MA Plymouth, MA Pocasset, MA Provincetown, MA Quincy, MA Randolph, MA Raynham, MA Reading, MA Revere, MA Rockland, MA Rockport, MA Roslindale, MA Rowley, MA Roxbury, MA Roxbury Crossing, MA Sagamore Beach, MA Salem, MA Sandwich, MA Saugus, MA Scituate, MA Seekonk, MA Sharon, MA Shirley, MA Shrewsbury, MA Somerset, MA Somerville, MA South Dartmouth, MA South Deerfield, MA South Easton, MA South Hadley, MA South Hamilton, MA South Lancaster, MA South Wellfleet, MA South Weymouth, MA South Yarmouth, MA Southampton, MA Southborough, MA Southbridge, MA Southwick, MA Spencer, MA Springfield, MA Sterling, MA Stockbridge, MA Stoneham, MA Stoughton, MA Stow, MA STURBRIDGE, MA Sudbury, MA Swampscott, MA Swansea, MA Taunton, MA Tewksbury, MA Three Rivers, MA Topsfield, MA Townsend, MA Turners Falls, MA Tyngsboro, MA Uxbridge, MA Vineyard Haven, MA Wakefield, MA Walpole, MA Waltham, MA Ware, MA Wareham, MA Watertown, MA Wayland, MA Webster, MA Wellesley, MA Wellesley Hills, MA Wenham, MA West Barnstable, MA West Boylston, MA West Bridgewater, MA West Brookfield, MA West Newton, MA West Roxbury, MA West Springfield, MA West Yarmouth, MA Westborough, MA Westfield, MA Westford, MA Weston, MA Westport, MA Westwood, MA Weymouth, MA Whitinsville, MA Whitman, MA Wilbraham, MA Williamstown, MA Wilmington, MA Winchendon, MA Winchester, MA Winthrop, MA Woburn, MA Worcester, MA Worthington, MA Wrentham, MA Yarmouth Port, MA Select... Aberdeen, MD Aberdeen Proving Ground, MD Abingdon, MD Andrews Air Force Base, MD Annapolis, MD Arnold, MD Baltimore, MD Bel Air, MD Belcamp, MD Beltsville, MD Berlin, MD Bethesda, MD Bishopville, MD Boonsboro, MD Bowie, MD Brandywine, MD Brooklyn, MD Brunswick, MD Burtonsville, MD California, MD Cambridge, MD Catonsville, MD Cecilton, MD Centreville, MD Charlotte Hall, MD Chester, MD Chestertown, MD Chevy Chase, MD Churchville, MD Clarksburg, MD Clarksville, MD Clinton, MD Cockeysville, MD College Park, MD Columbia, MD Conowingo, MD Crofton, MD Crownsville, MD Cumberland, MD Curtis Bay, MD Damascus, MD Davidsonville, MD Deale, MD Derwood, MD District Heights, MD Dundalk, MD Dunkirk, MD Easton, MD Edgewater, MD Edgewood, MD Elkridge, MD Elkton, MD Ellicott City, MD Essex, MD Fallston, MD Federalsburg, MD Finksburg, MD Forest Hill, MD Fork, MD Fort George G Meade, MD Fort Washington, MD Frederick, MD Frostburg, MD Fulton, MD Gaithersburg, MD Gambrills, MD Germantown, MD Glen Burnie, MD Glenn Dale, MD Glenwood, MD Glyndon, MD Goldsboro, MD Great Mills, MD Greenbelt, MD Gunpowder, MD Gwynn Oak, MD Hagerstown, MD Halethorpe, MD Hampstead, MD Hanover, MD Havre de Grace, MD Hunt Valley, MD Hyattsville, MD Ijamsville, MD Indian Head, MD Jessup, MD Joppa, MD Kensington, MD La Plata, MD Lanham, MD Laurel, MD Leonardtown, MD Lexington Park, MD Linthicum Heights, MD Lisbon, MD Lutherville Timonium, MD Manchester, MD Marriottsville, MD Mc Henry, MD Mechanicsville, MD Middle River, MD Middletown, MD Midland, MD Millersville, MD Monkton, MD Montgomery Village, MD Mount Airy, MD New Market, MD North East, MD Nottingham, MD Oakland, MD Ocean City, MD Odenton, MD Olney, MD Owings, MD Owings Mills, MD Oxon Hill, MD Parkton, MD Parkville, MD Pasadena, MD Patuxent River, MD Perry Hall, MD Perry Point, MD Pikesville, MD Pomfret, MD Potomac, MD Prince Frederick, MD Princess Anne, MD Randallstown, MD Reisterstown, MD Riverdale, MD Rock Hall, MD Rockville, MD Rosedale, MD Salisbury, MD Sandy Spring, MD Severna Park, MD Shady Side, MD Silver Spring, MD Smithsburg, MD Snow Hill, MD Solomons, MD Sparks Glencoe, MD Spencerville, MD Stevensville, MD Suitland, MD Sykesville, MD Takoma Park, MD Taneytown, MD Temple Hills, MD Thurmont, MD Towson, MD Union Bridge, MD Upper Marlboro, MD Waldorf, MD Walkersville, MD West Friendship, MD Westernport, MD Westminster, MD White Marsh, MD White Plains, MD Williamsport, MD Windsor Mill, MD Woodbine, MD Woodsboro, MD Select... Albion, ME Auburn, ME Augusta, ME Baileyville, ME Bangor, ME Bar Harbor, ME Bar Mills, ME Bath, ME Belfast, ME Bethel, ME Biddeford, ME Bingham, ME Blue Hill, ME Boothbay Harbor, ME Brewer, ME Bridgton, ME Brunswick, ME Bucksport, ME Buxton, ME Camden, ME Cape Elizabeth, ME Caribou, ME Castine, ME Cumberland Center, ME Cumberland Foreside, ME Damariscotta, ME Dexter, ME Dover Foxcroft, ME Ellsworth, ME Fairfield, ME Falmouth, ME Farmingdale, ME Farmington, ME Fort Fairfield, ME Fort Kent, ME Freeport, ME Fryeburg, ME Glen Cove, ME Gorham, ME Hampden, ME Hartland, ME Houlton, ME Kennebunk, ME Kennebunkport, ME Kittery, ME Lewiston, ME Lincoln, ME Lincolnville, ME Machias, ME Madison, ME Milbridge, ME Millinocket, ME New Gloucester, ME Newport, ME Norway, ME Old Town, ME Orient, ME Orono, ME Perry, ME Pittsfield, ME Poland, ME Portland, ME Presque Isle, ME Rangeley, ME Rockland, ME Rockport, ME Rumford, ME Saco, ME Sanford, ME Scarborough, ME Skowhegan, ME Sorrento, ME South Portland, ME Springvale, ME Standish, ME Thomaston, ME Topsham, ME Turner, ME Waterboro, ME Waterville, ME Wells, ME Westbrook, ME Windham, ME Windsor, ME Wiscasset, ME Yarmouth, ME York, ME York Harbor, ME Select... Ada, MI Adrian, MI Albion, MI Allegan, MI Allen Park, MI Allendale, MI Alma, MI Alpena, MI Ann Arbor, MI Armada, MI Athens, MI Atlanta, MI Auburn, MI Auburn Hills, MI Bad Axe, MI Baldwin, MI Bangor, MI Battle Creek, MI Bay City, MI Beaver Island, MI Belding, MI Belleville, MI Bellevue, MI Belmont, MI Benton Harbor, MI Berkley, MI Berrien Springs, MI Beulah, MI Big Rapids, MI Birch Run, MI Birmingham, MI Blanchard, MI Blissfield, MI Bloomfield Hills, MI Boyne City, MI Bridgman, MI Brighton, MI Brimley, MI Bronson, MI Brooklyn, MI Brown City, MI Buchanan, MI Burton, MI Byron Center, MI Cadillac, MI Caledonia, MI Camden, MI Canton, MI Caro, MI Carson City, MI Cass City, MI Cassopolis, MI Cedar Springs, MI Cedarville, MI Center Line, MI Centreville, MI Charlevoix, MI Charlotte, MI Cheboygan, MI Chelsea, MI Chesaning, MI Clare, MI Clarkston, MI Clawson, MI Clinton, MI Clinton Township, MI CLINTON TWP., MI Clio, MI Coldwater, MI Coloma, MI Colon, MI Columbiaville, MI Commerce Township, MI Comstock Park, MI Coopersville, MI Corunna, MI Croswell, MI Davisburg, MI Davison, MI Dearborn, MI Dearborn Heights, MI Decatur, MI Detroit, MI Dewitt, MI Dexter, MI Dimondale, MI Douglas, MI Dowagiac, MI Dundee, MI Durand, MI East China, MI East Jordan, MI East Lansing, MI East Tawas, MI Eastpointe, MI Eaton Rapids, MI Elk Rapids, MI Empire, MI Escanaba, MI Essexville, MI Farmington, MI Farwell, MI Fennville, MI Fenton, MI Ferndale, MI Flat Rock, MI Flint, MI Flushing, MI Fort Gratiot, MI Fowlerville, MI Frankenmuth, MI Frankfort, MI Franklin, MI Fraser, MI Freeland, MI Fremont, MI Fruitport, MI Galesburg, MI Garden City, MI Gaylord, MI Gladstone, MI Gladwin, MI Goodrich, MI Grand Blanc, MI Grand Haven, MI Grand Ledge, MI Grand Rapids, MI Grandville, MI Grant, MI Grass Lake, MI Grayling, MI Greenville, MI Grosse Ile, MI Grosse Pointe, MI Gwinn, MI Hamburg, MI Hamilton, MI Hamtramck, MI Hancock, MI Harbor Beach, MI Harbor Springs, MI Harper Woods, MI Harrison, MI Hart, MI Hartford, MI Hartland, MI Haslett, MI Hastings, MI Highland, MI Highland Park, MI Hillsdale, MI Holland, MI Holly, MI Holt, MI Houghton, MI Houghton Lake, MI Howard City, MI Howell, MI Hudson, MI Hudsonville, MI Huntington Woods, MI Imlay City, MI Indian River, MI Inkster, MI Interlochen, MI Ionia, MI Iron Mountain, MI Ishpeming, MI Ithaca, MI Jackson, MI Jenison, MI Kalamazoo, MI Kalkaska, MI Keego Harbor, MI Kent City, MI Kincheloe, MI Kingsford, MI Lake Odessa, MI Lake Orion, MI Lakeview, MI Lambertville, MI Lanse, MI Lansing, MI Lapeer, MI Leland, MI Leonard, MI Leslie, MI Lewiston, MI Lincoln Park, MI Linden, MI Livonia, MI Lowell, MI Ludington, MI Macomb, MI Madison Heights, MI Mancelona, MI Manchester, MI Manistee, MI Manistique, MI Marine City, MI Marquette, MI Marshall, MI Martin, MI Marysville, MI Mason, MI Mattawan, MI Mecosta, MI Melvindale, MI Memphis, MI Mendon, MI Menominee, MI Merrill, MI Mesick, MI Metamora, MI Michigan Center, MI Middleville, MI Midland, MI Milan, MI Milford, MI Millington, MI Monroe, MI Montague, MI Montrose, MI Mount Clemens, MI Mount Morris, MI Mount Pleasant, MI Munising, MI Muskegon, MI Napoleon, MI Nashville, MI Negaunee, MI New Baltimore, MI New Era, MI New Haven, MI New Hudson, MI Newaygo, MI Newberry, MI Niles, MI North Branch, MI Northville, MI Norway, MI Novi, MI Oak Park, MI Oakland, MI Okemos, MI Olivet, MI Onsted, MI Ontonagon, MI Ortonville, MI Oscoda, MI Otisville, MI Otsego, MI Owosso, MI Oxford, MI Paw Paw, MI Perry, MI Petoskey, MI Pickford, MI Pigeon, MI Pinckney, MI Plainwell, MI Pleasant Ridge, MI Plymouth, MI Pontiac, MI Port Huron, MI Portage, MI Portland, MI Potterville, MI Powers, MI Pullman, MI Quincy, MI Ravenna, MI Redford, MI Richland, MI Richmond, MI Riverview, MI Rochester, MI Rockford, MI Rogers City, MI Romeo, MI Romulus, MI Roscommon, MI Roseville, MI Royal Oak, MI Saginaw, MI Saint Clair, MI Saint Clair Shores, MI Saint Helen, MI Saint Ignace, MI Saint Johns, MI Saint Joseph, MI Saint Louis, MI Saline, MI Sandusky, MI Sanford, MI Saranac, MI Saugatuck, MI Sault Sainte Marie, MI Sawyer, MI Schoolcraft, MI Sebewaing, MI Smiths Creek, MI Somerset Center, MI South Haven, MI South Lyon, MI Southfield, MI Southgate, MI Spalding, MI Sparta, MI Spring Arbor, MI Standish, MI Stanton, MI Stephenson, MI Sterling Heights, MI Stevensville, MI Stockbridge, MI Sturgis, MI Suttons Bay, MI Swartz Creek, MI Tawas City, MI Taylor, MI Tecumseh, MI Temperance, MI Three Oaks, MI Three Rivers, MI Traverse City, MI Trenton, MI Troy, MI Union City, MI Utica, MI Vicksburg, MI Walled Lake, MI Warren, MI Washington, MI Waterford, MI Watersmeet, MI Wayland, MI Wayne, MI West Bloomfield, MI West Branch, MI Westland, MI White Cloud, MI White Lake, MI White Pigeon, MI Whitehall, MI Whitmore Lake, MI Williamston, MI Wixom, MI Wyandotte, MI Wyoming, MI Ypsilanti, MI Zeeland, MI Select... Adams, MN Aitkin, MN Albany, MN Albert Lea, MN Albertville, MN Alexandria, MN Andover, MN Annandale, MN Anoka, MN Appleton, MN Arlington, MN Austin, MN Avon, MN Babbitt, MN Bagley, MN Balaton, MN Barnesville, MN Battle Lake, MN Baxter, MN Bayport, MN Becker, MN Belgrade, MN Belle Plaine, MN Bemidji, MN Benson, MN Big Lake, MN Biwabik, MN Blackduck, MN Blooming Prairie, MN Blue Earth, MN Braham, MN Brainerd, MN Breckenridge, MN Buffalo, MN Burnsville, MN Byron, MN Caledonia, MN Cambridge, MN Cannon Falls, MN Cass Lake, MN Champlin, MN Chanhassen, MN Chaska, MN Chisago City, MN Chisholm, MN Circle Pines, MN Clarissa, MN Clarkfield, MN Clearbrook, MN Cloquet, MN Cokato, MN Cold Spring, MN Coleraine, MN Cook, MN Cottage Grove, MN Crookston, MN Crosby, MN Crosslake, MN Dawson, MN Dayton, MN Deerwood, MN Delano, MN Detroit Lakes, MN Dilworth, MN Duluth, MN East Grand Forks, MN Eden Prairie, MN Elbow Lake, MN Elk River, MN Ely, MN Excelsior, MN Fairmont, MN Faribault, MN Farmington, MN Fergus Falls, MN Floodwood, MN Foley, MN Forest Lake, MN Fosston, MN Gilbert, MN Glencoe, MN Glenwood, MN Grand Marais, MN Grand Rapids, MN Granite Falls, MN Halstad, MN Hamel, MN Hampton, MN Hancock, MN Hastings, MN Hawley, MN Hendricks, MN Hibbing, MN Hinckley, MN Hopkins, MN Houston, MN Hugo, MN Hutchinson, MN International Falls, MN Inver Grove Heights, MN Isle, MN Jackson, MN Karlstad, MN Kasson, MN Kenyon, MN Lake City, MN Lake Elmo, MN Lakeland, MN Lakeville, MN Le Center, MN Le Sueur, MN Lindstrom, MN Litchfield, MN Little Falls, MN Long Lake, MN Long Prairie, MN Lonsdale, MN Luverne, MN Madelia, MN Madison, MN Mankato, MN Maple Plain, MN Marshall, MN McGregor, MN Melrose, MN Menahga, MN Milaca, MN Minneapolis, MN Minnetonka, MN Montevideo, MN Montgomery, MN Monticello, MN Moorhead, MN Moose Lake, MN Mora, MN Morris, MN Nashwauk, MN Navarre, MN Nett Lake, MN New Prague, MN New Ulm, MN New York Mills, MN Newport, MN Nicollet, MN Nisswa, MN North Branch, MN Northfield, MN Norwood Young America, MN Ogilvie, MN Onamia, MN Osseo, MN Owatonna, MN Park Rapids, MN Paynesville, MN Pelican Rapids, MN Perham, MN Pierz, MN Pillager, MN Pine City, MN Pine Island, MN Pine River, MN Pipestone, MN Plainview, MN Princeton, MN Prior Lake, MN Red Wing, MN Redwood Falls, MN Remer, MN Renville, MN Rice, MN Richmond, MN Rochester, MN Rockford, MN Rogers, MN Roseau, MN Rosemount, MN Rush City, MN Rushford, MN Saint Charles, MN Saint Cloud, MN Saint Francis, MN Saint James, MN Saint Joseph, MN Saint Michael, MN Saint Paul, MN Saint Peter, MN Sandstone, MN Sartell, MN Sauk Centre, MN Sauk Rapids, MN Savage, MN Scandia, MN Shakopee, MN Slayton, MN Sleepy Eye, MN South Saint Paul, MN Spicer, MN Spring Park, MN Spring Valley, MN Staples, MN Stewartville, MN Stillwater, MN Taylors Falls, MN Thief River Falls, MN Truman, MN Two Harbors, MN Virginia, MN Wabasha, MN Waconia, MN Wadena, MN Waite Park, MN Walker, MN Warroad, MN Waseca, MN Wayzata, MN Wells, MN Wheaton, MN Willmar, MN Windom, MN Winona, MN Winsted, MN Worthington, MN Wyoming, MN Zumbrota, MN Select... Albany, MO Anderson, MO Appleton City, MO Arnold, MO Aurora, MO Ava, MO Ballwin, MO Belle, MO Belton, MO Bethany, MO Bismarck, MO Blue Springs, MO Bolivar, MO Bonne Terre, MO Boonville, MO Branson, MO Bridgeton, MO Brookfield, MO Brookline, MO Buffalo, MO Butler, MO California, MO Camdenton, MO Cameron, MO Cape Girardeau, MO Carrollton, MO Carthage, MO Chaffee, MO Chesterfield, MO Chillicothe, MO Clinton, MO Cole Camp, MO Columbia, MO Crane, MO Crystal City, MO Cuba, MO De Soto, MO Dexter, MO Edina, MO El Dorado Springs, MO Eldon, MO Ellington, MO Eureka, MO Excelsior Springs, MO Farmington, MO Fenton, MO Festus, MO Florissant, MO Fordland, MO Forsyth, MO Fort Leonard Wood, MO Fredericktown, MO Fulton, MO Garden City, MO Glasgow, MO Grain Valley, MO Grandview, MO Grant City, MO Greenfield, MO Grover, MO Hannibal, MO Harrisonville, MO Hawk Point, MO Hazelwood, MO Hermann, MO Higginsville, MO Hillsboro, MO House Springs, MO Houston, MO Huntsville, MO Imperial, MO Independence, MO Jackson, MO Jefferson City, MO Joplin, MO Kahoka, MO Kansas City, MO Kearney, MO Kimberling City, MO Kirksville, MO Knob Noster, MO Lake Ozark, MO Lake Saint Louis, MO Laurie, MO Lawson, MO Lebanon, MO Lees Summit, MO Liberty, MO Linn Creek, MO Louisiana, MO Macon, MO Marble Hill, MO Marshall, MO Marshfield, MO Maryland Heights, MO Maryville, MO Mexico, MO Milan, MO Moberly, MO Monett, MO Monroe City, MO Montgomery City, MO Mount Vernon, MO Mountain Grove, MO Neosho, MO Nevada, MO New Haven, MO New Melle, MO Nixa, MO O Fallon, MO Odessa, MO Osage Beach, MO Ozark, MO Pacific, MO Palmyra, MO Park Hills, MO Peculiar, MO Perry, MO Perryville, MO Pevely, MO Platte City, MO Plattsburg, MO Pleasant Hill, MO Poplar Bluff, MO Potosi, MO Raymore, MO Republic, MO Richland, MO Riverside, MO Rolla, MO Saint Charles, MO Saint Clair, MO Saint James, MO Saint Joseph, MO Saint Louis, MO Saint Peters, MO Saint Robert, MO Sainte Genevieve, MO Salem, MO Savannah, MO Sedalia, MO Shelbina, MO Sikeston, MO Smithville, MO Springfield, MO Stanberry, MO Sullivan, MO Sweet Springs, MO Thayer, MO Tipton, MO Trenton, MO Troy, MO Union, MO Unionville, MO Van Buren, MO Vandalia, MO Vienna, MO Warrensburg, MO Warrenton, MO Warsaw, MO Washington, MO Waynesville, MO Webb City, MO Wentzville, MO West Plains, MO Westphalia, MO Willard, MO Willow Springs, MO Select... Ackerman, MS Amory, MS Baldwyn, MS Batesville, MS Bay Saint Louis, MS Bay Springs, MS Belzoni, MS Biloxi, MS Booneville, MS Brandon, MS Brookhaven, MS Byhalia, MS Byram, MS Calhoun City, MS Carriere, MS Carrollton, MS Carthage, MS Centreville, MS Charleston, MS Clarksdale, MS Cleveland, MS Clinton, MS Coldwater, MS Collins, MS Columbia, MS Columbus, MS Corinth, MS Crystal Springs, MS De Kalb, MS Diamondhead, MS Diberville, MS Ellisville, MS Escatawpa, MS Eupora, MS Florence, MS Flowood, MS Forest, MS Fulton, MS Gautier, MS Greenville, MS Greenwood, MS Grenada, MS Gulfport, MS Hattiesburg, MS Hazlehurst, MS Hernando, MS Hollandale, MS Holly Springs, MS Horn Lake, MS Houston, MS Indianola, MS Jackson, MS Kiln, MS Kosciusko, MS Laurel, MS Leakesville, MS Leland, MS Lexington, MS Long Beach, MS Louisville, MS Lucedale, MS Lumberton, MS Maben, MS Macon, MS Madison, MS Magee, MS Magnolia, MS McComb, MS Meadville, MS Mendenhall, MS Meridian, MS Monticello, MS Morton, MS Moss Point, MS Mount Olive, MS Natchez, MS Nesbit, MS Nettleton, MS New Albany, MS New Augusta, MS Newton, MS Ocean Springs, MS Olive Branch, MS Oxford, MS Pascagoula, MS Pass Christian, MS Pearl, MS Pelahatchie, MS Petal, MS Philadelphia, MS Picayune, MS Poplarville, MS Port Gibson, MS Prentiss, MS Purvis, MS Quitman, MS Raleigh, MS Richland, MS Ridgeland, MS Ripley, MS Rosedale, MS Ruleville, MS Saltillo, MS Senatobia, MS Southaven, MS Starkville, MS Summit, MS Sumrall, MS Taylorsville, MS Tupelo, MS Tylertown, MS Union, MS Vicksburg, MS Water Valley, MS Waynesboro, MS Weir, MS Wesson, MS West Point, MS Wiggins, MS Winona, MS Woodville, MS Yazoo City, MS Select... Anaconda, MT Baker, MT Basin, MT Belgrade, MT Bigfork, MT Billings, MT Box Elder, MT Bozeman, MT Browning, MT Butte, MT Chester, MT Choteau, MT Columbia Falls, MT Columbus, MT Condon, MT Crow Agency, MT Deer Lodge, MT Florence, MT Fort Benton, MT Frenchtown, MT Glendive, MT Great Falls, MT Hamilton, MT Hardin, MT Harlem, MT Havre, MT Helena, MT Joliet, MT Kalispell, MT Lakeside, MT Lame Deer, MT Laurel, MT Lewistown, MT Libby, MT Livingston, MT Lolo, MT Malmstrom AFB, MT Malta, MT Manhattan, MT Miles City, MT Missoula, MT Plains, MT Plentywood, MT Polson, MT Poplar, MT Red Lodge, MT Ronan, MT Saint Ignatius, MT Scobey, MT Seeley Lake, MT Sidney, MT Stevensville, MT Superior, MT Thompson Falls, MT Three Forks, MT Townsend, MT Troy, MT Victor, MT Whitefish, MT Whitehall, MT Select... Aberdeen, NC Advance, NC Ahoskie, NC Alamance, NC Albemarle, NC Andrews, NC Angier, NC Apex, NC Arden, NC Asheboro, NC Asheville, NC Atlantic Beach, NC Bailey, NC Banner Elk, NC Bayboro, NC Beaufort, NC Belhaven, NC Belmont, NC Benson, NC Bethel, NC Beulaville, NC Black Mountain, NC Bladenboro, NC Blanch, NC Blowing Rock, NC Bolivia, NC Boone, NC Brevard, NC Bunn, NC Burlington, NC Burnsville, NC Camp Lejeune, NC Candler, NC Carolina Beach, NC Carrboro, NC Carthage, NC Cary, NC Cashiers, NC Chapel Hill, NC Charlotte, NC Cherokee, NC Cherryville, NC Chocowinity, NC Claremont, NC Clayton, NC Clemmons, NC Cleveland, NC Clinton, NC Clyde, NC Coinjock, NC Columbus, NC Concord, NC Conover, NC Cornelius, NC Creedmoor, NC Dallas, NC Davidson, NC Denton, NC Denver, NC Dobson, NC Dunn, NC Durham, NC East Bend, NC Eden, NC Edenton, NC Elizabeth City, NC Elizabethtown, NC Elkin, NC Etowah, NC Fair Bluff, NC Fairmont, NC Faison, NC Farmville, NC Fayetteville, NC Fletcher, NC Forest City, NC Fort Bragg, NC Franklin, NC Fremont, NC Frisco, NC Fuquay Varina, NC Garner, NC Gastonia, NC Gibsonville, NC Goldsboro, NC Graham, NC Granite Falls, NC Granite Quarry, NC Greensboro, NC Greenville, NC Hamlet, NC Hampstead, NC Harrells, NC Harrisburg, NC Havelock, NC Hayesville, NC Henderson, NC Hendersonville, NC Hickory, NC High Point, NC Highlands, NC Hildebran, NC Hillsborough, NC Holly Springs, NC Hope Mills, NC Hudson, NC Huntersville, NC Indian Trail, NC Jacksonville, NC Jamestown, NC Jamesville, NC Kannapolis, NC Kenansville, NC Kernersville, NC Kill Devil Hills, NC Kings Mountain, NC Kinston, NC Kitty Hawk, NC Knightdale, NC La Grange, NC Landis, NC Laurinburg, NC Leland, NC Lenoir, NC Lexington, NC Liberty, NC Lillington, NC Lincolnton, NC Linville, NC Locust, NC Louisburg, NC Lumberton, NC Madison, NC Maggie Valley, NC Maiden, NC Manteo, NC Marble, NC Marion, NC Mars Hill, NC Marshall, NC Matthews, NC Mayodan, NC Mebane, NC Midland, NC Mocksville, NC Moncure, NC Monroe, NC Mooresville, NC Morehead City, NC Morganton, NC Morrisville, NC Mount Airy, NC Mount Holly, NC Mount Olive, NC Mount Pleasant, NC Murphy, NC Nags Head, NC Nashville, NC New Bern, NC Newport, NC Newton, NC North Wilkesboro, NC Norwood, NC Oak Island, NC Oak Ridge, NC Ocean Isle Beach, NC Oriental, NC Oxford, NC Pembroke, NC Pilot Mountain, NC Pinehurst, NC Pineville, NC Pink Hill, NC Pittsboro, NC Pleasant Garden, NC Plymouth, NC Pope Army Airfield, NC Prospect Hill, NC Raeford, NC Raleigh, NC Randleman, NC Reidsville, NC Roanoke Rapids, NC Robbinsville, NC Rockingham, NC Rocky Mount, NC Rolesville, NC Rose Hill, NC Roseboro, NC Roxboro, NC Rural Hall, NC Rutherford College, NC Rutherfordton, NC Salisbury, NC Sanford, NC Selma, NC Shallotte, NC Shelby, NC Smithfield, NC Snow Hill, NC Southern Pines, NC Southport, NC Sparta, NC Spindale, NC Spring Lake, NC Spruce Pine, NC Stanley, NC Statesville, NC Stedman, NC Stokesdale, NC Sunset Beach, NC Supply, NC Swansboro, NC Sylva, NC Tarboro, NC Taylorsville, NC Thomasville, NC Troutman, NC Troy, NC Tryon, NC Wadesboro, NC Wake Forest, NC Wallace, NC Wanchese, NC Warrenton, NC Washington, NC Waxhaw, NC Waynesville, NC Weaverville, NC Wendell, NC West End, NC West Jefferson, NC Whiteville, NC Whittier, NC Wilkesboro, NC Willard, NC Williamston, NC Wilmington, NC Wilson, NC Windsor, NC Winston Salem, NC Yadkinville, NC Yanceyville, NC Zebulon, NC Select... Belcourt, ND Beulah, ND Bismarck, ND Bottineau, ND Bowman, ND Carrington, ND Casselton, ND Cavalier, ND Cooperstown, ND Devils Lake, ND Dickinson, ND Ellendale, ND Fargo, ND Grafton, ND Grand Forks, ND Harvey, ND Hazen, ND Hettinger, ND Hillsboro, ND Horace, ND Jamestown, ND Larimore, ND Lidgerwood, ND Linton, ND Mandan, ND Mayville, ND Minot, ND Mohall, ND Mott, ND New Leipzig, ND New Rockford, ND Park River, ND Rolla, ND Rugby, ND Trenton, ND Turtle Lake, ND Wahpeton, ND West Fargo, ND Williston, ND Select... Ainsworth, NE Albion, NE Alliance, NE Alma, NE Ashland, NE Auburn, NE Aurora, NE Battle Creek, NE Beatrice, NE Bellevue, NE Blair, NE Broken Bow, NE Burwell, NE Cambridge, NE Central City, NE Chadron, NE Columbus, NE Cortland, NE Cozad, NE Crawford, NE Crete, NE Crofton, NE Eagle, NE Elkhorn, NE Fairbury, NE Falls City, NE Fremont, NE Gering, NE Gordon, NE Gothenburg, NE Grand Island, NE Grant, NE Gretna, NE Hartington, NE Hastings, NE Hickman, NE Holdrege, NE Kearney, NE Kimball, NE La Vista, NE Lexington, NE Lincoln, NE Mc Cook, NE Milford, NE Minden, NE Morrill, NE Nebraska City, NE Neligh, NE Norfolk, NE North Bend, NE North Platte, NE Offutt AFB, NE Ogallala, NE Omaha, NE Oneill, NE Ord, NE Overton, NE Papillion, NE Pawnee City, NE Pierce, NE Plainview, NE Plattsmouth, NE Schuyler, NE Scottsbluff, NE Shelton, NE Sidney, NE South Sioux City, NE Springfield, NE Stromsburg, NE Superior, NE Syracuse, NE Valentine, NE Verdigre, NE Wahoo, NE Wayne, NE Weeping Water, NE West Point, NE Wood River, NE York, NE Select... Amherst, NH Antrim, NH Auburn, NH Barrington, NH Bedford, NH Belmont, NH Berlin, NH Bow, NH Bradford, NH Bristol, NH Charlestown, NH Chester, NH Claremont, NH Colebrook, NH Concord, NH Contoocook, NH Conway, NH Derry, NH Dover, NH Durham, NH East Hampstead, NH Epping, NH Exeter, NH Farmington, NH Gilford, NH Goffstown, NH Gorham, NH Greenland, NH Hampstead, NH Hampton, NH Hanover, NH Hillsborough, NH Hollis, NH Hooksett, NH Hudson, NH Jaffrey, NH Keene, NH Kingston, NH Laconia, NH Lancaster, NH Lebanon, NH Litchfield, NH Littleton, NH Londonderry, NH Loudon, NH Manchester, NH Meredith, NH Merrimack, NH Milford, NH Moultonborough, NH Nashua, NH New Boston, NH Newmarket, NH Newport, NH North Conway, NH North Hampton, NH Pelham, NH Peterborough, NH Pittsfield, NH Plaistow, NH Plymouth, NH Portsmouth, NH Raymond, NH Rindge, NH Rochester, NH Rye, NH Salem, NH Sanbornville, NH Seabrook, NH Somersworth, NH Stratham, NH Suncook, NH Swanzey, NH Tilton, NH Walpole, NH Weare, NH West Lebanon, NH Whitefield, NH Wilton, NH Windham, NH Winnisquam, NH Wolfeboro, NH Wolfeboro Falls, NH Select... Absecon, NJ Allendale, NJ Allenhurst, NJ Allentown, NJ Andover, NJ Annandale, NJ Asbury, NJ Asbury Park, NJ Atco, NJ Atlantic City, NJ Atlantic Highlands, NJ Audubon, NJ Augusta, NJ Avenel, NJ Avon by the Sea, NJ Barnegat, NJ Barrington, NJ Basking Ridge, NJ Bayonne, NJ Bayville, NJ Beach Haven, NJ Bedminster, NJ Belleville, NJ Belmar, NJ Belvidere, NJ Bergenfield, NJ Berkeley Heights, NJ Berlin, NJ Bernardsville, NJ Beverly, NJ Blackwood, NJ Blairstown, NJ Bloomfield, NJ Bloomingdale, NJ Bogota, NJ Boonton, NJ Bordentown, NJ Bound Brook, NJ Branchville, NJ Brick, NJ Bridgeton, NJ Bridgewater, NJ Brielle, NJ Brigantine, NJ Browns Mills, NJ Budd Lake, NJ Burlington, NJ Butler, NJ Caldwell, NJ Califon, NJ Camden, NJ Cape May, NJ Cape May Court House, NJ Carlstadt, NJ Carteret, NJ Cedar Grove, NJ Cedar Knolls, NJ Chatham, NJ Cherry Hill, NJ Chester, NJ Clark, NJ Clementon, NJ Cliffside Park, NJ Clifton, NJ Clinton, NJ Closter, NJ Collingswood, NJ Colonia, NJ Colts Neck, NJ Columbus, NJ Cranbury, NJ Cranford, NJ Cream Ridge, NJ Cresskill, NJ Dayton, NJ Deal, NJ Denville, NJ Dover, NJ Dumont, NJ Dunellen, NJ East Brunswick, NJ East Hanover, NJ East Orange, NJ East Rutherford, NJ Eatontown, NJ Edgewater, NJ Edison, NJ Egg Harbor City, NJ Egg Harbor Township, NJ Elizabeth, NJ Elmer, NJ Elmwood Park, NJ Emerson, NJ Englewood, NJ Englewood Cliffs, NJ Englishtown, NJ Fair Haven, NJ Fair Lawn, NJ Fairfield, NJ Fairview, NJ Fanwood, NJ Far Hills, NJ Farmingdale, NJ Flanders, NJ Flemington, NJ Florence, NJ Florham Park, NJ Fords, NJ Forked River, NJ Fort Dix, NJ Fort Lee, NJ Franklin Lakes, NJ Franklin Park, NJ Franklinville, NJ Freehold, NJ Garfield, NJ Garwood, NJ Gibbsboro, NJ Gibbstown, NJ Glassboro, NJ Glen Ridge, NJ Glen Rock, NJ Gloucester City, NJ Green Village, NJ Hackensack, NJ Hackettstown, NJ Haddon Heights, NJ Haddonfield, NJ Hainesport, NJ Haledon, NJ Hamburg, NJ Hammonton, NJ Harrison, NJ Hasbrouck Heights, NJ Haworth, NJ Hawthorne, NJ Hazlet, NJ Highland Park, NJ Hightstown, NJ Hillsborough, NJ Hillsdale, NJ Hillside, NJ Ho Ho Kus, NJ Hoboken, NJ Holmdel, NJ Hopewell, NJ Howell, NJ Irvington, NJ Iselin, NJ Jackson, NJ Jersey City, NJ Keansburg, NJ Kearny, NJ Kendall Park, NJ Kenilworth, NJ Keyport, NJ Kingston, NJ Lake Hiawatha, NJ Lake Hopatcong, NJ Lakehurst, NJ Lakewood, NJ Lambertville, NJ Lanoka Harbor, NJ Lavallette, NJ Lawrence Township, NJ Lebanon, NJ Leonia, NJ Liberty Corner, NJ Lincoln Park, NJ Lincroft, NJ Linden, NJ Linwood, NJ Little Falls, NJ Little Ferry, NJ Little Silver, NJ Livingston, NJ Lodi, NJ Long Branch, NJ Long Valley, NJ Lumberton, NJ Lyndhurst, NJ Lyons, NJ Madison, NJ Magnolia, NJ Mahwah, NJ Manahawkin, NJ Manasquan, NJ Manchester Township, NJ Mantua, NJ Manville, NJ Maple Shade, NJ Maplewood, NJ Margate City, NJ Marlboro, NJ Marlton, NJ Marmora, NJ Martinsville, NJ Matawan, NJ Mays Landing, NJ Maywood, NJ Mc Afee, NJ Medford, NJ Mendham, NJ Merchantville, NJ Metuchen, NJ Middlesex, NJ Middletown, NJ Midland Park, NJ Millburn, NJ Millstone Township, NJ Milltown, NJ Millville, NJ Minotola, NJ Monmouth Junction, NJ Monroe Township, NJ Montclair, NJ Montvale, NJ Montville, NJ Moorestown, NJ Morganville, NJ Morris Plains, NJ Morristown, NJ Mount Arlington, NJ Mount Ephraim, NJ Mount Freedom, NJ Mount Holly, NJ Mount Laurel, NJ Mountain Lakes, NJ Mountainside, NJ Mullica Hill, NJ Neptune, NJ Netcong, NJ New Brunswick, NJ New Milford, NJ New Providence, NJ Newark, NJ Newton, NJ North Arlington, NJ North Bergen, NJ North Brunswick, NJ Northfield, NJ Northvale, NJ Norwood, NJ Nutley, NJ Oakhurst, NJ Oakland, NJ Oaklyn, NJ Ocean City, NJ Ocean Grove, NJ Oceanport, NJ Old Bridge, NJ Oradell, NJ Orange, NJ Palisades Park, NJ Paramus, NJ Park Ridge, NJ Parlin, NJ Parsippany, NJ Passaic, NJ Paterson, NJ Paulsboro, NJ Pemberton, NJ Pennington, NJ Penns Grove, NJ Pennsauken, NJ Pennsville, NJ Perth Amboy, NJ Phillipsburg, NJ Pine Beach, NJ Pine Brook, NJ Piscataway, NJ Pitman, NJ Plainfield, NJ Plainsboro, NJ Pleasantville, NJ Point Pleasant Beach, NJ Pompton Lakes, NJ Pompton Plains, NJ Pottersville, NJ Princeton, NJ Princeton Junction, NJ Rahway, NJ Ramsey, NJ Randolph, NJ Raritan, NJ Red Bank, NJ Ridgefield, NJ Ridgefield Park, NJ Ridgewood, NJ Ringwood, NJ Rio Grande, NJ River Edge, NJ Riverdale, NJ Riverside, NJ Riverton, NJ Rochelle Park, NJ Rockaway, NJ Rocky Hill, NJ Roseland, NJ Roselle, NJ Roselle Park, NJ Rumson, NJ Runnemede, NJ Rutherford, NJ Saddle Brook, NJ Saddle River, NJ Scotch Plains, NJ Sea Girt, NJ Sea Isle City, NJ Secaucus, NJ Sergeantsville, NJ Sewell, NJ Short Hills, NJ Shrewsbury, NJ Sicklerville, NJ Skillman, NJ Somerdale, NJ Somers Point, NJ Somerset, NJ Somerville, NJ South Amboy, NJ South Bound Brook, NJ South Orange, NJ South Plainfield, NJ South River, NJ Sparta, NJ Spotswood, NJ Spring Lake, NJ Springfield, NJ Stillwater, NJ Stockholm, NJ Stratford, NJ Succasunna, NJ Summit, NJ Sussex, NJ Swedesboro, NJ Teaneck, NJ Tenafly, NJ Thorofare, NJ Toms River, NJ Totowa, NJ Township of Washington, NJ Trenton, NJ Tuckerton, NJ Union, NJ Union City, NJ Ventnor City, NJ Vernon, NJ Verona, NJ Vincentown, NJ Vineland, NJ Voorhees, NJ Waldwick, NJ Wallington, NJ Warren, NJ Washington, NJ Watchung, NJ Wayne, NJ West Berlin, NJ West Long Branch, NJ West Milford, NJ West New York, NJ West Orange, NJ Westfield, NJ Westwood, NJ Wharton, NJ Whippany, NJ Whitehouse Station, NJ Wildwood, NJ Williamstown, NJ Willingboro, NJ Wood Ridge, NJ Woodbine, NJ Woodbridge, NJ Woodbury, NJ Woodbury Heights, NJ Woodcliff Lake, NJ Woodstown, NJ Wrightstown, NJ Wyckoff, NJ Select... Alamogordo, NM Albuquerque, NM Algodones, NM Angel Fire, NM Artesia, NM Aztec, NM Belen, NM Bernalillo, NM Bloomfield, NM Cannon AFB, NM Carlsbad, NM Cedar Crest, NM Clovis, NM Corrales, NM Cuba, NM Deming, NM Dexter, NM Dulce, NM Edgewood, NM El Rito, NM Embudo, NM Espanola, NM Farmington, NM Gallup, NM Grants, NM Hobbs, NM Jemez Pueblo, NM Kirtland, NM Kirtland AFB, NM Las Cruces, NM Las Vegas, NM Lordsburg, NM Los Alamos, NM Los Lunas, NM Mescalero, NM Mora, NM Moriarty, NM Placitas, NM Portales, NM Pueblo of Acoma, NM Raton, NM Rio Rancho, NM Roswell, NM Ruidoso, NM San Fidel, NM San Ysidro, NM Santa Fe, NM Santa Rosa, NM Shiprock, NM Silver City, NM Socorro, NM Sunland Park, NM Taos, NM Truth or Consequences, NM Tucumcari, NM Zuni, NM Select... Boulder City, NV Carson City, NV Dayton, NV Elko, NV Ely, NV Eureka, NV Fallon, NV Fernley, NV Gardnerville, NV Henderson, NV Las Vegas, NV Laughlin, NV Mesquite, NV Minden, NV Nellis AFB, NV North Las Vegas, NV Overton, NV Pahrump, NV Reno, NV Schurz, NV Sparks, NV Spring Creek, NV Stateline, NV Sun Valley, NV Winnemucca, NV Yerington, NV Zephyr Cove, NV Select... Addison, NY Akron, NY Albany, NY Albertson, NY Albion, NY Alden, NY Alexandria Bay, NY Alfred, NY Allegany, NY Altamont, NY Amityville, NY Amsterdam, NY Ancram, NY Angola, NY Arcade, NY Ardsley, NY Armonk, NY Arverne, NY Astoria, NY Attica, NY Auburn, NY Averill Park, NY Avon, NY Babylon, NY Bainbridge, NY Baldwin, NY Baldwinsville, NY Ballston Lake, NY Ballston Spa, NY Barneveld, NY Batavia, NY Bath, NY Bay Shore, NY Bayport, NY Bayside, NY Bayville, NY Beacon, NY Bedford, NY Bedford Hills, NY Bellerose, NY Bellmore, NY Bellport, NY Belmont, NY Bethpage, NY Billings, NY Binghamton, NY Blauvelt, NY Bohemia, NY Boston, NY Breezy Point, NY Brentwood, NY Brewster, NY Briarcliff Manor, NY Brightwaters, NY Broadalbin, NY Brockport, NY Bronx, NY Bronxville, NY Brookhaven, NY Brooklyn, NY Buchanan, NY Buffalo, NY Burnt Hills, NY Caledonia, NY Cambria Heights, NY Cambridge, NY Camillus, NY Canandaigua, NY Canastota, NY Candor, NY Canton, NY Carle Place, NY Carmel, NY Carthage, NY Castleton on Hudson, NY Cato, NY Catskill, NY Cazenovia, NY Cedarhurst, NY Center Moriches, NY Centereach, NY Centerport, NY Central Islip, NY Central Square, NY Central Valley, NY Champlain, NY Chappaqua, NY Chatham, NY Chenango Bridge, NY Chester, NY Chittenango, NY Cicero, NY Clarence, NY Clarence Center, NY Clayton, NY Clifton Park, NY Clifton Springs, NY Clintondale, NY Cobleskill, NY Cohoes, NY Cold Spring, NY Colden, NY College Point, NY Commack, NY Congers, NY Conklin, NY Cooperstown, NY Copiague, NY Coram, NY Corinth, NY Corning, NY Cornwall, NY Cornwall on Hudson, NY Corona, NY Cortland, NY Cortlandt Manor, NY Cross River, NY Croton Falls, NY Croton on Hudson, NY Cuba, NY Cutchogue, NY Dansville, NY Deer Park, NY Delevan, NY Delhi, NY Delmar, NY Depew, NY Derby, NY Dobbs Ferry, NY Dolgeville, NY Dover Plains, NY Duanesburg, NY Dunkirk, NY Durham, NY East Amherst, NY East Aurora, NY East Elmhurst, NY East Greenbush, NY East Hampton, NY East Islip, NY East Meadow, NY East Moriches, NY East Northport, NY East Norwich, NY East Rochester, NY East Rockaway, NY East Setauket, NY East Syracuse, NY Eastchester, NY Eden, NY Elbridge, NY Elizabethtown, NY Ellenville, NY Elma, NY Elmhurst, NY Elmira, NY Elmont, NY Elmsford, NY Endicott, NY Fairport, NY Far Rockaway, NY Farmingdale, NY Farmington, NY Farmingville, NY Fayetteville, NY Fillmore, NY Fishkill, NY Floral Park, NY Flushing, NY Fly Creek, NY Fonda, NY Forest Hills, NY Fort Drum, NY Fort Plain, NY Franklin Square, NY Franklinville, NY Fredonia, NY Freeport, NY Freeville, NY Fresh Meadows, NY Fulton, NY Galway, NY Gansevoort, NY Garden City, NY Gasport, NY Geneseo, NY Geneva, NY Getzville, NY Glen Cove, NY Glen Head, NY Glen Oaks, NY Glenmont, NY Glens Falls, NY Gloversville, NY Goshen, NY Gouverneur, NY Gowanda, NY Grand Island, NY Granville, NY Great Neck, NY Greene, NY Greenlawn, NY Greenvale, NY Greenville, NY Greenwich, NY Groton, NY Guilderland, NY Hamburg, NY Hamilton, NY Hamlin, NY Hammondsport, NY Hampton Bays, NY Hancock, NY Harris, NY Harrison, NY Hartsdale, NY Hastings on Hudson, NY Hauppauge, NY Haverstraw, NY Hawthorne, NY Hempstead, NY Henrietta, NY Herkimer, NY Hewlett, NY Hicksville, NY Highland, NY Highland Falls, NY Highland Mills, NY Hillsdale, NY Hilton, NY Holbrook, NY Holley, NY Hollis, NY Holtsville, NY Homer, NY Honeoye, NY Honeoye Falls, NY Hopewell Junction, NY Hornell, NY Horseheads, NY Houghton, NY Howard Beach, NY Hudson, NY Hudson Falls, NY Huntington, NY Huntington Station, NY Hyde Park, NY Ilion, NY Irving, NY Irvington, NY Island Park, NY Islandia, NY Islip, NY Islip Terrace, NY Ithaca, NY Jackson Heights, NY Jamaica, NY Jamesport, NY Jamestown, NY Jamesville, NY Jay, NY Jefferson Valley, NY Jericho, NY Johnson City, NY Johnstown, NY Katonah, NY Kerhonkson, NY Kew Gardens, NY Kings Park, NY Kingston, NY Kirkwood, NY La Fayette, NY Lagrangeville, NY Lake George, NY Lake Grove, NY Lake Katrine, NY Lake Placid, NY Lakeville, NY Lakewood, NY Lancaster, NY Larchmont, NY Latham, NY Lawrence, NY Levittown, NY Lewiston, NY Liberty, NY Lima, NY Lindenhurst, NY Little Falls, NY Little Neck, NY Liverpool, NY Livonia, NY Lockport, NY Locust Valley, NY Long Beach, NY Long Island City, NY Lowville, NY Lynbrook, NY Lyons, NY Macedon, NY Mahopac, NY Malone, NY Malverne, NY Mamaroneck, NY Manhasset, NY Manlius, NY Manorville, NY Marcellus, NY Margaretville, NY Marion, NY Maspeth, NY Massapequa, NY Massapequa Park, NY Massena, NY Mattituck, NY Maybrook, NY Mayville, NY Mechanicville, NY Medford, NY Medina, NY Melville, NY Merrick, NY Mexico, NY Middle Island, NY Middle Village, NY Middletown, NY Miller Place, NY Mineola, NY Minoa, NY Mohawk, NY Mohegan Lake, NY Monroe, NY Monsey, NY Montgomery, NY Monticello, NY Montrose, NY Moriches, NY Mount Kisco, NY Mount Sinai, NY Mount Vernon, NY Nanuet, NY Naples, NY Nesconset, NY New City, NY New Hartford, NY New Hyde Park, NY New Paltz, NY New Rochelle, NY New Windsor, NY New York, NY New York Mills, NY Newark, NY Newburgh, NY Newfane, NY Niagara Falls, NY North Babylon, NY North Chili, NY North Tonawanda, NY Northport, NY Northville, NY Norwich, NY Nyack, NY Oakdale, NY Oakland Gardens, NY Oceanside, NY Ogdensburg, NY Old Forge, NY Old Westbury, NY Olean, NY Oneida, NY Oneonta, NY Ontario, NY Orangeburg, NY Orchard Park, NY Ossining, NY Oswego, NY Otego, NY Owego, NY Oyster Bay, NY Ozone Park, NY Palmyra, NY Patchogue, NY Patterson, NY Pawling, NY Pearl River, NY Peekskill, NY Pelham, NY Penfield, NY Penn Yan, NY Perry, NY Phelps, NY Philadelphia, NY Philmont, NY Phoenix, NY Piermont, NY Pine Bush, NY Pittsford, NY Plainview, NY Plattsburgh, NY Pleasant Valley, NY Pleasantville, NY Point Lookout, NY Pomona, NY Port Chester, NY Port Ewen, NY Port Jefferson, NY Port Jefferson Station, NY Port Jervis, NY Port Washington, NY Portville, NY Potsdam, NY Poughkeepsie, NY Poughquag, NY Pulaski, NY Pultneyville, NY Purchase, NY Purdys, NY Putnam Station, NY Queens Village, NY Queensbury, NY Ravena, NY Red Hook, NY Rego Park, NY Rensselaer, NY Rhinebeck, NY Richmond Hill, NY Ridge, NY Ridgewood, NY Rifton, NY Riverhead, NY Rochester, NY Rock Hill, NY Rockaway Park, NY Rockville Centre, NY Rocky Point, NY Rome, NY Ronkonkoma, NY Roosevelt, NY Rosedale, NY Rosendale, NY Roslyn, NY Roslyn Heights, NY Rush, NY Rye, NY Sag Harbor, NY Saint Albans, NY Saint James, NY Salamanca, NY Salisbury Mills, NY Saranac Lake, NY Saratoga Springs, NY Saugerties, NY Sayville, NY Scarsdale, NY Schenectady, NY Schoharie, NY Sea Cliff, NY Selden, NY Seneca Falls, NY Shelter Island, NY Sherrill, NY Shirley, NY Shokan, NY Shoreham, NY Shrub Oak, NY Sidney, NY Silver Creek, NY Skaneateles, NY Slingerlands, NY Smithtown, NY Sodus, NY Somers, NY South Glens Falls, NY South Ozone Park, NY South Richmond Hill, NY South Salem, NY Southampton, NY Southold, NY Sparkill, NY Spencerport, NY Speonk, NY Spring Valley, NY Springville, NY Staten Island, NY Stone Ridge, NY Stony Brook, NY Stony Point, NY Suffern, NY Sunnyside, NY Syosset, NY Syracuse, NY Tappan, NY Tarrytown, NY Thornwood, NY Ticonderoga, NY Tonawanda, NY Troy, NY Tuckahoe, NY Tupper Lake, NY Tuxedo Park, NY Uniondale, NY Utica, NY Vails Gate, NY Valatie, NY Valhalla, NY Valley Cottage, NY Valley Stream, NY Vestal, NY Victor, NY Voorheesville, NY Wading River, NY Wainscott, NY Walden, NY Wallkill, NY Walton, NY Walworth, NY Wantagh, NY Wappingers Falls, NY Warrensburg, NY Warsaw, NY Warwick, NY Washingtonville, NY Water Mill, NY Waterloo, NY Watertown, NY Watervliet, NY Watkins Glen, NY Waverly, NY Wayland, NY Webster, NY Wellsville, NY West Babylon, NY West Coxsackie, NY West Harrison, NY West Haverstraw, NY West Hempstead, NY West Hurley, NY West Islip, NY West Nyack, NY West Point, NY West Sayville, NY West Winfield, NY Westbury, NY Westfield, NY Westhampton Beach, NY White Plains, NY Whitesboro, NY Whitestone, NY Williamson, NY Williston Park, NY Woodbury, NY Woodhaven, NY Woodmere, NY Woodside, NY Woodstock, NY Wurtsboro, NY Wynantskill, NY Yonkers, NY Yorktown Heights, NY Youngstown, NY Select... Addyston, OH Akron, OH Alexandria, OH Alliance, OH Amelia, OH Amherst, OH Andover, OH Ashland, OH Ashtabula, OH Athens, OH Attica, OH Aurora, OH Avon, OH Avon Lake, OH Barberton, OH Barnesville, OH Batavia, OH Bay Village, OH Beachwood, OH Bedford, OH Bellbrook, OH Bellefontaine, OH Bellevue, OH Bellville, OH Belpre, OH Berea, OH Berlin, OH Bethel, OH Blacklick, OH Bowling Green, OH Brecksville, OH Bridgeport, OH Broadview Heights, OH Brookfield, OH Brookpark, OH Brookville, OH Brunswick, OH Bryan, OH Bucyrus, OH Burton, OH Caldwell, OH Cambridge, OH Canal Fulton, OH Canal Winchester, OH Canfield, OH Canton, OH Carrollton, OH Celina, OH Centerburg, OH Chagrin Falls, OH Chardon, OH Chesapeake, OH Chillicothe, OH Chippewa Lake, OH Cincinnati, OH Circleville, OH Cleveland, OH Coldwater, OH Columbia Station, OH Columbiana, OH Columbus, OH Columbus Grove, OH Conneaut, OH Cortland, OH Coshocton, OH Covington, OH Crestline, OH Cuyahoga Falls, OH Dayton, OH Defiance, OH Delaware, OH Delphos, OH Delta, OH Dover, OH Doylestown, OH Dublin, OH East Liverpool, OH Eastlake, OH Eaton, OH Elmore, OH Elyria, OH Englewood, OH Enon, OH Euclid, OH Fairborn, OH Fairfield, OH Findlay, OH Fort Loramie, OH Fostoria, OH Franklin, OH Fredericktown, OH Fremont, OH Galion, OH Gallipolis, OH Galloway, OH Garrettsville, OH Geneva, OH Genoa, OH Germantown, OH Girard, OH Glandorf, OH Goshen, OH Grafton, OH Granville, OH Greenfield, OH Greenville, OH Greenwich, OH Grove City, OH Groveport, OH Hamilton, OH Harrison, OH Hartville, OH Heath, OH Hebron, OH Hicksville, OH Hilliard, OH Hillsboro, OH Hinckley, OH Holland, OH Hubbard, OH Hudson, OH Huron, OH Independence, OH Ironton, OH Jackson, OH Jefferson, OH Kent, OH Kenton, OH Kidron, OH Lagrange, OH Lakewood, OH Lancaster, OH Lebanon, OH Leetonia, OH Leipsic, OH Lewis Center, OH Lima, OH Logan, OH London, OH Lorain, OH Loudonville, OH Louisville, OH Loveland, OH Macedonia, OH Madison, OH Maineville, OH Mansfield, OH Maple Heights, OH Marengo, OH Marietta, OH Marion, OH Martins Ferry, OH Marysville, OH Mason, OH Massillon, OH Maumee, OH Mc Comb, OH McConnelsville, OH Mechanicsburg, OH Medina, OH Mentor, OH Miamisburg, OH Middlefield, OH Middletown, OH Milford, OH Millersburg, OH Minster, OH Mogadore, OH Monroe, OH Monroeville, OH Montpelier, OH Morrow, OH Mount Gilead, OH Mount Orab, OH Mount Sterling, OH Mount Vernon, OH Munroe Falls, OH Napoleon, OH Navarre, OH New Albany, OH New Lebanon, OH New Lexington, OH New London, OH New Middletown, OH New Philadelphia, OH Newark, OH Newton Falls, OH Niles, OH North Canton, OH North Jackson, OH North Kingsville, OH North Lima, OH North Olmsted, OH North Ridgeville, OH North Royalton, OH Northfield, OH Northwood, OH Norwalk, OH Oak Harbor, OH Oberlin, OH Olmsted Falls, OH Oregon, OH Orrville, OH Ottawa, OH Owensville, OH Oxford, OH Painesville, OH Pataskala, OH Paulding, OH Peebles, OH Pemberville, OH Perry, OH Perrysburg, OH Pickerington, OH Piketon, OH Piqua, OH Plain City, OH Pomeroy, OH Port Clinton, OH Portsmouth, OH Powell, OH Racine, OH Ravenna, OH Reynoldsburg, OH Richfield, OH Rittman, OH Rocky River, OH Rossford, OH Saint Clairsville, OH Saint Marys, OH Salem, OH Sandusky, OH Seaman, OH Sebring, OH Seville, OH Shadyside, OH Shelby, OH Sidney, OH Solon, OH South Point, OH Springboro, OH Springfield, OH Steubenville, OH Stow, OH Streetsboro, OH Strongsville, OH Struthers, OH Sunbury, OH Swanton, OH Sycamore, OH Sylvania, OH Tallmadge, OH Thornville, OH Tiffin, OH Tipp City, OH Toledo, OH Trenton, OH Troy, OH Twinsburg, OH Uhrichsville, OH Uniontown, OH Upper Sandusky, OH Urbana, OH Van Wert, OH Vandalia, OH Vermilion, OH Versailles, OH Vienna, OH Wadsworth, OH Walbridge, OH Walnut Creek, OH Wapakoneta, OH Warren, OH Washington Court House, OH Waterville, OH Wauseon, OH Waverly, OH Waynesburg, OH Waynesville, OH Wellington, OH West Chester, OH West Jefferson, OH West Milton, OH West Union, OH Westerville, OH Westfield Center, OH Westlake, OH Weston, OH Wheelersburg, OH Wickliffe, OH Willard, OH Willoughby, OH Wilmington, OH Woodville, OH Wooster, OH Xenia, OH Yellow Springs, OH Youngstown, OH Zanesville, OH Select... Ada, OK Altus, OK Altus AFB, OK Alva, OK Anadarko, OK Ardmore, OK Atoka, OK Bartlesville, OK Bethany, OK Bixby, OK Blackwell, OK Blanchard, OK Braggs, OK Bristow, OK Broken Arrow, OK Broken Bow, OK Catoosa, OK Chandler, OK Checotah, OK Cherokee, OK Cheyenne, OK Chickasha, OK Choctaw, OK Claremore, OK Cleveland, OK Clinton, OK Collinsville, OK Coweta, OK Dewey, OK Drumright, OK Duncan, OK Durant, OK Edmond, OK El Reno, OK Elk City, OK Enid, OK Eufaula, OK Fairfax, OK Fort Gibson, OK Fort Sill, OK Frederick, OK Glenpool, OK Grove, OK Guthrie, OK Guymon, OK Harrah, OK Healdton, OK Helena, OK Henryetta, OK Hobart, OK Holdenville, OK Hominy, OK Hugo, OK Idabel, OK Jay, OK Jenks, OK Keyes, OK Kingfisher, OK Kingston, OK Konawa, OK Lawton, OK Lindsay, OK Lone Grove, OK Mangum, OK Mannford, OK Marlow, OK McAlester, OK McLoud, OK Miami, OK Mill Creek, OK Muldrow, OK Muskogee, OK Mustang, OK Newcastle, OK Norman, OK Nowata, OK Okarche, OK Oklahoma, OK Oklahoma City, OK Okmulgee, OK Oologah, OK Owasso, OK Pauls Valley, OK Pawhuska, OK Pawnee, OK Perry, OK Piedmont, OK Ponca City, OK Poteau, OK Prague, OK Pryor, OK Purcell, OK Roland, OK Sallisaw, OK Sand Springs, OK Sapulpa, OK Shattuck, OK Shawnee, OK Skiatook, OK Spencer, OK Spiro, OK Stillwater, OK Stilwell, OK Stroud, OK Sulphur, OK Taft, OK Tahlequah, OK Talihina, OK Tecumseh, OK Tishomingo, OK Tonkawa, OK Tulsa, OK Tuttle, OK Valliant, OK Vian, OK Vinita, OK Wagoner, OK Warner, OK Watonga, OK Weatherford, OK Wewoka, OK Wilburton, OK Woodward, OK Yukon, OK Select... Albany, OR ALOHA, OR Ashland, OR Astoria, OR Baker City, OR Bandon, OR Beaverton, OR Bend, OR Boardman, OR Brookings, OR Burns, OR Canby, OR Central Point, OR Chiloquin, OR Clackamas, OR Clatskanie, OR Coos Bay, OR Cornelius, OR Corvallis, OR Cottage Grove, OR Creswell, OR Dallas, OR Dundee, OR Eagle Point, OR Enterprise, OR Estacada, OR Eugene, OR Florence, OR Forest Grove, OR Gladstone, OR Glendale, OR Gleneden Beach, OR Gold Hill, OR Grand Ronde, OR Grants Pass, OR Gresham, OR Happy Valley, OR Hermiston, OR Hillsboro, OR Hood River, OR Independence, OR Jacksonville, OR John Day, OR Junction City, OR Klamath Falls, OR La Grande, OR La Pine, OR Lake Oswego, OR Lakeview, OR Lebanon, OR Lincoln City, OR Lowell, OR Madras, OR McMinnville, OR Medford, OR Mill City, OR Milton Freewater, OR Mitchell, OR Molalla, OR Monmouth, OR Mount Angel, OR Myrtle Creek, OR Newberg, OR Newport, OR North Bend, OR Nyssa, OR Ontario, OR Oregon City, OR Pacific City, OR Pendleton, OR Philomath, OR Portland, OR Prineville, OR Rainier, OR Redmond, OR Reedsport, OR Richland, OR Roseburg, OR Saint Helens, OR Salem, OR Sandy, OR Scappoose, OR Seaside, OR Shady Cove, OR Sheridan, OR Sherwood, OR Siletz, OR Silverton, OR Sisters, OR Springfield, OR Stayton, OR Sutherlin, OR Sweet Home, OR The Dalles, OR Tillamook, OR Toledo, OR Troutdale, OR Tualatin, OR Veneta, OR Waldport, OR Warm Springs, OR Warrenton, OR Welches, OR West Linn, OR Wilsonville, OR Woodburn, OR Select... Abington, PA Alburtis, PA Alexandria, PA Aliquippa, PA Allentown, PA Allenwood, PA Allison Park, PA Altoona, PA Alum Bank, PA Ambler, PA Ambridge, PA Annville, PA Apollo, PA Archbald, PA Ardmore, PA Aston, PA Athens, PA Atlasburg, PA Avis, PA Avonmore, PA Baden, PA Bala Cynwyd, PA Bangor, PA Barto, PA Bartonsville, PA Bath, PA Beallsville, PA Beaver, PA Beaver Falls, PA Bedford, PA Belle Vernon, PA Bellefonte, PA Belleville, PA Bellwood, PA Bensalem, PA Bentleyville, PA Benton, PA Berlin, PA Bernville, PA Berwick, PA Berwyn, PA Bethel Park, PA Bethlehem, PA Biglerville, PA Blairsville, PA Blandon, PA Bloomsburg, PA Blossburg, PA Blue Bell, PA Boiling Springs, PA Boyertown, PA Bradford, PA Breinigsville, PA Bridgeport, PA Bridgeville, PA Bristol, PA Brodheadsville, PA Brookhaven, PA Brookville, PA Broomall, PA Brownsville, PA Bryn Mawr, PA Buckingham, PA Burgettstown, PA Butler, PA Cabot, PA California, PA Cambridge Springs, PA Camp Hill, PA Canonsburg, PA Canton, PA Carbondale, PA Carlisle, PA Carmichaels, PA Carnegie, PA Carrolltown, PA Carversville, PA Catasauqua, PA Center Valley, PA Central City, PA Centre Hall, PA Chadds Ford, PA Chalfont, PA Chambersburg, PA Charleroi, PA Cheltenham, PA Chester, PA Chester Springs, PA Chicora, PA Christiana, PA Clairton, PA Clarion, PA Clarks Summit, PA Claysville, PA Clearfield, PA Clifton Heights, PA Coalport, PA Coatesville, PA Collegeville, PA Colmar, PA Columbia, PA Concordville, PA Conneaut Lake, PA Conneautville, PA Connellsville, PA Conshohocken, PA Conyngham, PA Coopersburg, PA Coplay, PA Coraopolis, PA Corry, PA Coudersport, PA Cranberry, PA Cranberry Township, PA Cresson, PA Croydon, PA Dallas, PA Dallastown, PA Dalton, PA Danville, PA Darby, PA Davidsville, PA Dayton, PA Delmont, PA Denver, PA Derry, PA Devon, PA Dilliner, PA Dillsburg, PA Dingmans Ferry, PA Douglassville, PA Dover, PA Downingtown, PA Doylestown, PA Dravosburg, PA Dresher, PA Drexel Hill, PA Dry Run, PA Du Bois, PA Dublin, PA Duncansville, PA Dushore, PA East Berlin, PA East Earl, PA East Mc Keesport, PA East Petersburg, PA East Stroudsburg, PA East Texas, PA Easton, PA Ebensburg, PA Edinboro, PA Eighty Four, PA Elderton, PA Elizabeth, PA Elizabethtown, PA Elkins Park, PA Elkland, PA Ellwood City, PA Elverson, PA Elysburg, PA Emlenton, PA Emmaus, PA Emporium, PA Enola, PA Ephrata, PA Erie, PA Etters, PA Everett, PA Export, PA Exton, PA Factoryville, PA Fairchance, PA Fairfield, PA Fairless Hills, PA Fairview, PA Falls Creek, PA Farmington, PA Farrell, PA Feasterville Trevose, PA Fishertown, PA Fleetwood, PA Flourtown, PA Folsom, PA Ford City, PA Forest City, PA Fort Washington, PA Fountainville, PA Frackville, PA Franklin, PA Fredericksburg, PA Fredericktown, PA Freedom, PA Freeland, PA Freeport, PA Fryburg, PA Furlong, PA Gallitzin, PA Gap, PA Gardners, PA Garnet Valley, PA Gettysburg, PA Gibsonia, PA Gilbertsville, PA Girard, PA Glen Mills, PA Glen Riddle Lima, PA Glen Rock, PA Glenmoore, PA Glenolden, PA Glenshaw, PA Glenside, PA Gordonville, PA Greencastle, PA Greensburg, PA Greenville, PA Grove City, PA Halifax, PA Hamburg, PA Hamlin, PA Hanover, PA Harleysville, PA Harmony, PA Harrisburg, PA Hatboro, PA Hatfield, PA Haverford, PA Havertown, PA Hawley, PA Hazleton, PA Hegins, PA Hellertown, PA Hermitage, PA Hershey, PA Holicong, PA Hollidaysburg, PA Holmes, PA Homestead, PA Honesdale, PA Honey Brook, PA Hopwood, PA Horsham, PA Houtzdale, PA Howard, PA Hughesville, PA Hummelstown, PA Huntingdon, PA Huntingdon Valley, PA Imperial, PA Indiana, PA Ingomar, PA Irwin, PA Jamison, PA Jeannette, PA Jenkintown, PA Jersey Shore, PA Jim Thorpe, PA Johnstown, PA Jonestown, PA Kane, PA Kennett Square, PA King of Prussia, PA Kingston, PA Kittanning, PA Knox, PA Kulpmont, PA Kutztown, PA La Belle, PA Lafayette Hill, PA Lake Ariel, PA Lake City, PA Lake Winola, PA Lamar, PA Lancaster, PA Landenberg, PA Landisville, PA Langhorne, PA Lansdale, PA Lansdowne, PA Latrobe, PA Lawrenceville, PA Lebanon, PA Leechburg, PA Leesport, PA Lehighton, PA Lemont Furnace, PA Lemoyne, PA Leola, PA Levittown, PA Lewisberry, PA Lewisburg, PA Lewistown, PA Ligonier, PA Lilly, PA Linesville, PA Lititz, PA Littlestown, PA Lock Haven, PA Loretto, PA Loysville, PA Lyndora, PA Macungie, PA Malvern, PA Manchester, PA Manheim, PA Mansfield, PA Marcus Hook, PA Marietta, PA Mars, PA Martinsburg, PA Marysville, PA Mc Connellsburg, PA Mc Donald, PA Mc Elhattan, PA Mc Kean, PA Mc Kees Rocks, PA McKeesport, PA McMurray, PA Meadville, PA Mechanicsburg, PA Media, PA Mercer, PA Merion Station, PA Mertztown, PA Meshoppen, PA Meyersdale, PA Middleburg, PA Middletown, PA Mifflintown, PA Milford, PA Mill Hall, PA Millersburg, PA Millerstown, PA Millersville, PA Milton, PA Minersville, PA Monaca, PA Monessen, PA Monongahela, PA Monroeville, PA Montgomeryville, PA Montoursville, PA Montrose, PA Moosic, PA Morgantown, PA Morrisville, PA Morton, PA Moscow, PA Mount Bethel, PA Mount Carmel, PA Mount Gretna, PA Mount Joy, PA Mount Morris, PA Mount Pleasant, PA Mount Pocono, PA Mount Union, PA Mount Wolf, PA Mountain Top, PA Mountville, PA Muncy, PA Murrysville, PA Myerstown, PA Nanticoke, PA Narberth, PA Natrona Heights, PA Nazareth, PA New Alexandria, PA New Brighton, PA New Castle, PA New Cumberland, PA New Freedom, PA New Holland, PA New Hope, PA New Kensington, PA New Kingstown, PA New Milford, PA New Oxford, PA New Paris, PA New Stanton, PA New Tripoli, PA Newtown, PA Newtown Square, PA Newville, PA Norristown, PA North East, PA North Versailles, PA North Wales, PA Northampton, PA Northern Cambria, PA Northumberland, PA Norwood, PA Noxen, PA Oakdale, PA Oakmont, PA Oaks, PA Oil City, PA Old Forge, PA Oley, PA Olyphant, PA Orbisonia, PA Orefield, PA Oreland, PA Orwigsburg, PA Osceola Mills, PA Ottsville, PA Oxford, PA Palmerton, PA Palmyra, PA Paoli, PA Parker, PA Parkesburg, PA Patton, PA Paxinos, PA Pen Argyl, PA Pennsburg, PA Perkasie, PA Philadelphia, PA Philipsburg, PA Phoenixville, PA Pine Grove, PA Pipersville, PA Pittsburgh, PA Pittston, PA Plymouth, PA Plymouth Meeting, PA Pocono Lake, PA Pocono Pines, PA Pocono Summit, PA Port Allegany, PA Port Matilda, PA Port Trevorton, PA Portage, PA Pottstown, PA Pottsville, PA Presto, PA Prospect Park, PA Punxsutawney, PA Quakertown, PA Quarryville, PA Reading, PA Red Hill, PA Red Lion, PA Reno, PA Republic, PA Rices Landing, PA Richboro, PA Richland, PA Ridgway, PA Ridley Park, PA Riegelsville, PA Rillton, PA Roaring Spring, PA Robesonia, PA Rochester, PA Royersford, PA Russellton, PA Saegertown, PA Saint Clair, PA Saint Marys, PA Salisbury, PA Sandy Lake, PA Sarver, PA Saxonburg, PA Sayre, PA Schnecksville, PA Schuylkill Haven, PA Schwenksville, PA Scottdale, PA Scranton, PA Selinsgrove, PA Sellersville, PA Seneca, PA Sewickley, PA Shamokin, PA Sharon Hill, PA Sharpsville, PA Shavertown, PA Shermans Dale, PA Shippensburg, PA Shoemakersville, PA Shrewsbury, PA Silverdale, PA Skippack, PA Slippery Rock, PA Slovan, PA Smithfield, PA Smoketown, PA Snow Shoe, PA Somerset, PA Souderton, PA South Park, PA Southampton, PA Spring Grove, PA Spring House, PA Spring Mills, PA Springdale, PA Springfield, PA Stahlstown, PA State College, PA Stevens, PA Stewartstown, PA Stoneboro, PA Strasburg, PA Strattanville, PA Stroudsburg, PA Sugar Grove, PA Sugarloaf, PA Summit Hill, PA Sunbury, PA Swarthmore, PA Tamaqua, PA Tannersville, PA Tarentum, PA Taylor, PA Temple, PA Terre Hill, PA Thorndale, PA Titusville, PA Tobyhanna, PA Torrance, PA Towanda, PA Trafford, PA Tremont, PA Trexlertown, PA Troy, PA Tunkhannock, PA Turbotville, PA Turtle Creek, PA Tyrone, PA Uniontown, PA Upper Darby, PA Uwchland, PA Valencia, PA Valley Forge, PA Verona, PA Villanova, PA Wallingford, PA Walnutport, PA Warfordsburg, PA Warminster, PA Warren, PA Warrendale, PA Warrington, PA Washington, PA Washington Crossing, PA Waterford, PA Watsontown, PA Waverly, PA Waymart, PA Wayne, PA Waynesboro, PA Waynesburg, PA Wellsboro, PA West Chester, PA West Grove, PA West Mifflin, PA West Newton, PA Wexford, PA White Haven, PA Whitehall, PA Wilkes Barre, PA Williamsport, PA Williamstown, PA WILLOW GROVE, PA Willow Street, PA Wind Gap, PA Windber, PA Womelsdorf, PA Woodlyn, PA Wyalusing, PA Wyncote, PA Wynnewood, PA Wyoming, PA York, PA York New Salem, PA Youngwood, PA Zelienople, PA Select... Bayamon, PR Cayey, PR Cidra, PR Guaynabo, PR Las Piedras, PR Luquillo, PR Mayaguez, PR San Juan, PR Toa Baja, PR Vega Baja, PR Select... Barrington, RI Charlestown, RI Chepachet, RI Coventry, RI Cranston, RI Cumberland, RI East Greenwich, RI East Providence, RI Greenville, RI Harrisville, RI Jamestown, RI Johnston, RI Lincoln, RI Middletown, RI Narragansett, RI Newport, RI North Kingstown, RI North Providence, RI North Smithfield, RI Pascoag, RI Pawtucket, RI Portsmouth, RI Providence, RI Riverside, RI Rumford, RI Saunderstown, RI Slatersville, RI Smithfield, RI Tiverton, RI Wakefield, RI Warren, RI Warwick, RI West Greenwich, RI West Warwick, RI Westerly, RI Woonsocket, RI Select... Abbeville, SC Aiken, SC Anderson, SC Andrews, SC Bamberg, SC Barnwell, SC Batesburg, SC Beaufort, SC Belton, SC Bennettsville, SC Bishopville, SC Bluffton, SC Blythewood, SC Boiling Springs, SC Camden, SC Cameron, SC Cayce, SC Chapin, SC Charleston, SC Charleston AFB, SC Cheraw, SC Chesnee, SC Chester, SC Clemson, SC Clinton, SC Clover, SC Columbia, SC Conway, SC Cowpens, SC Darlington, SC Denmark, SC Dillon, SC Duncan, SC Easley, SC Edgefield, SC Fairfax, SC Florence, SC Folly Beach, SC Fort Mill, SC Fountain Inn, SC Gaffney, SC Georgetown, SC Goose Creek, SC Greenville, SC Greenwood, SC Greer, SC Hampton, SC Hanahan, SC Hardeeville, SC Hartsville, SC Hemingway, SC Hilton Head Island, SC Hodges, SC Honea Path, SC Hopkins, SC Inman, SC Irmo, SC Isle of Palms, SC Johns Island, SC Johnsonville, SC Kershaw, SC Kingstree, SC Ladson, SC Lake City, SC Lancaster, SC Landrum, SC Latta, SC Laurens, SC Lexington, SC Liberty, SC Little River, SC Loris, SC Lugoff, SC Lyman, SC Manning, SC Marion, SC Mauldin, SC Mc Clellanville, SC Mc Coll, SC Moncks Corner, SC Mount Pleasant, SC Mullins, SC MURRELLS INLET, SC Myrtle Beach, SC Newberry, SC North Augusta, SC North Charleston, SC North Myrtle Beach, SC Okatie, SC Orangeburg, SC Pageland, SC Pamplico, SC Parris Island, SC Pawleys Island, SC Pelzer, SC Pendleton, SC Pickens, SC Piedmont, SC Port Royal, SC Ravenel, SC Ridge Spring, SC Ridgeland, SC Ridgeway, SC Rock Hill, SC Roebuck, SC Saint George, SC Saint Matthews, SC Saint Stephen, SC Salem, SC Saluda, SC Seneca, SC Simpsonville, SC Society Hill, SC Spartanburg, SC Summerville, SC Sumter, SC Taylors, SC Timmonsville, SC Travelers Rest, SC Turbeville, SC Union, SC Wagener, SC Walhalla, SC Walterboro, SC Ware Shoals, SC West Columbia, SC West Union, SC Westminster, SC Whitmire, SC Williamston, SC Williston, SC Winnsboro, SC Woodruff, SC York, SC Select... Aberdeen, SD Belle Fourche, SD Brandon, SD Brookings, SD Canton, SD Chamberlain, SD Clark, SD Clear Lake, SD Custer, SD Deadwood, SD Dell Rapids, SD Eagle Butte, SD Ellsworth AFB, SD Fort Pierre, SD Fort Thompson, SD Freeman, SD Gettysburg, SD Gregory, SD Harrisburg, SD Hartford, SD Hill City, SD Hot Springs, SD Howard, SD Huron, SD Kyle, SD Lead, SD Lennox, SD Madison, SD Marion, SD Milbank, SD Miller, SD Mitchell, SD Mobridge, SD North Sioux City, SD Parker, SD Philip, SD Pierre, SD Pine Ridge, SD Platte, SD Rapid City, SD Redfield, SD Rosebud, SD Rosholt, SD Sioux Falls, SD Sisseton, SD Spearfish, SD Sturgis, SD Tea, SD Tripp, SD Vermillion, SD Wagner, SD Watertown, SD Wessington Springs, SD Winner, SD Yankton, SD Select... Adamsville, TN Alamo, TN Alcoa, TN Alexandria, TN Antioch, TN Ashland City, TN Athens, TN Atoka, TN Bells, TN Benton, TN Blountville, TN Bolivar, TN Brentwood, TN Bristol, TN Brownsville, TN Burns, TN Camden, TN Carthage, TN Chattanooga, TN Church Hill, TN Clarksville, TN Cleveland, TN Clinton, TN Collegedale, TN Collierville, TN Columbia, TN Cookeville, TN Cordova, TN Covington, TN Crossville, TN Dayton, TN Decatur, TN Decaturville, TN Decherd, TN Dickson, TN Dover, TN Dresden, TN Dunlap, TN Dyersburg, TN Eads, TN Elizabethton, TN Erin, TN Erwin, TN Fairview, TN Fayetteville, TN Franklin, TN Gainesboro, TN Gallatin, TN Gatlinburg, TN Germantown, TN Gleason, TN Goodlettsville, TN Greenbrier, TN Greeneville, TN Harriman, TN Harrison, TN Hartsville, TN Hendersonville, TN Hermitage, TN Hixson, TN Humboldt, TN Huntingdon, TN Jacksboro, TN Jackson, TN Jamestown, TN Jasper, TN Jefferson City, TN Joelton, TN Johnson City, TN Jonesborough, TN Kingsport, TN Kingston, TN Knoxville, TN Kodak, TN La Follette, TN La Vergne, TN Lafayette, TN Lawrenceburg, TN Lebanon, TN Lenoir City, TN Lewisburg, TN Lexington, TN Linden, TN Livingston, TN Lookout Mountain, TN Loudon, TN Madison, TN Madisonville, TN Manchester, TN Martin, TN Maryville, TN Maynardville, TN Mc Kenzie, TN McMinnville, TN Memphis, TN Milan, TN Millington, TN Morristown, TN Mount Juliet, TN Munford, TN Murfreesboro, TN Nashville, TN Newport, TN Nolensville, TN Oak Ridge, TN Old Hickory, TN Oliver Springs, TN Oneida, TN Ooltewah, TN Paris, TN Pikeville, TN Pleasant View, TN Portland, TN Powell, TN Pulaski, TN Ripley, TN Rockwood, TN Rutherford, TN Rutledge, TN Savannah, TN Selmer, TN Sevierville, TN Seymour, TN Shelbyville, TN Signal Mountain, TN Smithville, TN Smyrna, TN Soddy Daisy, TN Somerville, TN South Pittsburg, TN Sparta, TN Spring Hill, TN Springfield, TN Strawberry Plains, TN Sweetwater, TN Tazewell, TN Thompsons Station, TN Trenton, TN Tullahoma, TN Union City, TN Vonore, TN Walling, TN Wartburg, TN Watertown, TN Waynesboro, TN White Bluff, TN White House, TN White Pine, TN Winchester, TN Select... Abilene, TX Addison, TX Aledo, TX Alice, TX Allen, TX Alpine, TX Alvin, TX Amarillo, TX Angleton, TX Anna, TX Anthony, TX Aransas Pass, TX Argyle, TX Arlington, TX Athens, TX Atlanta, TX Aubrey, TX Austin, TX Azle, TX Balch Springs, TX Bartlett, TX Bastrop, TX Bay City, TX Baytown, TX Beaumont, TX Bedford, TX Beeville, TX Bellaire, TX Belton, TX Big Spring, TX Bishop, TX Blanco, TX Blue Ridge, TX Boerne, TX Bonham, TX Borger, TX Bowie, TX Brady, TX Breckenridge, TX Brenham, TX Bridge City, TX Bridgeport, TX Brownfield, TX Brownsboro, TX Brownsville, TX Brownwood, TX Bryan, TX Buda, TX Bullard, TX Bulverde, TX Burkburnett, TX Burleson, TX Burnet, TX Caldwell, TX Canton, TX Canyon, TX Carrizo Springs, TX Carrollton, TX Carthage, TX Cedar Hill, TX Cedar Park, TX Celina, TX Center, TX Centerville, TX Channelview, TX Childress, TX Cibolo, TX Cisco, TX Cleburne, TX Cleveland, TX Clifton, TX Coldspring, TX Coleman, TX College Station, TX Colleyville, TX Colorado City, TX Comfort, TX Commerce, TX Conroe, TX Coppell, TX Copperas Cove, TX Corpus Christi, TX Corsicana, TX Crockett, TX Crosby, TX Crowley, TX Crystal City, TX Cuero, TX Cypress, TX Dalhart, TX Dallas, TX Dayton, TX De Kalb, TX Decatur, TX Deer Park, TX Del Rio, TX Del Valle, TX Denison, TX Denton, TX Desoto, TX Devine, TX Dickinson, TX Donna, TX Dripping Springs, TX Dublin, TX Dumas, TX Duncanville, TX Dyess AFB, TX Eagle Pass, TX Edinburg, TX El Campo, TX El Paso, TX Elgin, TX Elsa, TX Emory, TX Ennis, TX Euless, TX Fairfield, TX Farmersville, TX Ferris, TX Flint, TX Floresville, TX Flower Mound, TX Floydada, TX Forney, TX Fort Bliss, TX Fort Hood, TX Fort Worth, TX Frankston, TX Fredericksburg, TX Fresno, TX Friendswood, TX Frisco, TX Fritch, TX Fulshear, TX Gainesville, TX Galveston, TX Ganado, TX Garland, TX Gatesville, TX Georgetown, TX Giddings, TX Gilmer, TX Gladewater, TX Goldthwaite, TX Goliad, TX Gonzales, TX Goodfellow AFB, TX Graham, TX Granbury, TX Grand Prairie, TX Grand Saline, TX Grandview, TX Grapeland, TX Grapevine, TX Greenville, TX Groesbeck, TX Groves, TX Hallettsville, TX Hallsville, TX Haltom City, TX Hamilton, TX Hamlin, TX Harker Heights, TX Harlingen, TX Haslet, TX Hearne, TX Helotes, TX Hemphill, TX Hempstead, TX Henderson, TX Hereford, TX Hewitt, TX Highlands, TX Hillsboro, TX Hitchcock, TX Hockley, TX Hondo, TX Honey Grove, TX Horseshoe Bay, TX Houston, TX Hull, TX Humble, TX Huntsville, TX Hurst, TX Hutto, TX Idalou, TX Ingleside, TX Ingram, TX Iowa Park, TX Irving, TX Italy, TX Jacksonville, TX Jarrell, TX Jasper, TX Jefferson, TX Karnes City, TX Katy, TX Kaufman, TX Keller, TX Kemp, TX Kendalia, TX Kenedy, TX Kermit, TX Kerrville, TX Kilgore, TX Killeen, TX Kingsland, TX Kingsville, TX Kingwood, TX Kountze, TX Krum, TX Kyle, TX La Feria, TX La Grange, TX La Marque, TX La Porte, TX La Vernia, TX Lackland A F B, TX Lake Jackson, TX Lampasas, TX Lancaster, TX Laredo, TX League City, TX Leander, TX Levelland, TX Lewisville, TX Liberty, TX Liberty Hill, TX Lindale, TX Linden, TX Little Elm, TX Little River Academy, TX Livingston, TX Llano, TX Lockhart, TX Lone Star, TX Longview, TX Los Fresnos, TX Lovelady, TX Lubbock, TX Lufkin, TX Luling, TX Lumberton, TX Mabank, TX Madisonville, TX Magnolia, TX Manor, TX Mansfield, TX Manvel, TX Marble Falls, TX Marshall, TX Mason, TX Mc Gregor, TX McAllen, TX McKinney, TX Melissa, TX Mercedes, TX Mesquite, TX Mexia, TX Midland, TX Midlothian, TX Mineola, TX Mineral Wells, TX Mission, TX Missouri City, TX Montgomery, TX Moulton, TX Mount Pleasant, TX Mount Vernon, TX Muenster, TX Muleshoe, TX Nacogdoches, TX Naples, TX Nederland, TX Needville, TX New Boston, TX New Braunfels, TX New Caney, TX North Richland Hills, TX Odessa, TX Olney, TX Omaha, TX Orange, TX Palacios, TX Palestine, TX Pampa, TX Paris, TX Pasadena, TX Pearland, TX Pearsall, TX Perryton, TX Pflugerville, TX Pharr, TX Pinehurst, TX Pipe Creek, TX Pittsburg, TX Plainview, TX Plano, TX Pleasanton, TX Pollok, TX Port Arthur, TX Port Lavaca, TX Port Neches, TX Porter, TX Portland, TX Princeton, TX Prosper, TX Quanah, TX Quinlan, TX Randolph AFB, TX Red Oak, TX Richardson, TX Richmond, TX Rio Grande City, TX Roanoke, TX Robstown, TX Rockdale, TX Rockport, TX Rockwall, TX Roma, TX Rosenberg, TX Rosharon, TX Round Rock, TX Rowlett, TX Rusk, TX Sachse, TX San Angelo, TX San Antonio, TX San Augustine, TX San Benito, TX San Elizario, TX San Juan, TX San Marcos, TX Sanger, TX Santa Fe, TX Schertz, TX Schulenburg, TX Seagoville, TX Sealy, TX Seguin, TX Seminole, TX Sheppard AFB, TX Sherman, TX Silsbee, TX Slaton, TX Smithville, TX Snyder, TX South Houston, TX South Padre Island, TX Southlake, TX Spearman, TX Spicewood, TX Spring, TX Spring Branch, TX Springtown, TX Stafford, TX Stephenville, TX Stockdale, TX Sugar Land, TX Sulphur Springs, TX Sunnyvale, TX Sweetwater, TX Taft, TX Taylor, TX Teague, TX Temple, TX Terrell, TX Texarkana, TX Texas City, TX The Colony, TX Tomball, TX Trinity, TX Troup, TX Tyler, TX Universal City, TX Uvalde, TX Van Alstyne, TX Vernon, TX Victoria, TX Vidor, TX Waco, TX Waxahachie, TX Weatherford, TX Webster, TX Weslaco, TX West Columbia, TX Wharton, TX Wheeler, TX White Oak, TX Whitesboro, TX Whitney, TX Wichita Falls, TX Willis, TX Wills Point, TX Wimberley, TX Winters, TX Woodville, TX Woodway, TX Wylie, TX Yoakum, TX Yorktown, TX Zapata, TX Select... Alpine, UT American Fork, UT Beaver, UT Bicknell, UT Bountiful, UT Brigham City, UT Cedar City, UT Centerville, UT Clearfield, UT Delta, UT Draper, UT Eagle Mountain, UT Eden, UT Ephraim, UT Fairview, UT Farmington, UT Fort Duchesne, UT Garden City, UT Garland, UT Gunnison, UT Heber City, UT Helper, UT Herriman, UT Hill AFB, UT Holden, UT Huntsville, UT Hurricane, UT Hyrum, UT Ivins, UT Kanab, UT Kaysville, UT La Verkin, UT Layton, UT Lehi, UT Lindon, UT Logan, UT Magna, UT Manti, UT Mapleton, UT Midvale, UT Midway, UT Moab, UT Monroe, UT Montezuma Creek, UT Monticello, UT Mount Pleasant, UT Nephi, UT North Salt Lake, UT Ogden, UT Orem, UT Park City, UT Parowan, UT Payson, UT Pleasant Grove, UT Price, UT Providence, UT Provo, UT Richfield, UT Richmond, UT Riverton, UT Roosevelt, UT Roy, UT Saint George, UT Salem, UT Salina, UT Salt Lake City, UT Sandy, UT Santaquin, UT Saratoga Springs, UT Smithfield, UT South Jordan, UT Spanish Fork, UT Springville, UT Syracuse, UT Tooele, UT Tremonton, UT Vernal, UT Washington, UT West Jordan, UT Woods Cross, UT Select... Abingdon, VA Accomac, VA Afton, VA Aldie, VA Alexandria, VA Altavista, VA Amelia Court House, VA Amherst, VA Annandale, VA Appomattox, VA Arlington, VA Ashburn, VA Ashland, VA Aylett, VA Bealeton, VA Bedford, VA Berryville, VA Big Stone Gap, VA Blacksburg, VA Blackstone, VA Bowling Green, VA Boydton, VA Boykins, VA Bridgewater, VA Bristol, VA Bristow, VA Broadway, VA Buena Vista, VA Burgess, VA Burke, VA Cana, VA Cape Charles, VA Castlewood, VA Centreville, VA Chantilly, VA Charles City, VA Charlottesville, VA Chatham, VA Chesapeake, VA Chester, VA Chesterfield, VA Chilhowie, VA Christiansburg, VA Clarksville, VA Clifton Forge, VA Clintwood, VA Coeburn, VA Collinsville, VA Colonial Heights, VA Covington, VA Crewe, VA Crozet, VA Culpeper, VA Daleville, VA Danville, VA Dayton, VA Dillwyn, VA Dublin, VA Dumfries, VA Dunn Loring, VA Earlysville, VA Elkton, VA Emporia, VA Ewing, VA Exmore, VA Fairfax, VA Fairfax Station, VA Falls Church, VA Farmville, VA Fishersville, VA Floyd, VA Forest, VA Fort Belvoir, VA Fort Eustis, VA Fort Lee, VA Fort Myer, VA Franklin, VA Franktown, VA Fredericksburg, VA Front Royal, VA Gainesville, VA Galax, VA Gate City, VA Glasgow, VA Glen Allen, VA Gloucester, VA Goode, VA Gordonsville, VA Great Falls, VA Hampton, VA Harrisonburg, VA Hayes, VA Haymarket, VA Heathsville, VA Henrico, VA Herndon, VA Hillsville, VA Honaker, VA Hopewell, VA Hot Springs, VA Hudgins, VA Hurt, VA Independence, VA Jarratt, VA Keysville, VA Kilmarnock, VA King George, VA Lawrenceville, VA Lebanon, VA Leesburg, VA Lexington, VA Locust Grove, VA Lorton, VA Louisa, VA Lovingston, VA Luray, VA Lynchburg, VA Madison, VA Madison Heights, VA Manakin Sabot, VA Manassas, VA Manquin, VA Marion, VA Martinsville, VA Mc Kenney, VA Mc Lean, VA Mechanicsville, VA Middleburg, VA Midlothian, VA Mineral, VA Moneta, VA Monterey, VA Montross, VA Narrows, VA New Canton, VA New Castle, VA New Church, VA New Market, VA Newport News, VA Nokesville, VA Norfolk, VA Norton, VA Oakton, VA Oakwood, VA Onley, VA Painter, VA Parksley, VA Pennington Gap, VA Petersburg, VA Poquoson, VA Portsmouth, VA Powhatan, VA Pulaski, VA Purcellville, VA Quantico, VA Quinton, VA Radford, VA Reston, VA Richlands, VA Richmond, VA Roanoke, VA Rocky Mount, VA Round Hill, VA Rural Retreat, VA Rustburg, VA Ruther Glen, VA Salem, VA Saluda, VA Sandston, VA Shawsville, VA Shenandoah, VA Smithfield, VA South Boston, VA South Hill, VA Spotsylvania, VA Springfield, VA Stafford, VA Staunton, VA Stephens City, VA Sterling, VA Strasburg, VA Stuart, VA Stuarts Draft, VA Suffolk, VA Sutherland, VA Tazewell, VA Timberville, VA Toano, VA Verona, VA Vienna, VA Vinton, VA Virginia Beach, VA Warrenton, VA Warsaw, VA Washington, VA Waverly, VA Waynesboro, VA West Point, VA Williamsburg, VA Winchester, VA Windsor, VA Wise, VA Woodbridge, VA Woodstock, VA Wytheville, VA Yorktown, VA Select... Barre, VT Beecher Falls, VT Bennington, VT Bradford, VT Brandon, VT Brattleboro, VT Bristol, VT Burlington, VT Cambridge, VT Castleton, VT Chester, VT Colchester, VT Essex Junction, VT Fair Haven, VT Hardwick, VT Jericho, VT Lyndonville, VT Manchester Center, VT Middlebury, VT Milton, VT Montpelier, VT Morrisville, VT Newport, VT Norwich, VT Plainfield, VT Poultney, VT Randolph, VT Rutland, VT Saint Albans, VT Saint Johnsbury, VT Shaftsbury, VT Shelburne, VT South Burlington, VT Springfield, VT Stowe, VT Swanton, VT Townshend, VT Vergennes, VT Waitsfield, VT Wallingford, VT Waterbury, VT White River Junction, VT Wilder, VT Williston, VT Wilmington, VT Winooski, VT Woodstock, VT Select... Aberdeen, WA Anacortes, WA Arlington, WA Auburn, WA Bainbridge Island, WA Battle Ground, WA Bellevue, WA Bellingham, WA Black Diamond, WA Bonney Lake, WA Bothell, WA Bremerton, WA Brewster, WA Bridgeport, WA Burlington, WA Camano Island, WA Camas, WA Castle Rock, WA Cathlamet, WA Centralia, WA Chattaroy, WA Chehalis, WA Chelan, WA Cheney, WA Chewelah, WA Clarkston, WA Cle Elum, WA Colfax, WA College Place, WA Colville, WA Concrete, WA Davenport, WA Dayton, WA Deer Park, WA Dupont, WA Duvall, WA East Wenatchee, WA Eastsound, WA Eatonville, WA Edmonds, WA Ellensburg, WA Enumclaw, WA Ephrata, WA Everett, WA Everson, WA Federal Way, WA Ferndale, WA Forks, WA Freeland, WA Friday Harbor, WA Gig Harbor, WA Graham, WA Grandview, WA Granite Falls, WA Inchelium, WA Issaquah, WA Kelso, WA Kenmore, WA Kennewick, WA Kent, WA Kettle Falls, WA Kingston, WA Kirkland, WA La Conner, WA Lacey, WA Lake Stevens, WA Lakebay, WA Lakewood, WA Langley, WA Leavenworth, WA Liberty Lake, WA Longview, WA Lopez Island, WA Lynden, WA Lynnwood, WA Manson, WA Maple Valley, WA Marysville, WA McChord AFB, WA McCleary, WA Mead, WA Medical Lake, WA Mercer Island, WA Milton, WA Monroe, WA Moses Lake, WA Mount Vernon, WA Mountlake Terrace, WA Mukilteo, WA Neah Bay, WA Nespelem, WA Nine Mile Falls, WA North Bend, WA Oak Harbor, WA Ocean Shores, WA Okanogan, WA Olympia, WA Omak, WA Oroville, WA Orting, WA Othello, WA Pasco, WA Pomeroy, WA Port Angeles, WA Port Orchard, WA Port Townsend, WA Poulsbo, WA Prosser, WA Pullman, WA Puyallup, WA Quincy, WA Redmond, WA Renton, WA Richland, WA Ridgefield, WA Rock Island, WA Sammamish, WA Seattle, WA Sedro Woolley, WA Selah, WA Sequim, WA Shelton, WA Silverdale, WA Snohomish, WA Snoqualmie, WA Spangle, WA Spokane, WA Stanwood, WA Steilacoom, WA Stevenson, WA Sumner, WA Sunnyside, WA Tacoma, WA Tenino, WA Tokeland, WA Tonasket, WA Toppenish, WA Twisp, WA University Place, WA Vancouver, WA Vashon, WA Veradale, WA Walla Walla, WA Washougal, WA Wellpinit, WA Wenatchee, WA West Richland, WA Woodinville, WA Woodland, WA Yakima, WA Yelm, WA Zillah, WA Select... Abbotsford, WI Alma, WI Altoona, WI Amery, WI Amherst, WI Aniwa, WI Antigo, WI Appleton, WI Ashland, WI Baldwin, WI Baraboo, WI Bayfield, WI Beaver Dam, WI Beloit, WI Berlin, WI Black Creek, WI Black River Falls, WI Blair, WI Bloomer, WI Boscobel, WI Bowler, WI Brookfield, WI Bruce, WI Burlington, WI Butler, WI Cambridge, WI Cashton, WI Cassville, WI Cedarburg, WI Chetek, WI Chilton, WI Chippewa Falls, WI Clinton, WI Clintonville, WI Colfax, WI Columbus, WI Cottage Grove, WI Crandon, WI Crivitz, WI Cuba City, WI Cudahy, WI Cumberland, WI Darlington, WI De Forest, WI De Pere, WI Delafield, WI Delavan, WI Denmark, WI Dodgeville, WI Dousman, WI Durand, WI Eagle River, WI East Troy, WI Eau Claire, WI Edgar, WI Edgerton, WI Elkhorn, WI Elm Grove, WI Elroy, WI Evansville, WI Fennimore, WI Fond du Lac, WI Fontana, WI Fort Atkinson, WI Fox Lake, WI Franklin, WI Fredonia, WI Fremont, WI Germantown, WI Gillett, WI Glenwood City, WI Grafton, WI Green Bay, WI Greendale, WI Greenville, WI Hales Corners, WI Hartford, WI Hartland, WI Hayward, WI Hilbert, WI Hillsboro, WI Holmen, WI Horicon, WI Hortonville, WI Hudson, WI Hustisford, WI Independence, WI Iola, WI Iron River, WI Jackson, WI Janesville, WI Jefferson, WI Johnson Creek, WI Kaukauna, WI Kenosha, WI Kewaskum, WI Kiel, WI Kimberly, WI La Crosse, WI La Farge, WI Lake Geneva, WI Lake Mills, WI Lake Nebagamon, WI Lakewood, WI Lancaster, WI Land O Lakes, WI Little Chute, WI Lodi, WI Luck, WI Luxemburg, WI Madison, WI Manawa, WI Manitowish Waters, WI Manitowoc, WI Marathon, WI Marinette, WI Marion, WI Markesan, WI Marshfield, WI Mauston, WI Mayville, WI Medford, WI Menasha, WI Menomonee Falls, WI Menomonie, WI Mequon, WI Merrill, WI Middleton, WI Milton, WI Milwaukee, WI Mineral Point, WI Minocqua, WI Mishicot, WI Mondovi, WI Monroe, WI Monticello, WI Mosinee, WI Mount Horeb, WI Mukwonago, WI Muskego, WI Neenah, WI Neillsville, WI New Berlin, WI New Holstein, WI New Lisbon, WI New Richmond, WI North Lake, WI Oak Creek, WI Oconomowoc, WI Oconto, WI Oconto Falls, WI Okauchee, WI Onalaska, WI Oneida, WI Oregon, WI Osceola, WI Oshkosh, WI Osseo, WI Park Falls, WI Pepin, WI Peshtigo, WI Pewaukee, WI Phillips, WI Pittsville, WI Platteville, WI Pleasant Prairie, WI Plover, WI Plymouth, WI Port Edwards, WI Port Washington, WI Portage, WI Prairie du Chien, WI Prairie du Sac, WI Prentice, WI Prescott, WI Pulaski, WI Racine, WI Randolph, WI Reedsburg, WI Rhinelander, WI Rice Lake, WI Richfield, WI Richland Center, WI Ripon, WI River Falls, WI Saint Croix Falls, WI Saint Francis, WI Salem, WI Schofield, WI Seymour, WI Shawano, WI Sheboygan, WI Sheboygan Falls, WI Shell Lake, WI Sherwood, WI Siren, WI Sister Bay, WI Slinger, WI South Milwaukee, WI Sparta, WI Spooner, WI Spring Valley, WI Stanley, WI Stevens Point, WI Stoughton, WI Strum, WI Sturgeon Bay, WI Sturtevant, WI Sun Prairie, WI Superior, WI Suring, WI Sussex, WI Three Lakes, WI Tomah, WI Tomahawk, WI Turtle Lake, WI Twin Lakes, WI Two Rivers, WI Union Grove, WI Valders, WI Verona, WI Viroqua, WI Wales, WI Washburn, WI Waterford, WI Watertown, WI Waukesha, WI Waunakee, WI Waupaca, WI Waupun, WI Wausau, WI Wautoma, WI Webster, WI West Bend, WI West Salem, WI Westby, WI Westfield, WI Weyauwega, WI Whitehall, WI Whitewater, WI Windsor, WI Winneconne, WI Wisconsin Dells, WI Wisconsin Rapids, WI Woodruff, WI Select... Athens, WV Baker, WV Barboursville, WV Beckley, WV Belmont, WV Berkeley Springs, WV Blacksville, WV Bluefield, WV Bridgeport, WV Bruceton Mills, WV Buckhannon, WV Cabin Creek, WV Capon Bridge, WV Charles Town, WV Charleston, WV Chester, WV Clarksburg, WV Clay, WV Clendenin, WV Crab Orchard, WV Craigsville, WV Danville, WV Dunbar, WV Elkins, WV Elkview, WV Fairmont, WV Fayetteville, WV Fort Gay, WV Gary, WV Glen Dale, WV Grafton, WV Grantsville, WV Green Bank, WV Hamlin, WV Harpers Ferry, WV Harts, WV Hico, WV Hinton, WV Huntington, WV Hurricane, WV Inwood, WV Kenova, WV Kermit, WV Keyser, WV Kingwood, WV Lewisburg, WV Logan, WV Lookout, WV Madison, WV Mannington, WV Marlinton, WV Martinsburg, WV Matewan, WV Maxwelton, WV McMechen, WV Mineral Wells, WV Montgomery, WV Moorefield, WV Morgantown, WV Moundsville, WV New Martinsville, WV Nitro, WV Oak Hill, WV Oceana, WV Parkersburg, WV Philippi, WV Poca, WV Point Pleasant, WV Princeton, WV Rainelle, WV Ravenswood, WV Richwood, WV Ripley, WV Romney, WV Ronceverte, WV Saint Albans, WV Saint Marys, WV Scott Depot, WV Shady Spring, WV Shepherdstown, WV Sophia, WV Surveyor, WV Union, WV Vienna, WV Wayne, WV Weirton, WV Wellsburg, WV West Hamlin, WV Weston, WV Wheeling, WV White Sulphur Springs, WV Williamson, WV Winfield, WV Select... Afton, WY Buffalo, WY Casper, WY Cheyenne, WY Cody, WY Diamondville, WY Douglas, WY Evanston, WY Fe Warren Afb, WY Fort Washakie, WY Gillette, WY Glenrock, WY Green River, WY Jackson, WY Kemmerer, WY Lander, WY Laramie, WY Lovell, WY Lyman, WY Moorcroft, WY Newcastle, WY Pine Bluffs, WY Pinedale, WY Powell, WY Riverton, WY Rock Springs, WY Sheridan, WY Thermopolis, WY Torrington, WY Wheatland, WY Worland, WY